Motherboard. Pexels Image.
This article compares the profitability and margin of Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited (TSMC) with Intel Corporation.
Let’s take a look! You may find related statistic of TSMC on these pages:
- TSMC revenue breakdown by platform: HPC, Smartphone, IoT, Automotive, etc.,
- TSMC revenue by country – U.S., China, Taiwan, Japan, etc., and
- TSMC revenue by product – wafer sales and other products.
Please use the table of contents to navigate this page.
Table Of Contents
Definitions And Overview
O2. Why does TSMC generate much better profit margin than Intel Corporation?
Profitability
A1. Gross Profit
Margins
B1. Gross Profit Margin
B2. Operating Profit Margin
B3. Net Profit Margin
Conclusion And Reference
S1. Conclusion
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
Definitions
To help readers understand the content better, the following terms and glossaries have been provided.
Gross Profit: Gross profit is a financial metric representing the difference between a company’s revenue and the cost of goods sold (COGS).
It measures how efficiently a company is producing and selling its goods. The formula for calculating gross profit is:
Gross Profit = Revenue − Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Gross profit is a key indicator of a company’s core profitability before accounting for overhead, taxes, and other operating expenses.
It is typically used to assess a company’s production efficiency and cost management. Higher gross profit margin indicates better efficiency in producing and selling products, while lower gross profit margin may suggest issues in cost control or pricing strategies.
New Taiwan Dollar (TWD): The New Taiwan Dollar (TWD), abbreviated as NT$, is the official currency of Taiwan.
It is used in all forms of transactions within the country, from daily expenses to business dealings. The New Taiwan Dollar is issued by the Central Bank of the Republic of China (Taiwan) and is subdivided into 100 cents.
Its symbol is NT$, and it is known for its stability and wide acceptance in the region. The exchange rate of TWD to USD is NT$1,000 to US$30.30.
Why does TSMC generate much better profit margin than Intel Corporation?
TSMC (Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company) consistently generates better profit margins than Intel Corporation due to several key factors:
-
Business Model:
- TSMC operates as a pure-play foundry, meaning it manufactures semiconductor products for other companies based on their designs. This allows TSMC to focus solely on manufacturing efficiency and economies of scale.
- Intel, on the other hand, designs and manufactures its own chips, which involves higher R&D costs and capital expenditures.
-
Advanced Manufacturing Processes:
- TSMC is a leader in advanced manufacturing technologies, including 3nm, 5nm, and 7nm processes. These advanced nodes are in high demand and command higher prices, contributing to TSMC’s higher profit margins.
- Intel has faced delays and challenges in advancing its manufacturing processes, which has impacted its competitiveness and profitability.
-
Economies of Scale:
- TSMC’s large-scale operations and high production volumes enable it to achieve economies of scale, reducing per-unit costs and increasing profit margins.
- Intel’s integrated device manufacturing model, while comprehensive, does not benefit from the same level of scale efficiencies as TSMC’s foundry model.
-
Customer Base:
- TSMC serves a diverse range of customers, including major players like Apple, AMD, and Nvidia. This diversified customer base provides a steady stream of high-margin business.
- Intel primarily serves its own product lines and a smaller set of external customers, limiting its revenue streams.
-
Operational Efficiency:
- TSMC’s focus on manufacturing excellence and continuous improvement has led to high operational efficiency and lower production costs.
- Intel has faced operational challenges and higher costs associated with its integrated design and manufacturing approach.
-
Market Position:
- TSMC’s dominant position in the foundry market allows it to command premium pricing for its advanced manufacturing services
- Intel, while a leader in the CPU market, faces intense competition from AMD and other semiconductor companies, which pressures its pricing and margins.
These factors collectively contribute to TSMC’s superior profit margins compared to Intel Corporation.
