Night light on the highway. Pexels Image.
General Motors and Tesla are among the major players in the automotive sector. Tesla is the first mover in the EV space.
On the other hand, GM is a latecomer in the EV space but the company is established in the fossil-fueled vehicle segment. GM has existed for over a century while Tesla has operated for only a decade.
Tesla’s market strategy focuses on direct-to-consumer sales through its own stores and online platform, bypassing traditional dealership networks. The company also emphasizes software updates and connectivity, with features like Autopilot and Full Self-Driving.
GM primarily sells its vehicles through a network of dealerships. While the company is investing in advanced technologies, such as its Ultium battery platform and Super Cruise, its transition to EVs is more gradual compared to Tesla’s all-electric approach.
That said, this article compares Tesla with GM in several aspects, including vehicle revenue, margins, and profitability.
Let’s get started!
Investors interested in other key statistics of GM and Tesla may find more resources on these pages:
- GM vs Ford and Tesla: marketing and advertising expenses,
- Tesla sales and production by models, and
- GM revenue streams: sales of new and used car, services, and more.
Please use the table of contents to navigate this page.
Table Of Contents
Definitions And Overview
Revenue
A1. Revenue Per Car
Profit
B1. Profit Per Car
Margin
C1. Vehicle Margin
Consolidated Margin
D1. Operating Margin
Conclusion And Reference
S1. Conclusion
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
Definitions
To help readers understand the content better, the following terms and glossaries have been provided.
Revenue Per Car: Revenue Per Car is defined as automotive revenue excluding leasing, regulatory credits, non-automotive segments, etc., divided by vehicle sales.
Revenue Per Car = Automotive Revenue / Vehicle Sales
Vehicle sales represent vehicle wholesale in the case of General Motors and vehicle retail volume excluding leasing in the case of Tesla.
Profit Per Car: Profit Per Car is defined as automotive gross profit divided by vehicle sales
Profit Per Car = Automotive Gross Profit / Vehicle Sales
Vehicle sales represent vehicle wholesale in the case of General Motors and vehicle retail volume excluding leasing in the case of Tesla.
Vehicle Margin: Vehicle margin is defined as the ratio of automotive gross profit to automotive revenue.
Vehicle Margin = Automotive Gross Profit / Automotive Revenue
Automotive revenue represents car sales revenue excluding GM Financial in the case of General Motors and leasing, regulatory credits, and energy in the case of Tesla.
Operating Margin: Operating margin is a financial metric that measures a company’s efficiency in generating profit from its operations.
It is expressed as a percentage and is calculated by dividing operating income (also known as operating profit) by net sales (revenue).
Operating Margin = Operating Income / Total Net Revenue
Essentially, operating margin shows what percentage of revenue is left over after paying for variable costs of production, such as wages and raw materials.
It’s a key indicator of a company’s financial health and its ability to manage its operations effectively. The higher the operating margin, the more profitable the company is considered to be.
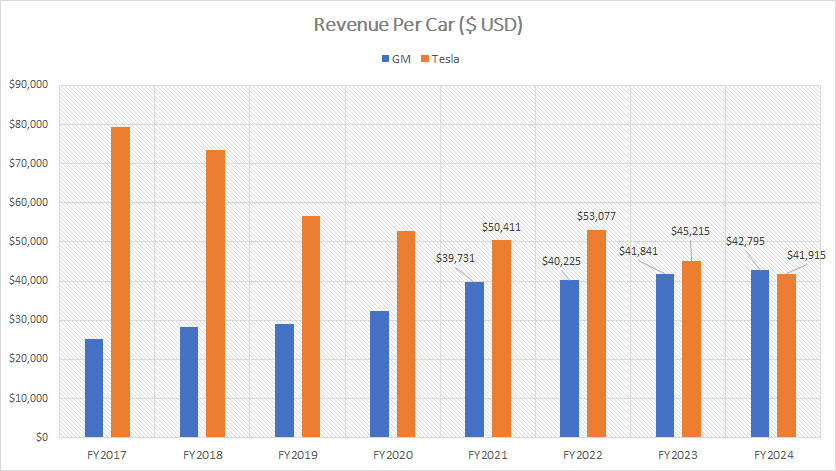
Revenue Per Car
gm-vs-tesla-in-revenue-per-car
(click image to expand)
The definition of revenue per car is available here: revenue per car.
