Ford Motor Company World Headquarters. Source: Flickr Image
This article presents the margins of Ford Motor Company (NYSE:F).
We will explore several aspects of the margins, which include the consolidated automotive margin, Ford Credit margin, and margin by segment.
For your information, Ford Motor Company is organized into several segments, each targeting different customer needs and markets. They consist of Ford Blue, Ford Model e, Ford Pro, Ford Next, and Ford Credit.
Let’s look at the details! You may find related statistic of Ford Motor on these pages:
- How does Ford generate revenue,
- Ford revenue by segment,
- Ford profit per car, and
- Ford revenue by region.
Please use the table of contents to navigate this page.
Table Of Contents
Definitions And Overview
Consolidated Results
A1. Vehicle Margin
Results By Segment (Automotive)
B1. Ford Blue, Ford Model e, And Ford Pro
Results By Segment (Non-Automotive)
C1. Ford Next
C2. Ford Credit
Conclusion And Reference
S1. Summary
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
Definitions
To help readers understand the content better, the following terms and glossaries have been provided.
Ford Blue: The Ford Blue segment focuses on iconic gas and hybrid vehicles. It aims to drive growth and profitability by leveraging Ford’s strong brand heritage and improving operational efficiencies.
This segment is dedicated to building out Ford’s traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles while relentlessly attacking costs, simplifying operations, and enhancing quality.
Ford Blue also produces and sells service parts, accessories, and digital services to retail customers. Iconic gas and hybrid vehicles developed under Ford Blue include the F-150, Bronco, and Mustang.
Ford Model e: The Ford Model e segment is dedicated to the development and production of electric vehicles (EVs) and digital capabilities. This segment focuses on innovation and the advancement of electric vehicle technology, aiming to provide cutting-edge EVs that cater to the growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly transportation.
Apart from EVs, Ford Model e also designs and creates digital vehicle technologies, including embedded software and all of Ford’s electric architecture. Ford Model e operates in North America, Europe, and China.
Ford Pro: Ford Pro is responsible for the sale of Ford and Lincoln ICE, hybrid, and electric vehicles, service parts, accessories, and services to commercial, government, and rental customers.
Ford Pro focuses on fleet sales to customers with large orders, such as those from commercial sectors, government, and rental companies.
Ford Pro’s vehicles sold in North America include the Super Duty and the Transit range of vans. In Europe, Ford Pro’s flagship vehicles include the Ranger. Ford Pro operates primarily in North America and Europe.
Ford Next: The Ford Next segment (formerly the Mobility segment) is a subsidiary of Ford Motor Company, established to develop and commercialize mobility services.
It focuses on creating innovative solutions for transportation challenges, including autonomous vehicles, connectivity, and smart urban mobility. Ford Next aims to enhance the customer experience and address societal issues related to transportation and mobility.
Ford Credit: Ford Credit, also known as Ford Motor Credit Company LLC, is the financial services arm of Ford Motor Company. Headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan, Ford Credit primarily focuses on financing Ford and Lincoln vehicles and supporting Ford and Lincoln dealers.
Key aspects of Ford Credit include:
- Automobile Financing: Providing loans and leases to consumers for purchasing Ford and Lincoln vehicles.
- Dealership Support: Offering financing options to dealerships to help them manage their inventory and operations.
- Commercial Financing: Providing commercial financing and lines of credit to dealerships selling Ford products.
- Customer Services: Offering various services such as GAP protection, extended service plans, and online account management tools to help customers manage their finances.
Ford Credit plays a crucial role in making vehicle ownership more accessible and affordable for customers while supporting the overall business operations of Ford Motor Company.
Vehicle Margin: The vehicle margin for an automobile company refers to the difference between the selling price of a vehicle and the cost associated with producing and selling that vehicle. It is a measure of profitability and can be expressed in two main ways:
1. Gross Vehicle Margin: This margin takes into account the cost of goods sold (COGS) from the revenue generated from the sale of the vehicle. It is calculated by dividing the gross profit per vehicle by the revenue per vehicle and multiplying by 100 to get a percentage. The formula is:
\[ Gross\ Vehicle\ Margin = \frac{Gross\ Profit\ Per\ Vehicle}{Revenuer\ Per\ Vehicle} \times 100\% \]
2. Net Vehicle Margin: This margin considers additional expenses beyond COGS, such as operating expenses, marketing costs, and other overheads. It provides a more comprehensive view of profitability by accounting for all costs associated with the sale of the vehicle. The formula is:
\[ Net\ Vehicle\ Margin = \frac{Net\ Profit\ Per\ Vehicle}{Revenuer\ Per\ Vehicle} \times 100\% \]
Vehicle margin is an important metric for assessing the financial health and efficiency of an automobile company, as it indicates how well the company is managing its costs and pricing its vehicles to maximize profit.