Gross Profit
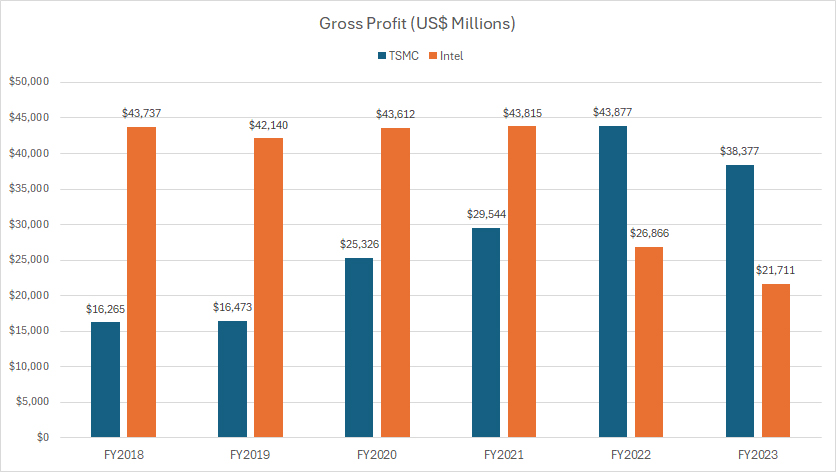
tsmc-vs-intel-in-gross-profit
(click image to expand)
The definition of gross profit is available here: gross profit.
TSMC reports its financial statements primarily in New Taiwan Dollars (TWD). You can find more information about the currency exchange rates between TWD and the US dollar here: New Taiwan Dollar (TWD).
Historically, Intel consistently generated much higher gross profits compared to TSMC, as illustrated in the chart above. For instance, between fiscal years 2018 and 2020, Intel’s gross profit averaged an impressive $43 billion, while TSMC’s gross profit during the same period averaged only $20 billion.
However, in subsequent years, TSMC experienced a significant surge in its gross profit, surpassing Intel’s gross profit starting from fiscal year 2022. In contrast, Intel’s gross profit faced a sharp decline, dropping to $26.9 billion in fiscal year 2022 and further plummeting to $21.7 billion in fiscal year 2023.
Despite a slight decrease in TSMC’s gross profit to $38.4 billion in fiscal year 2023, it remained substantially higher than Intel’s gross profit.
This shift in gross profit dynamics can be attributed to several key factors:
First, technological advancements have played a significant role. TSMC’s leadership in advanced manufacturing processes, such as 5nm and 3nm technologies, has allowed it to capture high-margin business, contributing to its robust gross profit growth. Intel, on the other hand, faced delays and challenges in advancing its manufacturing processes, impacting its ability to maintain high gross profits.
Second, market demand has influenced these trends. TSMC’s focus on producing semiconductors for a diverse range of customers, including major players like Apple and AMD, has driven strong demand for its services. In contrast, Intel’s primary focus on its own product lines, along with increased competition from AMD and other semiconductor companies, has affected its market position and gross profit.
These factors collectively explain why TSMC has managed to overtake Intel in terms of gross profit, despite the historical dominance of Intel in this financial metric. As the semiconductor industry continues to evolve, both companies will need to navigate technological advancements, market demands, and competitive pressures to sustain and grow their gross profits.
Gross Profit Margin
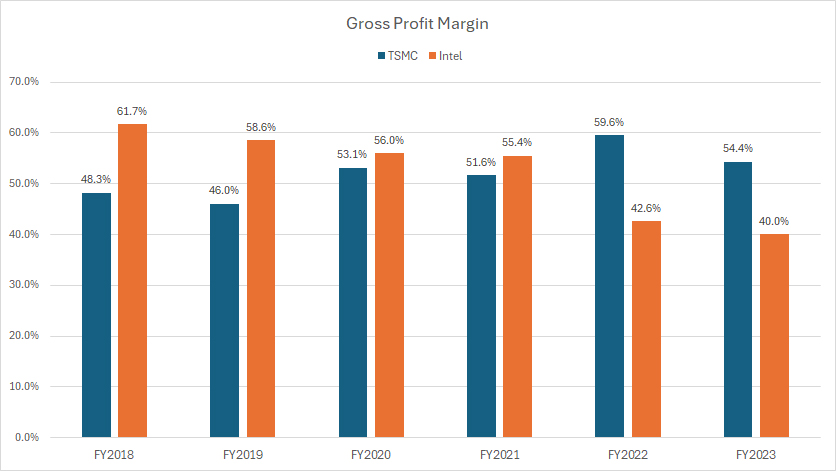
tsmc-vs-intel-in-gross-profit-margin
(click image to expand)
The definition of gross profit is available here: gross profit.