Historically, Tesla has demonstrated significantly higher revenue per vehicle compared to General Motors (GM), as illustrated in the provided chart. In the fiscal year 2017, Tesla’s revenue per vehicle approximated $80,000, whereas GM’s revenue per vehicle was under $30,000.
Over the years, Tesla’s revenue per vehicle has experienced a substantial decline. This downward trajectory was notably accelerated by the introduction of the Model 3 and Model Y. These models facilitated mass production, effectively reducing the average price of Tesla’s vehicles. Consequently, Tesla’s revenue per vehicle saw a downward adjustment, reflecting the company’s strategy to penetrate a broader market segment through more affordable vehicle offerings.
Conversely, GM’s revenue per vehicle has exhibited an upward trend. By the end of fiscal year 2024, GM’s revenue per vehicle escalated to $42,800. In comparison, Tesla’s revenue per vehicle had decreased to $42,000 during the same period. This marked the first instance in over a decade where Tesla’s revenue per vehicle fell below that of GM.
The increase in GM’s revenue per vehicle can be attributed to the company’s strategic focus on higher-margin vehicles, particularly trucks and SUVs. These vehicle categories have constituted over 90% of GM’s sales, as substantiated by the referenced data: GM truck and SUV sales. This shift towards larger, more profitable vehicles has bolstered GM’s average revenue per vehicle.
The revenue per vehicle gap between GM and Tesla has substantially narrowed over time. By fiscal year 2024, Tesla’s revenue per vehicle had decreased below GM’s for the first time in a decade. This shift underscores the evolving competitive dynamics within the automotive industry, highlighting GM’s effective strategy in increasing its vehicle revenue through a focus on profitable vehicle segments.
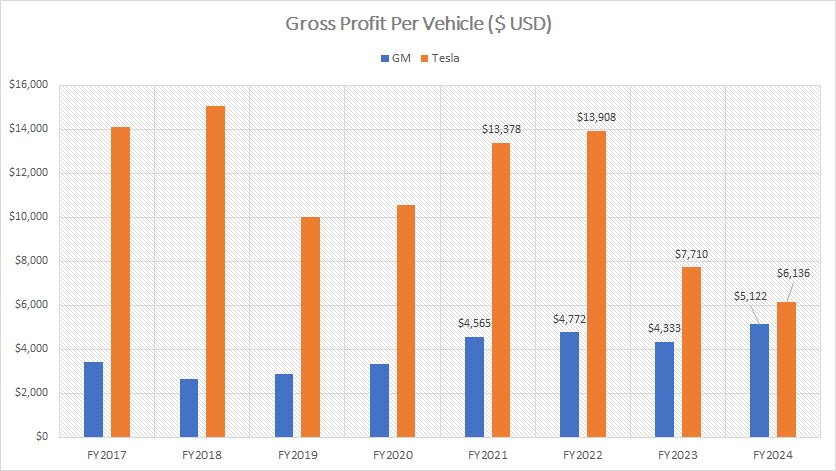
Profit Per Car
gm-vs-tesla-in-profit-per-vehicle
(click image to expand)
The definition of profit per car is available here: profit per car. Profit per car for both companies is evaluated based on the automotive gross profit.
Historically, Tesla has achieved substantially higher profit per vehicle compared to General Motors (GM), as demonstrated by the graph provided. For example, in fiscal year 2022, Tesla’s profit per vehicle was nearly $14,000, while GM’s profit per vehicle was only $4,300. The historical gap in profit margins has been considerable.
However, recent trends indicate a significant shift. Tesla’s profit per vehicle has notably declined, dropping to $6,100 by fiscal year 2024. Conversely, GM’s profit per vehicle has increased, reaching $5,100 in the same fiscal year. This change has resulted in a narrowing of the profit margin gap between the two companies. In the latest results, the difference in profit per vehicle between Tesla and GM was approximately $1,000.
