House roof. Pexels Image.
This article provides a detailed breakdown of Berkshire Hathaway’s profit margin within its insurance segment, categorized by divisions such as GEICO, the Primary Group, and the Reinsurance Group.
For the definitions of Berkshire’s insurance divisions, you may visit this section: Berkshire’s insurance segments.
Let’s take a look!
Investors looking for other statistics of Berkshire Hathaway may find more resources on these pages:
- Berkshire Hathaway insurance vs non-insurance revenue,
- Berkshire Hathaway insurance revenue by division, and
- Berkshire Hathaway insurance premiums by region.
Please use the table of contents to navigate this page.
Table Of Contents
Definitions And Overview
- Insurance Underwriting
- Investment Income
- GEICO
- Berkshire Hathaway Primary Group
- Berkshire Hathaway Reinsurance Group
- Earnings Before Income Taxes (EBIT)
O2. What May Drive Down The Profit Margins Of Berkshire’s Insurance Underwriting?
Consolidated Results For Insurance
A1. Profit Margin Of Total Insurance
Insurance Underwriting
A2. Profit Margin Of Insurance Underwriting
Investment Income
A3. Profit Margin Of Investment Income
Breakdown Of Insurance Underwriting
A4. Profit Margin Of GEICO, Primary Group, And Reinsurance Group
Summary And Reference
S1. Summary
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
Definitions
To help readers understand the content better, the following terms and glossaries have been provided.
Insurance Underwriting: Insurance underwriting is the process by which an insurance company evaluates the risks associated with insuring a person, property, or entity and determines the terms and conditions of the insurance policy.
This process helps the insurer decide whether to provide coverage and at what premium rate. Here are the key steps involved in insurance underwriting:
- Risk Assessment: Underwriters assess the potential risk factors associated with the applicant. This may include reviewing the applicant’s health, occupation, lifestyle, or the characteristics of the property being insured.
- Application Review: The underwriter examines the information provided in the insurance application, including any supporting documents, such as medical records or property appraisals.
- Data Analysis: Underwriters use statistical data, historical claims information, and other relevant data to estimate the likelihood of a claim being made and the potential cost of that claim.
- Decision Making: Based on the risk assessment and data analysis, the underwriter decides whether to approve or deny the insurance application. If approved, they determine the policy terms, coverage limits, exclusions, and the premium rate.
- Policy Issuance: Once the terms are agreed upon, the insurance policy is issued to the applicant, outlining the coverage details and the conditions under which claims will be paid.
Insurance underwriting ensures that the insurer can manage its risk portfolio effectively while providing appropriate coverage to policyholders.
Investment Income: Berkshire Hathaway’s investment income refers to the earnings generated from the investments made by its insurance subsidiaries, as well as other segments of the company. Here’s an overview:
- Insurance Float: Berkshire Hathaway’s insurance operations, such as GEICO and Berkshire Hathaway Reinsurance Group, collect premiums from policyholders. This pool of funds, known as “float,” represents money that the company holds until claims are paid out. Warren Buffett and his team invest this float in various financial assets to generate returns.
- Equity Investments: Berkshire Hathaway holds significant positions in publicly traded companies. These equity investments generate income through dividends and capital appreciation. Notable investments include large stakes in companies like Apple, Coca-Cola, and American Express.
- Fixed-Income Investments: The company also invests in fixed-income securities, such as bonds and Treasury bills. These investments provide regular interest income, contributing to the overall investment income.
- Private Investments: Berkshire Hathaway makes investments in private companies and businesses, often acquiring them outright. These investments contribute to the company’s investment income through dividends, interest, and the profits generated by these businesses.
- Real Estate Investments: Berkshire Hathaway invests in real estate properties, both directly and through its subsidiaries. These properties generate rental income and potential capital gains.
Overall, Berkshire Hathaway’s investment income is a critical component of its financial performance, allowing the company to leverage its insurance float and other capital to generate substantial returns.
GEICO: Berkshire Hathaway’s GEICO, also known as the Government Employees Insurance Company, is one of the largest auto insurance companies in the United States.
GEICO was founded in 1936 by Leo and Lillian Goodwin, initially targeting government employees and military personnel for affordable auto insurance. Over the years, GEICO has expanded its customer base to include the general public.
GEICO is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway, the multinational conglomerate led by Warren Buffett. As a subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway, GEICO benefits from the financial strength and stability of its parent company.