TSMC reports its financial statements primarily in New Taiwan Dollars (TWD). You can find more information about the currency exchange rates between TWD and the US dollar here: New Taiwan Dollar (TWD).
From fiscal years 2018 to 2020, Intel maintained a robust gross profit margin, averaging an impressive 59%. In contrast, TSMC’s gross profit margin averaged a more modest 49% during the same period, reflecting a much lower profitability compared to Intel.
However, in subsequent years, TSMC has successfully managed to boost its gross profit margin. The company saw an increase from 52% in fiscal year 2021 to nearly 60% in fiscal year 2022. By fiscal year 2023, TSMC’s gross profit margin stood at 54%, showcasing its improved efficiency and profitability.
Conversely, despite historically generating much better gross profit margins, Intel has faced a significant decline in recent years. The company’s gross profit margin nosedived from 55% in fiscal year 2021 to just 40% in fiscal year 2023.
Several factors have driven the shifts in gross profit margins for both companies. TSMC’s advancements in cutting-edge manufacturing processes, exceptional operational efficiency, economies of scale, and strategic investments in expanding production capacity and adopting advanced technologies have collectively contributed to the company’s increasing gross profit margin.
On the other hand, Intel has encountered several obstacles that have severely impacted its gross profit margin. These include challenges and delays in advancing its manufacturing technologies, increased competition from companies like AMD, and the complexities and overhead costs associated with its integrated device manufacturing model.
Additionally, execution challenges and competitive pressures have further exacerbated the situation, leading to a decline in its gross profit margin.
Operating Profit Margin
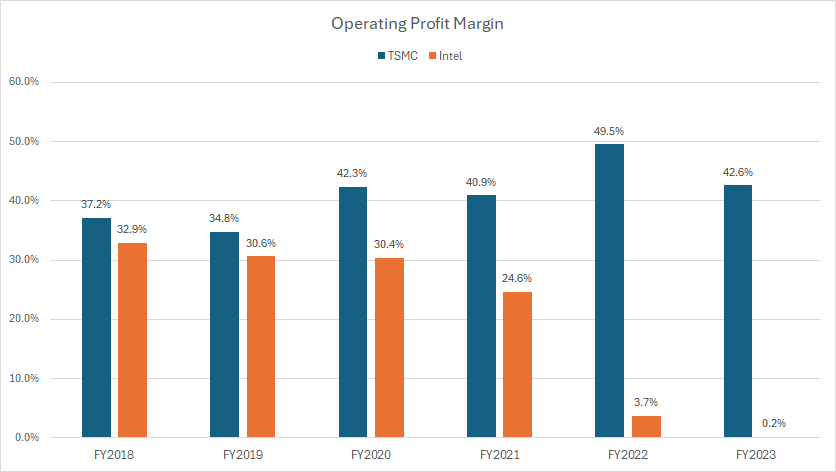
tsmc-vs-intel-in-operating-profit-margin
(click image to expand)
The definition of gross profit is available here: gross profit.
TSMC reports its financial statements primarily in New Taiwan Dollars (TWD). You can find more information about the currency exchange rates between TWD and the US dollar here: New Taiwan Dollar (TWD).
From an operational efficiency perspective, TSMC has consistently outperformed Intel, as depicted in the chart above. TSMC has generated significantly higher operating profit margins across all fiscal years, even during periods when it lagged behind Intel in terms of gross profit margin.
TSMC’s operational efficiency has shown notable improvement in recent years. The company’s operating profit margin rose from 41% in fiscal year 2021 to nearly 50% in fiscal year 2022.
Although there was a slight decline in fiscal year 2023, with the operating profit margin dropping to 43%, TSMC still maintained a strong performance.
In contrast, Intel’s operational efficiency has significantly deteriorated in recent years, as evidenced by the decreasing operating profit margin shown in the accompanying graph. From fiscal year 2021 to 2023, Intel’s operating profit margin plummeted from 25% to 0%, marking a dramatic decline.
TSMC’s success can be attributed to its robust operational management. The company’s emphasis on manufacturing excellence and continuous improvement has resulted in high operational efficiency and lower production costs.
