GM Cruise autonomous vehicle. Source: Flickr
Liquidity is king for a business. Without liquidity or cash flow, a profitable business can still succumb to bankruptcy.
It’s no exception for General Motors (NYSE:GM) especially when it’s an assets-heavy auto manufacturing company that runs on huge working capital.
As you will see in the following charts, one of GM’s liquidity ratios shows that the company has, in fact, boosted its cash reserves substantially through debts during the COVID crisis, indicating that the company will do whatever is necessary and at any cost to increase its liquidity even if it meant shouldering more debts.
Moreover, to maintain its liquidity during the COVID crisis, GM also suspended its share buyback program as well as the dividend indefinitely.
These practices show just how important liquidity is for General Motors especially when the company anticipates a possible liquidity crisis in the near future.
In this article, we will look at General Motors’ liquidity ratios which include the current ratio, working capital and quick ratio (or acid test ratio).
Keep in mind that these ratios are meant to check on the company’s short-term liquidity, usually within a year from the reported date of the company’s financial filings.
So, just sit tight and keep reading!
Table Of Contents
Liquidity Ratios
A1. Current Ratio
A2. Working Capital
Liquidity Under Stressed Test
B1. Quick Ratio (Acid Test Ratio)
Extra Liquidity
Summary And Reference
S1. Conclusion
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
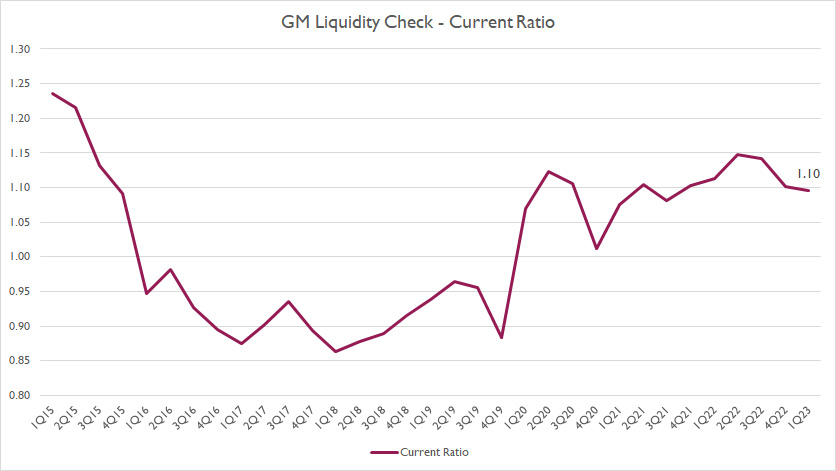
General Motors Current Ratio
GM current ratio
(click image to enlarge)
The current ratio is meant to measure the company’s short-term liquidity as it involves only current assets and current liabilities in the balance sheets.
According to the chart, GM’s current ratio improved significantly in recent years and had been able to stay above the 1.0X threshold since 2020.
As of 1Q 2023, GM’s current ratio topped 1.10X, one of the record highs since 2016.
Prior to 2020, GM’s current ratio dipped slightly below 1.0X, suggesting a deficit of current assets during those years.
However, it did not necessarily mean that GM could go bankrupt or face insolvency when the ratio dropped below 1.0X.
As long as GM could use a little help from its debt when there is a deficit in current assets, the company would be fine.
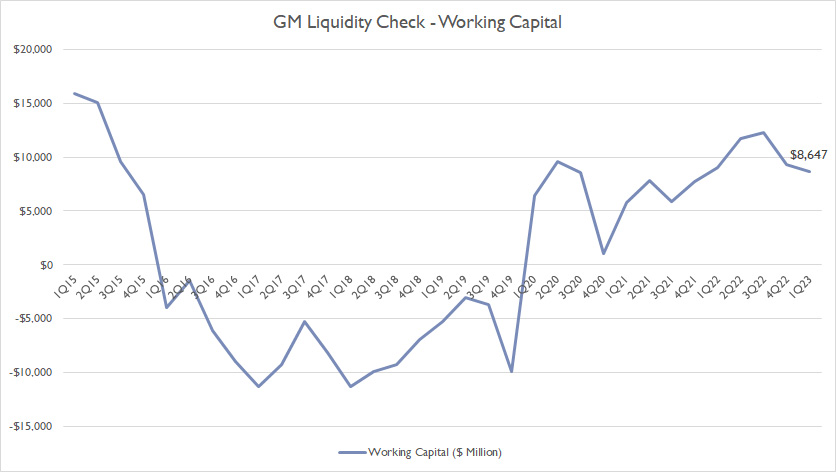
General Motors Working Capital
GM working capital
(click image to enlarge)
Similar to the current ratio, GM’s working capital dipped below $0 prior to 2020 but improved significantly in recent years.
As seen, GM’s working capital topped a massive $8.6 billion as of 1Q 2023, one of the record highs that has ever been measured since 2016.