GEICO is well-known for its innovative and memorable advertising campaigns, featuring characters like the GEICO Gecko and the Caveman. The company provides a variety of insurance products, including:
- Auto Insurance: Coverage for cars, motorcycles, and other vehicles.
- Homeowners Insurance: Protection for homes and personal property.
- Renters Insurance: Coverage for personal property in rental units.
- Condo Insurance: Protection for condominium owners.
- Boat Insurance: Coverage for boats and personal watercraft.
- Business Insurance: Various insurance products for small businesses.
GEICO is recognized for its excellent customer service and user-friendly online platform, which allows customers to obtain quotes, manage policies, and file claims efficiently.
Berkshire Hathaway Primary Group: Berkshire Hathaway Primary Group consists of multiple insurance operations that collectively offer a range of commercial insurance products.
These products include commercial motor vehicle insurance, workers’ compensation, commercial property, healthcare liability, business owners’ insurance, and other insurance offerings.
The Primary Group is one of the key segments within Berkshire Hathaway’s insurance operations, contributing significantly to the company’s overall revenue.
Berkshire Hathaway Reinsurance Group: Berkshire Hathaway Reinsurance Group is a division of Berkshire Hathaway Inc. This group is one of the largest reinsurance groups globally, providing insurance and reinsurance solutions to other insurance companies.
Here are some key points about the Berkshire Hathaway Reinsurance Group:
- Financial Strength: The group has unparalleled financial strength, enabling it to facilitate large, tailored solutions for insurance and reinsurance companies worldwide.
- Diverse Portfolio: It offers a diverse portfolio of reinsurance contracts, including treaty, facultative, quota-share, and excess reinsurance.
- Global Reach: The group operates in 26 countries, showcasing its extensive influence and reach in the global reinsurance market.
- Segments: The group includes divisions like Berkshire Hathaway Life, which specializes in large transactions for life and health risks, and other segments focusing on property/casualty reinsurance.
Berkshire Hathaway Reinsurance Group is known for its strategic acumen and resilience, contributing significantly to Berkshire Hathaway’s overall success.
Earnings Before Income Taxes (EBIT): Earnings Before Income Taxes (EBIT) is a financial metric used to assess a company’s profitability before accounting for income taxes. It is calculated by subtracting operating expenses, excluding interest and taxes, from total revenue.
Here’s the formula for EBIT:
\[\text{EBIT} = \text{Revenue – Operating Expenses (OPEX)} \]
EBIT is important because it helps investors and analysts understand a company’s operating performance without the influence of tax policies and interest expenses. It provides a clearer picture of the company’s core operations and profitability.
For example, if a company’s revenue is $1 million and its operating expenses (excluding taxes and interest) are $700,000, the EBIT would be:
\[\text{EBIT} = \text{\$1,000,000 − \$700,000} = \text{\$300,000} \]
In this case, the company’s earnings before income taxes are $300,000.
What May Drive Down The Profit Margins Of Berkshire’s Insurance Underwriting?
Several factors can contribute to the low profit margin of Berkshire Hathaway’s insurance underwriting:
- Catastrophic Events: Natural disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods can lead to substantial claims, which significantly reduce profit margins. The frequency and severity of such events directly impact the underwriting results.
- Higher-than-Expected Claims: Increased losses from prior year claims or unexpected large claims can strain the company’s financial resources and negatively affect profit margins. This includes claims from previous years that were not fully anticipated.
- High Loss and Loss Adjustment Expenses (LAE): The costs associated with investigating, processing, and settling claims (LAE) can be considerable. High LAE can erode underwriting profits, especially if claims frequency or severity increases.
- Market Competition: Intense competition in the insurance industry can lead to lower premium rates as companies strive to attract customers. Reduced premium rates can squeeze profit margins and affect overall profitability.
- Regulatory Changes: Changes in insurance regulations and compliance requirements can increase operational costs. New regulations may require additional resources and processes, impacting the cost structure and profitability of underwriting operations.
- Economic Conditions: Economic downturns can lead to higher claims frequency, particularly in areas like unemployment, health, and auto insurance. Additionally, economic conditions can affect the investment income that supports insurance operations.
- Investment Income Volatility: Although investment income supports Berkshire Hathaway’s insurance operations, fluctuations in financial markets can impact overall profitability. Poor investment returns can weaken the financial buffer for underwriting operations.