Conversely, Intel has encountered operational challenges, such as higher costs associated with its integrated design and manufacturing approach.
Net Profit Margin
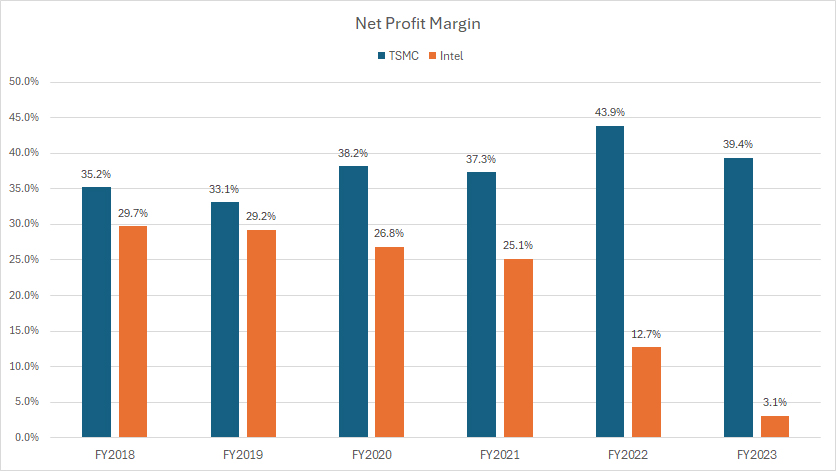
tsmc-vs-intel-in-net-profit-margin
(click image to expand)
The definition of gross profit is available here: gross profit.
TSMC reports its financial statements primarily in New Taiwan Dollars (TWD). You can find more information about the currency exchange rates between TWD and the US dollar here: New Taiwan Dollar (TWD).
In terms of net profit margin, TSMC has consistently outperformed Intel by a significant margin, as depicted in the chart above.
For instance, in fiscal year 2023, Intel’s net profit margin plummeted to just 3%, while TSMC’s net profit margin remained robust at 39% during the same period.
Over the three-year period from fiscal year 2021 to 2023, TSMC’s average net profit margin was an impressive 40%, in stark contrast to Intel’s average net profit margin of 14% over the same timeframe.
TSMC’s superior net profit margins can be attributed to its success in technological leadership, achieving significant economies of scale, maintaining a diverse customer base, and consistently improving operational efficiency.
On the flipped side, Intel has faced delays in technological advancements and increased competition. Additionally, Intel’s integrated device manufacturing model involves higher operational complexities and overhead costs. Furthermore, execution challenges and competitive pressures have further exacerbated Intel’s profitability issues.
These factors collectively explain why TSMC has been able to achieve much higher net profit margins compared to Intel.
Conclusion
TSMC’s ability to achieve higher profit margins than Intel highlights the importance of strategic focus and operational efficiency in the semiconductor industry. TSMC’s specialization as a pure-play foundry allows it to concentrate on manufacturing excellence, leading to economies of scale, lower production costs, and higher operational efficiency. Additionally, TSMC’s continuous investment in advanced technologies, such as 5nm and 3nm processes, positions it as a leader in the market, enabling it to command premium pricing.
On the other hand, Intel’s integrated device manufacturing model, while comprehensive, involves higher operational complexities and costs. The company’s challenges in advancing its manufacturing technologies, coupled with increased competition from companies like AMD, have further pressured its profit margins.
For investors and stakeholders, this comparison underscores the need to consider a company’s strategic positioning, technological advancements, and operational efficiency when evaluating its potential for long-term profitability and growth. As the semiconductor industry continues to evolve, the ability to adapt to market trends and maintain a competitive edge will be critical for sustained success.
Credits and References
1. All financial figures presented were obtained and referenced from TSMC’s annual reports published on the company’s investor relations page: TSMC Annual Reports.
2. Pexels Images.
Disclosure
We may use the assistance of artificial intelligence (AI) tools to produce some of the text in this article. However, the data is directly obtained from original sources and meticulously cross-checked by our editors multiple times to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media. Additionally, providing a link back to this article from any website can help us create more content like this in the future.
Thank you for your support and engagement! Your involvement helps us continue to provide high-quality, reliable content.