Adjusted EBIT: Adjusted EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) for an automobile company refers to the company’s earnings from its operations, excluding interest expenses and taxes, and adjusting for one-time items, non-operational income, and expenses.
This non-GAAP measure helps assess the company’s core operational profitability by removing the effects of financing decisions, tax environments, and extraordinary events or expenses unrelated to the daily operations of manufacturing and selling vehicles.
It provides a clearer view of the company’s operational performance and its ability to generate profit from its primary business activities.
According to Ford, pre-tax items iclude pension and OPEB remeasurement gains and losses, significant expenses, and other items that Ford management considers unrelated to ongoing operating activities.
While the adjusted EBIT is a non-GAAP measure, Ford generally provides guidance for this metric because the excluded items are hard to predict.
Vehicle Margin
Ford-vehicle-margin
(click image to expand)
Ford Motor’s vehicle margin is evaluated based on the gross vehicle margin, whose definition is available here: vehicle margin.
Ford’s vehicle margin has amounted to around 9% on average between fiscal year 2021 and 2023, as presented in the chart above. In fiscal year 2023, Ford’s vehicle margin was 9%.
However, in fiscal year 2020, Ford’s vehicle margin dipped significantly to just 3%, primarily driven by supply chain disruptions and production halts during the COVID period.
The pandemic caused significant semiconductor chip shortages, which impacted the production of vehicles. Additionally, Ford had to suspend production in several plants and reduce manufacturing capacity to comply with health and safety measures. These factors led to lower production volumes and higher costs, resulting in a decrease in vehicle margins.
The good news is that Ford’s vehicle margin showed a strong recovery in the post-pandemic periods. In fiscal year 2021, the automaker’s vehicle margin significantly increased to 9%, up from 3% the previous year.
Since 2021, Ford has been able to maintain its vehicle margin at the 9% level, illustrating the company’s resilience and effective cost management in post-pandemic periods.
Ford Blue, Ford Model e, And Ford Pro
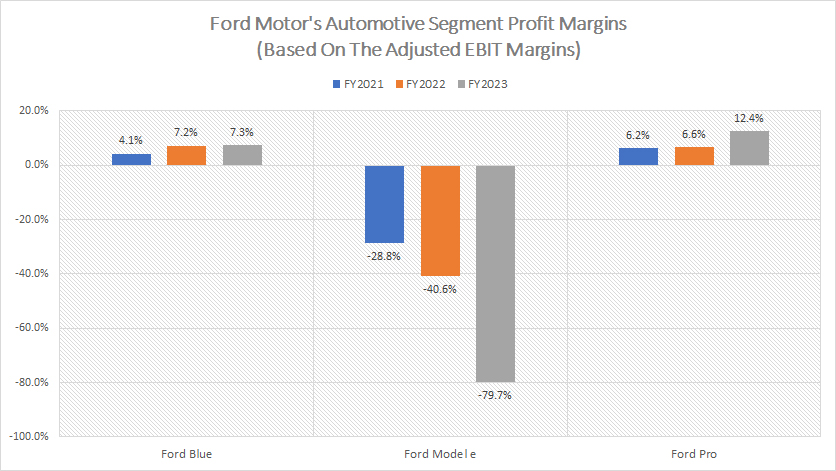
Ford-automotive-segment-profit-margin
(click image to expand)
The definitions of Ford Motor’s automotive segments are available here: Ford Blue, Ford Model e, and Ford Pro.
Ford’s automotive segment profit margins are evaluated based on the adjusted EBIT margin, whose definition is available here: adjusted EBIT margin.
Ford Motor generates significantly higher profit margin within the Ford Pro division, as shown in graph above. On average, Ford Pro’s profit margin has amounted to 8% over the last three years. In fiscal year 2023, Ford Pro’s profit margin increased significantly to 12%, more than doubling the figure from the previous year.
Ford Blue also is a highly profitable segment, with profit margin reaching 7% in fiscal year 2023. The average profit margin within the Ford Blue division was 6% in the last three years.
On the other hand, Ford Model e has not been a profitable segment, as depicted in the chart above. Ford Model e has been having negative profit margins since fiscal year 2021. In fiscal year 2023, the profit margin of Ford Model e worsened to -80%, roughly double the loss incurred in the previous year. Ford Model e’s deteriorating profit margin has been due to the price pressure on electric vehicles and other factors.
In short, Ford Pro can command a higher profit margin than Ford Blue due to several factors, which include higher pricing power, better operational efficiency, and a better product mix which usually consists of high-margin commercial vehicles and services.
However, Ford Pro delivers significantly smaller vehicle volumes than Ford Blue, as outlined in this article: Ford sales breakdown by segment. Ford Model e delivers an even smaller vehicle volumes compared to Ford Blue and Ford Pro, as shown in this article: Ford sales breakdown by segment.
Because of the difference in vehicle shipment volumes, Ford Blue earns significantly higher revenue than Ford Pro and Ford Model e, as shown in this article: Ford revenue by segment.
