Cloud computing. Pexels Images.
This article looks at Advanced Micro Devices (AMD)’s profitability and profit margin breakdown by segment. AMD’s segments consist of data center, client, gaming, and embedded.
AMD derives its profit primarily from the data center and embedded segments. These two segments alone accounted for nearly 80% of its total operating profit in fiscal year 2024.
Let’s look at the numbers!
For other key statistics of AMD, you may find more resources on these pages:
Revenue
- AMD revenue segments: data center, gaming, embedded, etc., and
- AMD revenue by region: U.S., Japan, China, Europe, Taiwan, etc.
Profit Margin
R&D Budget
- AMD vs Nvidia: research and development spending,
- AMD vs Intel: R&D cost
Debt
- AMD financial health: debt level, payment due, and liquidity
Please use the table of contents to navigate this page.
Table Of Contents
Definitions And Overview
O2. Why does AMD’s profit come primarily from the Data Center segment?
Profit Breakdown
A1. Profit In Data Center, Client, Gaming, And Embedded Segments
Profit Margin
B1. Profit Margin In Data Center, Client, Gaming, And Embedded Segments
Profit Breakdown In Percentage
C1. Percentage Of Profit In Data Center, Client, Gaming, And Embedded Segments
Profit Growth
D1. Growth Rates Of Profit In Data Center, Client, Gaming, And Embedded Segments
Summary And Reference
S1. Insight
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
Definitions Of Segments
To help readers understand the content better, the following terms and glossaries have been provided.
Data Center: AMD’s Data Center segment is dedicated to providing high-performance computing solutions for enterprise and cloud environments.
This segment includes server CPUs, such as the AMD EPYC™ processors, which are designed for scalability, energy efficiency, and robust security features. It also encompasses GPUs, AI accelerators, and adaptive SoC (System-on-Chip) products tailored for data centers.
The segment focuses on enabling advanced workloads like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and large-scale data processing. AMD’s innovations in this area have positioned it as a competitive player in the data center industry, driving significant revenue growth.
Client: AMD’s client segment primarily delivers high-performance microprocessors and graphics solutions for consumer devices. Key offerings include:
1. **CPUs for Desktops and Laptops**: The Ryzen series caters to gamers, content creators, and general users, providing efficient processing capabilities and multi-core performance.
2. **Graphics Cards**: AMD’s Radeon graphics cards enhance gaming experiences and support professional graphics work, making them popular among enthusiasts and industry professionals.
3. **Integrated Solutions**: AMD also develops APUs (Accelerated Processing Units) that combine CPU and GPU functionalities, delivering versatile performance for thin and light laptops.
This segment emphasizes innovation and performance. It competes with other major players by offering powerful and energy-efficient solutions suited to diverse consumer needs. With a focus on gaming and general computing, AMD aims to capture a significant share of the expanding client market.
Gaming: AMD’s gaming business delivers high-performance products tailored for gamers and enthusiasts. Key components include:
1. **Graphics Cards**: The Radeon series is at the forefront, designed to provide exceptional graphics performance, catering to both casual and professional gamers.
2. **CPUs**: The Ryzen processors, known for their multi-core capabilities, enhance gaming performance and support demanding applications, making them ideal for gaming rigs.
3. **APUs**: These Accelerated Processing Units integrate both CPU and GPU functionalities, offering versatile performance for lighter gaming needs in compact devices.
AMD aims to provide innovative, energy-efficient solutions that enhance gaming experiences while competing effectively in the dynamic gaming market. By focusing on performance and tailored technologies, AMD seeks to capture a significant portion of the growing gaming audience.
Embedded: AMD’s Embedded segment focuses on providing high-performance, scalable, and energy-efficient processors tailored for specialized applications.
These processors are designed for industries like automotive, industrial automation, networking, storage, and IoT (Internet of Things). The segment includes products like AMD EPYC™ Embedded and AMD Ryzen™ Embedded processors, which offer advanced security features, robust connectivity options, and long-term reliability.
The Embedded segment is particularly valuable for applications requiring consistent performance over extended lifecycles, such as ruggedized industrial machines, edge computing devices, and automotive systems.