GM’s surging working capital during the COVID crisis indicates the company’s ability to quickly deploy cash when necessary.
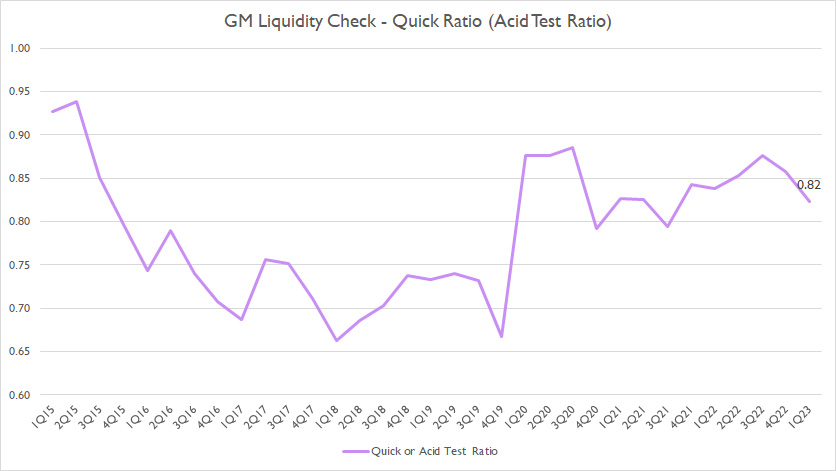
General Motors Quick Ratio
GM quick ratio
(click image to enlarge)
The quick ratio or acid test ratio measures GM’s liquidity during a stress test.
It excludes certain current assets such as inventory and prepaid expenses which are considered not as liquid as cash.
That said, GM’s quick ratio had been below 1.0X in all periods from fiscal 2015 to 2023, suggesting that the company’s cash and near-cash assets alone had not been sufficient to cover all short-term liabilities.
As of 1Q 2023, GM’s quick or acid test ratio came in at 0.82X, which wasn’t so bad because the figure was at the borderline.
Besides, GM’s quick or acid test ratio had significantly improved in recent years, illustrating the company’s growing liquidity.
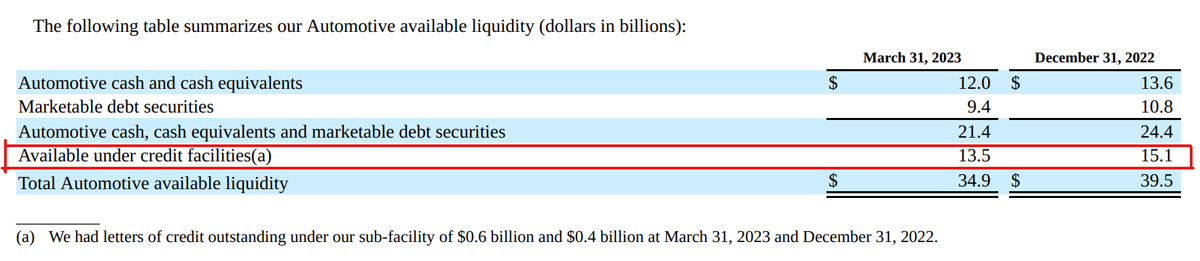
General Motors Extra Liquidity
GM automotive liquidity
(click image to enlarge)
Apart from its own cash, GM also uses short and long-term financing such as credit facilities to boost its liquidity when necessary.
Here is a quote extracted from GM’s 2023 10Q report regarding the company’s credit facilities:
-
“We use credit facilities as a mechanism to provide additional flexibility in managing our global liquidity.
Our Automotive borrowing capacity under credit facilities totaled $14.1 billion at March 31, 2023 and $15.5 billion at December 31, 2022, which consisted primarily of two credit facilities.”
Therefore, GM Automotive had roughly $14 billion of extra cash under its credit facilities as of 1Q 2023.
Of course, these are debt that needs to be paid off.
However, the extra cash can come in handy and provides financial flexibility to the company.
In short, GM should have no problem meeting its short-term obligations given the extra cash that the company has access to under its credit facilities.
Conclusion
The takeaway is that GM liquidity ratios, including the current ratio, working capital, and quick ratio, were all below 1.0X prior to 2020 but have since been on the rise and reached record highs in fiscal 2023.
In short, GM’s liquidity has improved significantly.
Apart from its own cash and near-cash assets, GM also has access to extra cash under its credit facilities, thereby further boosting its liquidity.
References and Credits
1. All financial numbers presented in this article were obtained and referenced from GM’s SEC filings, earnings reports, and other financial statements which are available in GM Investor Relation.
2. Featured images in this article are used under creative commons license and sourced from the following websites: waltarrrrr and James.
Disclosure
References and examples such as tables, charts, and diagrams are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant the full correctness of all content.
The content in this article is for informational purposes only and is neither a recommendation nor a piece of financial advice to purchase a stock.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media and also provide a link back to this article from any website so that more articles like this one can be created in the future.
Thank you!