- Underwriting Practices: Conservative underwriting practices, while minimizing risk, can also limit premium growth. Additionally, inadequate pricing or misestimating the risk associated with policies can lead to lower profit margins.
- Rising Reinsurance Costs: The cost of purchasing reinsurance to protect against large losses can increase, reducing profit margins. Reinsurance is essential for spreading risk, but higher reinsurance premiums can impact profitability.
- Healthcare and Litigation Costs: Increasing healthcare costs and litigation expenses related to claims can drive up the overall cost of underwriting. Legal disputes and settlements can be particularly costly, affecting profit margins.
By addressing these factors, Berkshire Hathaway can work towards maintaining and improving the profitability of its insurance underwriting operations. Effective risk management, accurate pricing, and efficient claims processing are crucial to overcoming these challenges.
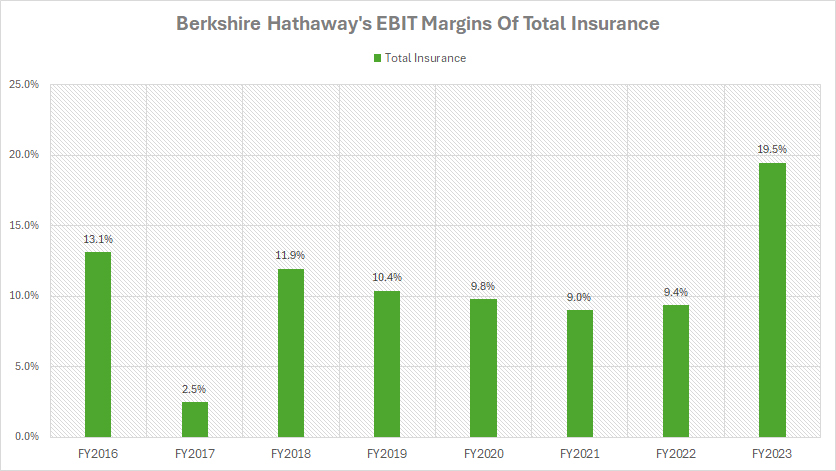
Profit Margin Of Total Insurance
berkshire-profit-margin-of-total-insurance
(click image to expand)
The profit margin of Berkshire’s total insurance is evaluated based on the EBIT margin provided by the company’s annual reports. You can find the definitions of Earnings Before Income Taxes (EBIT) here: Earnings Before Income Taxes (EBIT).
Berkshire Hathaway’s total insurance operations consist of both insurance underwriting and investment income. On a consolidated basis, Berkshire Hathaway witnessed a significant surge in profit margin within the total insurance unit in fiscal year 2023, reaching 19.5%, the highest level recorded over the past eight years.
In fiscal year 2022, Berkshire Hathaway generated a profit margin of just 9.4% for its total insurance segment. Despite this dip, on average, the profit margin of Berkshire Hathaway’s total insurance segment has amounted to 12.6% over the past three years.
Several factors can help explain the fluctuations in Berkshire Hathaway’s insurance profit margins. A notable reason is the impact of insurance claims and losses. For instance, variations in the frequency and severity of claims can significantly affect profit margins. Higher-than-expected claims or catastrophic events can lead to increased payouts, thus reducing profitability.
For other factors, you may refer to this section: potential causes of lower profit margins of Berkshire’s insurance operations.
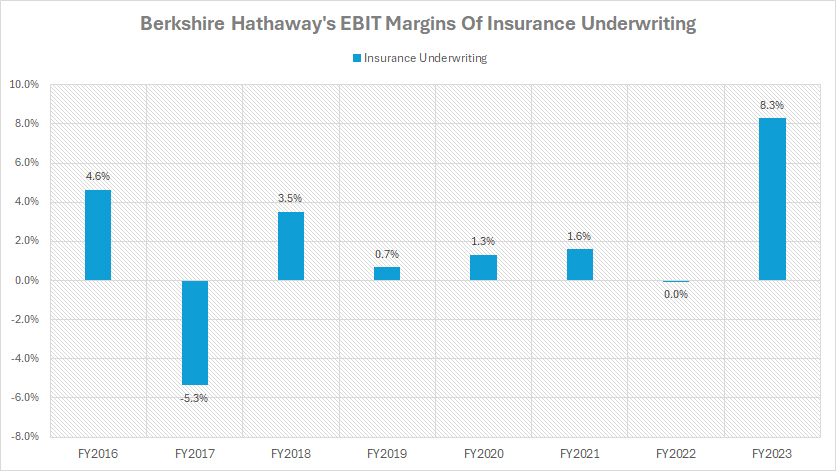
Profit Margin Of Insurance Underwriting
berkshire-profit-margin-of-insurance-underwriting
(click image to expand)
The profit margin of Berkshire’s insurance underwritng is evaluated based on the EBIT margin provided by the company’s annual reports. You can find the definitions of Earnings Before Income Taxes (EBIT) here: Earnings Before Income Taxes (EBIT).