AMD’s solutions in this area emphasize integration, flexibility, and power efficiency, making them ideal for diverse and demanding environments.
Why does AMD’s profit come primarily from the Data Center segment?
AMD’s profit is heavily driven by its Data Center segment due to the high demand for its EPYC processors, which are designed for enterprise applications like cloud computing and data analytics.
These processors are known for their scalability, energy efficiency, and robust security features, making them ideal for large-scale deployments. Additionally, AMD’s focus on high-performance computing solutions, including GPUs and AI accelerators, further strengthens its position in this lucrative market.
The Data Center segment benefits from higher margins compared to other segments, such as gaming or client solutions, due to the premium pricing of enterprise-grade products. This strategic emphasis on cutting-edge technology and enterprise solutions has positioned AMD as a key player in the data center industry.
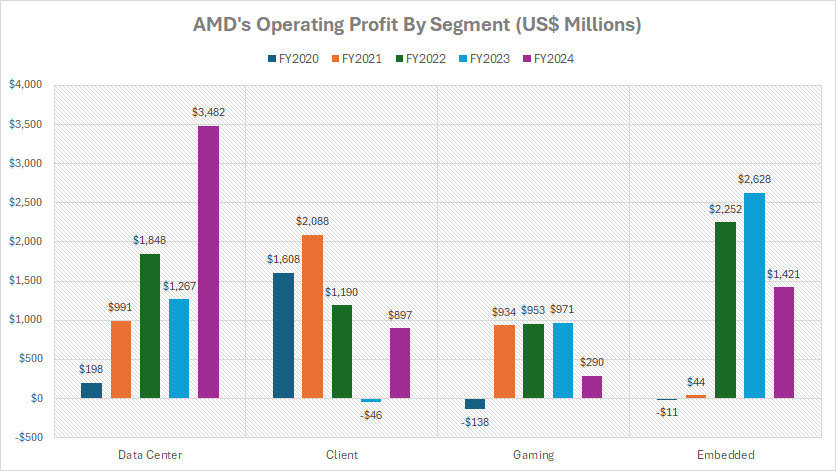
Profit In Data Center, Client, Gaming, And Embedded Segments
amd-operating-profit-breakdown-by-segment
(click image to expand)
AMD’s profit by segment is evaluated based on the operating profit of each segment, as depicted in the chart above. The definitions of AMD’s segments are available here: data center, client, gaming, and embedded.
Among all its segments, AMD’s Data Center segment remains the most profitable. In fiscal year 2024, it generated an operating profit of $3.5 billion, surpassing all other segments.
Over the past three years, the Data Center division has consistently performed well, with an average annual operating profit of $2.2 billion. This strong performance underscores the segment’s strategic importance as a key driver of AMD’s profitability, fueled by robust demand for EPYC processors and high-margin enterprise solutions.
The Embedded segment ranks as AMD’s second-largest contributor to operating profit. In fiscal year 2024, it delivered an operating profit of $1.4 billion, showcasing its significant role in the company’s financial structure.
Notably, over the last three years, the Embedded segment’s average annual operating profit reached $2.1 billion, just slightly trailing that of the Data Center business. This segment has benefited from the growing adoption of embedded solutions in industrial, automotive, and IoT applications.
In contrast, the Gaming segment contributed a relatively modest profit in fiscal year 2024. Its operating profit amounted to $290 million, the smallest among AMD’s segments. On a broader scale, between fiscal years 2022 and 2024, the Gaming division’s operating profit averaged $738 million annually, reflecting fluctuations in demand across the gaming hardware market and competition in this space.
Finally, AMD’s Client segment, which focuses on processors for personal computers and laptops, achieved a reasonable operating profit of $900 million in fiscal year 2024.
When assessed over a longer period, this segment’s average annual operating profit stood at $680 million over the past three years. While smaller in scale compared to the Data Center and Embedded segments, the Client business continues to play a steady role in AMD’s overall financial performance.