Ford Next
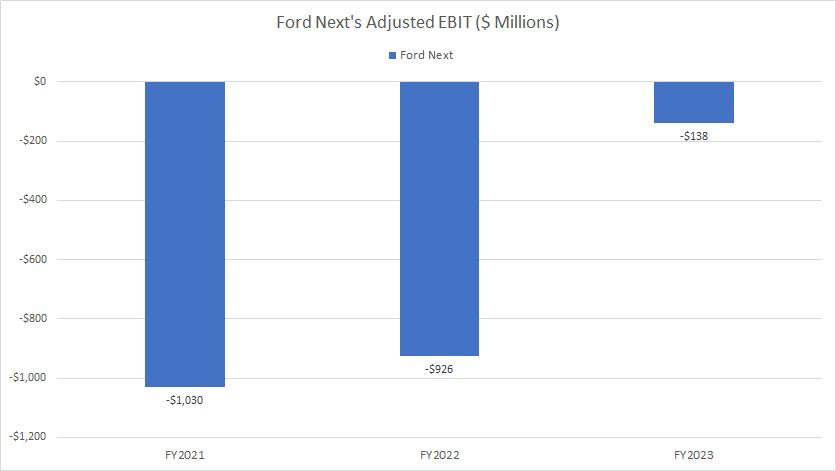
Ford-Next-profit-margin
(click image to expand)
The definitions of Ford Motor’s non-automotive segments are available here: Ford Next. The adjusted EBIT of Ford Next is defined here: adjusted EBIT.
Ford Next has yet to generate meaningful revenue since its establishment. Besides, this segment also has not been profitable, as reflected by the negative adjusted EBIT in the graph above. Therefore, there is no profit margin available for Ford Next.
The good news is that the losses in Ford Next has significantly narrowed in the last three years, as depicted in the chart above.
In fiscal year 2023, Ford Next’s losses decreased to just $138 million in adjusted EBIT, an $800 million improvement from the previous year.
Ford Credit
Ford-Credit-profit-margin
(click image to expand)
The definitions of Ford Motor’s non-automotive segments are available here: Ford Credit.
The profit margin for Ford Credit is evaluated based on the EBT margin which stands for earnings before taxes. It is similar to the adjusted EBIT margin. The only difference is that the interest expenses incurred in Ford Credit is not excluded under the EBT margin, as it is treated as one of the segment’s operating expenses.
That said, Ford Credit is a highly profitable segment, and earns significantly higher profit margin than the automotive segments, as shown in the chart above.
In fiscal year 2023, Ford Credit’s profit margin dipped to 13%, down from 30% in 2022. In fiscal year 2021, Ford Credit generated a staggering profit margin of 47%. The average profit margin of Ford Credit was 30% in the last three years.
A worrying trend is the decrease in profit margin of Ford Credit over the last several years. There are several factors that have been contributing to the decline.
One notable reason is Ford Credit’s lower financing margins. The division has experienced a decrease in the margins it earns from financing activities in the last several years. For example, since 2021, Ford Credit’s financing margin has decreased by over $1 billion, according to the 2023 annual report.
Also, Ford Credit has encountered an increased in credit losses. There has been an uptick in credit losses, which negatively impacts margins. For example, Ford Credit’s credit losses has increased by $600 million since 2021, according to the 2023 annual report.
The decline in Ford Credit’s leasing income also contributed to the depressed margins. Ford Credit’s lease residual has declined by over $1.4 billion since fiscal year 2021, according to the 2023 annual report.
Summary
Within Ford Motor’s automotive segment, Ford Blue and Ford Pro have been the most profitable, with profit margin averaging 6% and 8%, respectively, in the last three years.
However, Ford Model e has not been a profitable division. Its profit margin worsened to -80% in fiscal year 2023 from -41% the previous year.
Ford Next also has not been profitable. However, the losses in this segment has narrowed significanly since 2021. Ford Next’s losses were down to $138 million in adjusted EBIT as of fiscal year 2023 from over $900 million the previous year.
Ford Credit is the most profitable business among all divisions in Ford Motor. Its average profit margin was 30% over the last three years. Since fiscal year 2021, Ford Credit’s profit margin has been in decline, reaching just 13% in fiscal year 2023, driven by multiple factors, including lowering financing margin, growing credit losses, and decreasing lease residual.
References and Credits
1. All financial figures presented in this article were obtained and referenced from Ford’s quarterly and annual reports published in the Investors Relation page: Ford Investors Overview.
2. Flickr Images.
Disclosure
References and examples such as tables, charts, and diagrams are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant the full correctness of all content.
The content in this article is for informational purposes only and is neither a recommendation nor a piece of financial advice to purchase a stock.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media and also provide a link back to this article from any website so that more articles like this one can be created in the future.
Thank you!