To help you understand Berkshire’s insurance underwriting, a definition is provided here: insurance underwriting.
Berkshire Hathaway’s soaring profit margin in fiscal year 2023 is primarily attributed to the significant improvement in the profit margin of its insurance underwriting, as depicted in the chart above. The profit margin of Berkshire’s insurance underwriting surged to a record figure of 8.3% in fiscal year 2023, marking the highest number recorded over the past eight years.
However, in fiscal year 2022, Berkshire Hathaway recorded a profit margin of 0.0% for its insurance underwriting. This stagnant profit margin underscores the challenges faced during that period. On average, over the past three years, Berkshire’s insurance underwriting has generated profit margins hovering around 3%.
Variations in the frequency and severity of claims can significantly impact the profit margins of Berkshire’s insurance underwriting. For instance, in fiscal year 2022, higher-than-expected claims or catastrophic events likely led to increased payouts, reducing profitability.
Additionally, the occurrence of natural disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and wildfires can result in substantial claims, thereby diminishing profit margins.
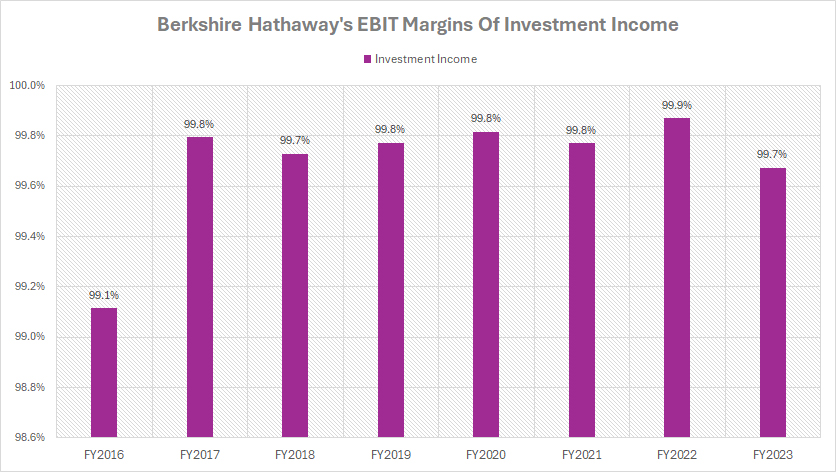
Profit Margin Of Investment Income
berkshire-profit-margin-of-investment-income
(click image to expand)
The profit margin of Berkshire’s investment income is evaluated based on the EBIT margin provided by the company’s annual reports. You can find the definitions of Earnings Before Income Taxes (EBIT) here: Earnings Before Income Taxes (EBIT).
To help you understand Berkshire’s investment income, a definition is provided here: investment income.
The profit margin of Berkshire Hathaway’s investment income has shown extraordinary results, as depicted in the chart above. In fiscal year 2023, the profit margin of Berkshire Hathaway’s investment income totaled 99.7%, compared to 99.9% a year ago. And it was 99.8% in fiscal year 2021.
Over the past three years, the profit margin has averaged nearly 100%, meaning that the company retains the entire profit from its investment income. This extraordinary profit margin illustrates the company’s exceptional ability to generate substantial returns from its investments while keeping costs remarkably low.
It’s important to note that the profit margins discussed are before income taxes. Nonetheless, the nearly 100% profit margin underscores the efficiency and effectiveness of Berkshire Hathaway’s investment strategy.
Several factors are driving the exceptional profit margins of Berkshire Hathaway’s investment income. A notable reason is Berkshire’s efficient cost management.
In this aspect, Berkshire Hathaway has been able to maintain low operating costs and overheads, which allows the company to maximize its income from investments. Efficient cost management is crucial to maintaining such high profit margins.
Another crucial reason is reinvested earnings. For instance, a significant portion of Berkshire Hathaway’s earnings is reinvested into new and existing investments. This reinvestment strategy further enhances the company’s income-generating capabilities.