In summary, AMD’s profitability hierarchy emphasizes its strategic reliance on the high-margin Data Center and Embedded segments, while the Gaming and Client segments contribute more modestly to the company’s bottom line.
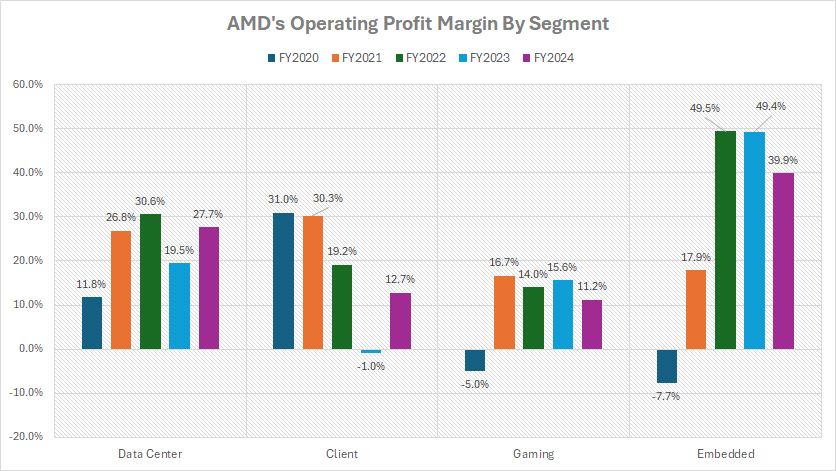
Profit Margin In Data Center, Client, Gaming, And Embedded Segments
amd-operating-profit-margin-by-segment
(click image to expand)
AMD’s margin by segment is evaluated based on the operating profit margin of each segment, as depicted in the chart above. The definitions of AMD’s segments are available here: data center, client, gaming, and embedded.
From the perspective of profit margin, AMD’s Embedded segment leads as the company’s most profitable division. In fiscal year 2024, the segment achieved an impressive operating margin of 40%, the highest among AMD’s business units.
Across the three fiscal years spanning 2022 to 2024, the Embedded segment maintained a remarkable average annual operating margin of 46%, cementing its status as the cornerstone of AMD’s profitability.
This high margin is driven by the premium pricing and steady demand for its specialized embedded solutions, which cater to industries such as industrial automation, automotive, and IoT.
Following closely is AMD’s Data Center segment, which also enjoys substantial profitability. In fiscal year 2024, this segment recorded an operating margin of 28%, reflecting its strategic role in meeting enterprise needs for high-performance computing solutions.
Over the three-year period from fiscal 2022 to 2024, the Data Center segment achieved an average annual operating margin of 26%, showcasing consistent financial strength bolstered by the widespread adoption of AMD’s EPYC processors and AI accelerators.
The Client segment, which focuses on processors for personal computers, experienced more volatility in profitability. Fiscal year 2023 was challenging, as the segment posted a negative operating margin of -1.0%, signaling an operating loss.
However, in fiscal year 2024, the Client segment rebounded significantly, achieving a profit margin of 13%. Over the past three years, its average annual operating margin stood at 10%, reflecting a steady, albeit smaller, contribution to AMD’s overall profitability. This turnaround highlights AMD’s adaptability in navigating market dynamics and driving improvements in the segment.
Lastly, AMD’s Gaming segment ranks as the least profitable among its business units. Between fiscal years 2022 and 2024, its average annual operating margin was 14%, a modest figure compared to the Embedded and Data Center segments.
In fiscal year 2024, the Gaming segment’s operating margin declined to 11%, marking the lowest margin among AMD’s segments that year. The relatively low profitability of this division is influenced by intense competition in the gaming hardware market and fluctuating demand for gaming GPUs and consoles.
In summary, AMD’s Embedded and Data Center segments dominate in terms of profit margins, driving the company’s financial success. Meanwhile, the Client and Gaming segments contribute more modestly, with varying degrees of profitability.
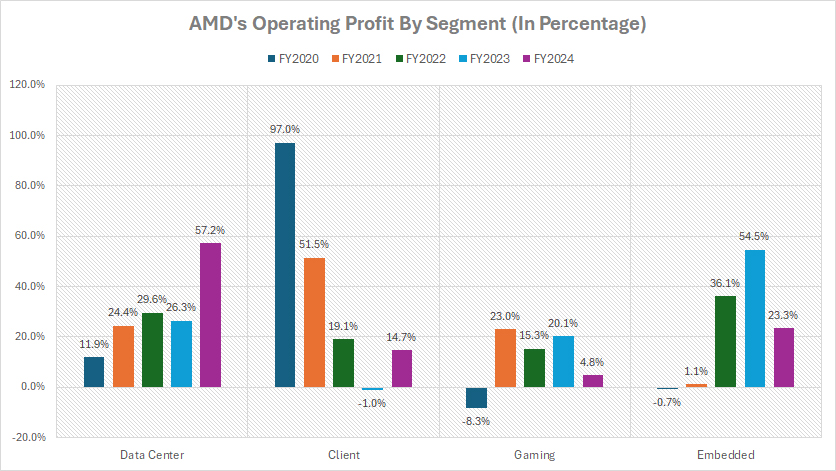
Percentage Of Profit In Data Center, Client, Gaming, And Embedded Segments
amd-operating-profit-breakdown-by-segment-in-percentage
(click image to expand)
AMD’s profit by segment is evaluated based on the operating profit of each segment, as depicted in the chart above. The definitions of AMD’s segments are available here: data center, client, gaming, and embedded.
In fiscal year 2024, AMD’s Data Center segment emerged as the company’s leading profit contributor, accounting for a substantial 57% of the total operating profit. This dominance highlights the strategic importance of AMD’s enterprise-focused offerings, including EPYC processors and AI accelerators.
Over the last three fiscal years (2022–2024), the Data Center segment consistently drove financial growth, averaging 38% of AMD’s operating profit share annually. This reflects its critical role in AMD’s overall profitability, fueled by high-margin products tailored to meet the demands of large-scale computing environments.
The Embedded segment ranked as AMD’s second-largest profit contributor in fiscal year 2024, with its share of operating profit reaching 23%. This division has proven to be a steady performer, benefiting from increasing demand in sectors like industrial automation, automotive, and IoT.
Between fiscal years 2022 and 2024, the Embedded segment rivaled the Data Center segment by averaging an annual operating profit share of 38%, demonstrating its competitive significance in AMD’s business structure.
Historically, the Client segment was AMD’s strongest profit generator. Back in fiscal year 2020, this segment achieved a staggering 97% of the company’s operating profit, reflecting its dominant position at the time.
However, this contribution has notably declined in recent years. By fiscal year 2024, the Client segment accounted for just 14% of AMD’s operating profit. Over the last three fiscal years, it contributed an average of 11% annually, illustrating its reduced financial impact due to shifting market dynamics and growing emphasis on AMD’s other segments.
The Gaming segment, while pivotal in targeting the consumer gaming market, contributed the smallest portion to AMD’s profitability. In fiscal year 2024, it delivered 5% of the total operating profit, making it the least profitable among AMD’s divisions for that year.
Nevertheless, over the three-year period from 2022 to 2024, the Gaming segment averaged 13% of AMD’s operating profit share annually, highlighting its relatively stable yet modest financial contribution amidst competitive pressures in the gaming hardware industry.
In conclusion, AMD’s profit distribution demonstrates a shift in focus toward higher-margin and enterprise-oriented segments, with the Data Center and Embedded divisions leading the charge. Meanwhile, the Client and Gaming segments, although still contributing, reflect a more modest impact on AMD’s financial landscape.