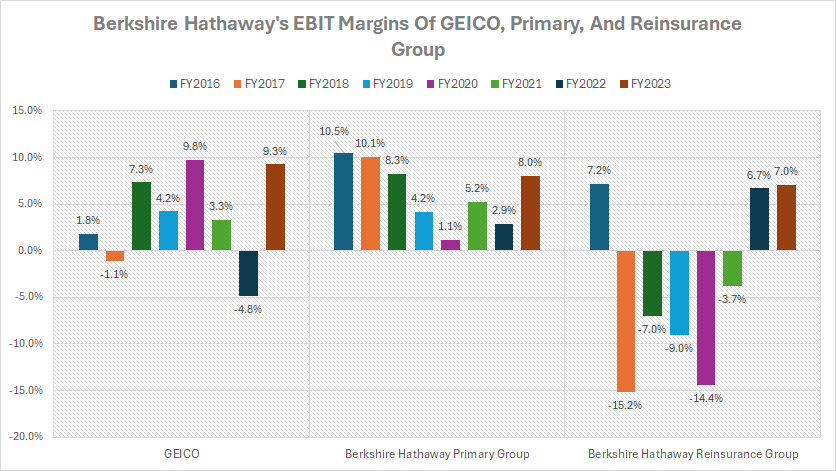
Profit Margin Of GEICO, Primary Group, And Reinsurance Group
berkshire-profit-margin-of-geico-primary-and-reinsurance-group
(click image to expand)
The profit margin of GEICO, Primary, and Reinsurance Group is evaluated based on the EBIT margin provided by the company’s annual reports. You can find the definitions of Earnings Before Income Taxes (EBIT) here: Earnings Before Income Taxes (EBIT).
To help you understand Berkshire’s insurance units, a definition is provided here: GEICO, Berkshire Primary Group, and Berkshire Reinsurance Group.
Of all the insurance units, Berkshire Hathaway’s GEICO and the Primary Group have been the most profitable, with profit margins averaging around 4% over the past five years. GEICO’s focus on direct sales, low-cost operations, and strong brand recognition has contributed to its consistent profitability.
The Primary Group, comprising Berkshire’s property and casualty insurance businesses, has benefited from conservative underwriting practices and stable operations, further boosting its profit margins.
On the other hand, Berkshire Hathaway’s Reinsurance Group has faced more significant challenges, generating an average profit margin of around -3% during the same period.
Reinsurance involves taking on large, complex risks that other companies may be unwilling or unable to write. This exposure to higher-risk policies and long-tail liabilities has impacted the Reinsurance Group’s profitability.
In fiscal year 2023, Berkshire’s GEICO insurance unit generated a pre-tax profit margin of 9.3%, while the pre-tax profit margin of the Primary Group was 8%. The Reinsurance Group had a pre-tax profit margin of 7% in the same period.
On a long-term basis, Berkshire Hathaway’s Primary Group has been the most profitable, with a pre-tax profit margin averaging around 6% since fiscal year 2016. In contrast, the profit margin of GEICO has averaged 4% during the same period.
Meanwhile, Berkshire Hathaway’s Reinsurance Group has faced more significant challenges, incurring pre-tax losses averaging around -4% between fiscal year 2016 and 2023.
The Reinsurance Group’s exposure to higher-risk policies and long-tail liabilities may have contributed to these losses. Additionally, catastrophic events and large-scale claims have further impacted the Reinsurance Group’s profitability.
Summary
Berkshire Hathaway’s diversified insurance operations show varying profit margins across different units. While GEICO and the Primary Group have demonstrated consistent profitability, the Reinsurance Group has faced more significant challenges due to higher-risk exposure and catastrophic events. However, the company’s strategic approach and diversified portfolio ensure overall financial stability and resilience.
Credits And References
1. All financial data presented were obtained and referenced from Berkshire Hathaway’s annual reports published on the company’s investor relations page: Berkshire’s Reports.
2. Pexels Images.
Disclosure
We may utilize the assistance of artificial intelligence (AI) tools to produce some of the text in this article. However, the data is directly obtained from original sources and meticulously cross-checked by our editors multiple times to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media. Additionally, providing a link back to this article from any website can help us create more content like this in the future.
Thank you for your support and engagement! Your involvement helps us continue to provide high-quality, reliable content.