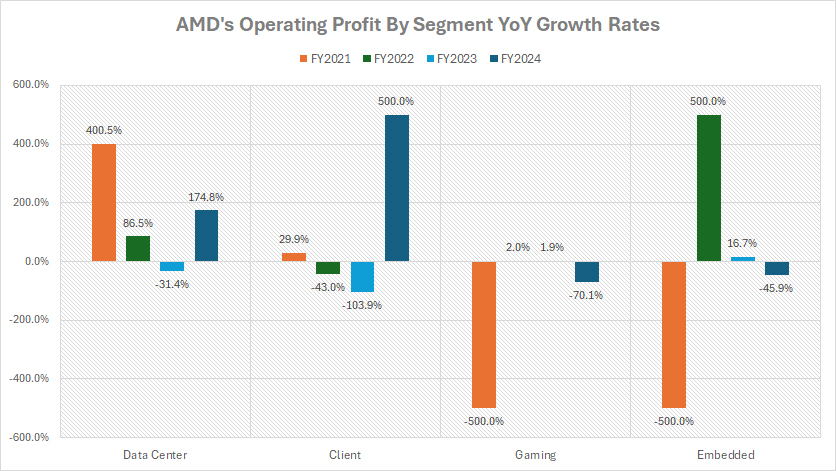
Growth Rates Of Profit In Data Center, Client, Gaming, And Embedded Segments
amd-growth-rates-of-operating-profit-by-segment
(click image to expand)
AMD’s profit by segment is evaluated based on the operating profit of each segment, as depicted in the chart above. The definitions of AMD’s segments are available here: data center, client, gaming, and embedded.
In terms of profit growth by segment, AMD’s Data Center division has demonstrated remarkable and consistent performance. Over the past three fiscal years (2022–2024), it achieved an average annual year-over-year (YoY) growth rate of an impressive 77%, highlighting its strategic importance and sustained demand.
This robust growth reflects the continued adoption of high-margin products like EPYC processors, AI accelerators, and high-performance computing solutions, which are critical for enterprise and cloud environments.
On the opposite end of the spectrum, AMD’s Gaming segment has struggled with profitability, making it the company’s worst-performing division in terms of growth. Since fiscal year 2022, the Gaming segment has reported an average annual YoY decline of -22%, indicative of challenges in the gaming hardware market, including heightened competition and fluctuating demand for gaming GPUs and consoles.
Both the Client and Embedded segments have exhibited significant fluctuations in profit growth over the same period. The Client segment, for instance, experienced a dramatic rebound in fiscal year 2024, when it returned to profitability after reporting an operating loss in fiscal year 2023.
This turnaround underscores the segment’s volatility, driven by changing market dynamics, including shifting consumer demand for PC processors and intense pricing pressure.
The Embedded segment is another case of pronounced variability. In fiscal year 2022, it saw a staggering YoY profit surge of over 500%, reflecting exceptional adoption of its solutions across industries like automotive, IoT, and industrial automation.
However, this momentum sharply reversed in the subsequent years, with profits declining significantly in fiscal years 2023 and 2024. This decline highlights the segment’s sensitivity to broader market conditions, such as industry-specific demand cycles and competitive dynamics.
In summary, AMD’s growth trajectory by segment reflects both successes and challenges. The Data Center division stands as a beacon of consistency and profitability, while the Gaming segment grapples with downward pressure. Meanwhile, the Client and Embedded segments reveal the complexities of fluctuating market conditions and varied performance trends.
Insight
AMD’s profitability is increasingly reliant on the Data Center and Embedded segments, driven by high-margin enterprise and embedded solutions.
The Client segment, though historically a significant contributor, now plays a more modest role, with inconsistent performance.
The Gaming segment continues to lag in both growth and margins, highlighting its lower profitability compared to AMD’s other businesses.
In summary, AMD’s profit dynamics reveal a strategic pivot toward enterprise and embedded markets, while its traditional consumer-oriented segments (Client and Gaming) face competitive and market pressures.
References and Credits
1. All financial figures presented were obtained and referenced from AMD’s quarterly and annual reports published on the company’s investor relations page: AMD Financial Reports.
2. Pexels Images.
Disclosure
We may use artificial intelligence (AI) tools to assist us in writing some of the text in this article. However, the data is directly obtained from original sources and meticulously cross-checked by our editors multiple times to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media. Additionally, providing a link back to this article from any website can help us create more content like this in the future.
Thank you for your support and engagement! Your involvement helps us continue to provide high-quality, reliable content.