Tesla’s declining profit per vehicle can be attributed to its decreasing revenue per vehicle, which we saw in earlier discussions. The company’s strategy of mass-producing more affordable models, such as the Model 3 and Model Y, has led to lower revenue and profit margins per unit. While this approach has enabled Tesla to expand its market share, it has also impacted the company’s profitability.
In contrast, GM’s increasing profit per vehicle is driven by its rising revenue per vehicle. The company’s focus on higher-margin vehicles, particularly trucks and SUVs, has contributed to this growth. These larger models constitute over 90% of GM’s sales, as indicated in the referenced data: GM truck and SUV sales. The shift towards more profitable vehicle segments has bolstered GM’s overall profit margins.
In summary, while Tesla has historically outperformed GM in terms of profit per vehicle, the recent narrowing of this gap underscores the dynamic and competitive nature of the automotive industry. Tesla’s focus on expanding its market through more affordable models has come at the cost of lower profit margins, whereas GM’s strategic emphasis on higher-margin vehicles has resulted in improved profitability.
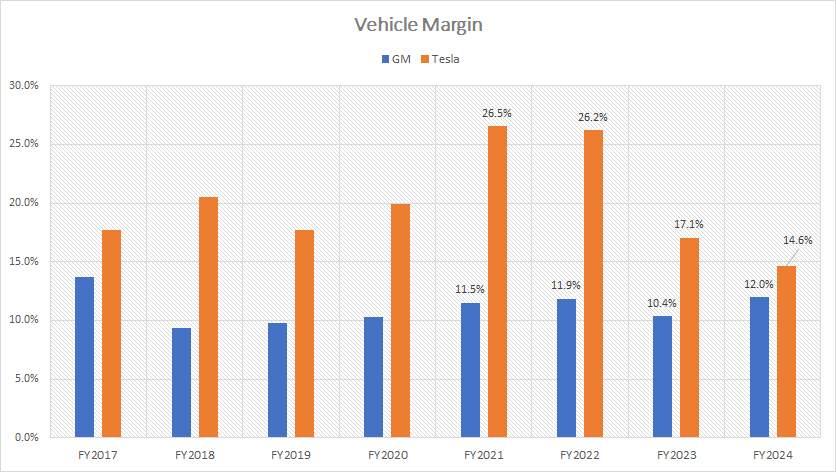
Vehicle Margin
gm-vs-tesla-in-vehicle-margin
(click image to expand)
The definition of vehicle margin is available here: vehicle margin. Vehicle margin for both companies is evaluated based on the automotive gross profit margin.
Similar to the profit per vehicle, Tesla has historically generated superior vehicle margins compared to General Motors (GM), as illustrated in the chart above. However, recent trends indicate a significant shift. Tesla’s margin per vehicle has notably declined, reaching just 15% by fiscal year 2024.
Conversely, GM’s vehicle margin has experienced an upward trend, increasing to 12% in fiscal year 2024. This is only slightly behind Tesla’s figure, marking a narrowing of the margin gap between the two companies.
Tesla’s declining vehicle margins can be attributed to several factors. The introduction of more affordable models like the Model 3 and Model Y has led to lower average selling prices, impacting overall margins. Additionally, the increased competition in the EV market and rising production costs have contributed to the downward pressure on Tesla’s margins.
On the other hand, GM’s rising vehicle margins are driven by the company’s strategic focus on higher-margin vehicle segments. The increased sales of trucks and SUVs, which typically command higher prices and margins, have played a significant role in this improvement. GM’s ongoing efforts to optimize production efficiencies and reduce costs have also contributed to the margin growth.
The narrowing gap in vehicle margins between Tesla and GM underscores the evolving competitive dynamics in the automotive industry. Tesla’s focus on mass-market EVs has led to a trade-off between market share and margin preservation. Meanwhile, GM’s emphasis on profitable vehicle segments has bolstered its margins, highlighting different strategic approaches by both automakers.
In summary, while Tesla has historically maintained better vehicle margins than GM, the recent trends indicate a convergence in margin performance. This shift reflects the broader changes in the automotive landscape, driven by market competition, strategic decisions, and cost management efforts by both companies.
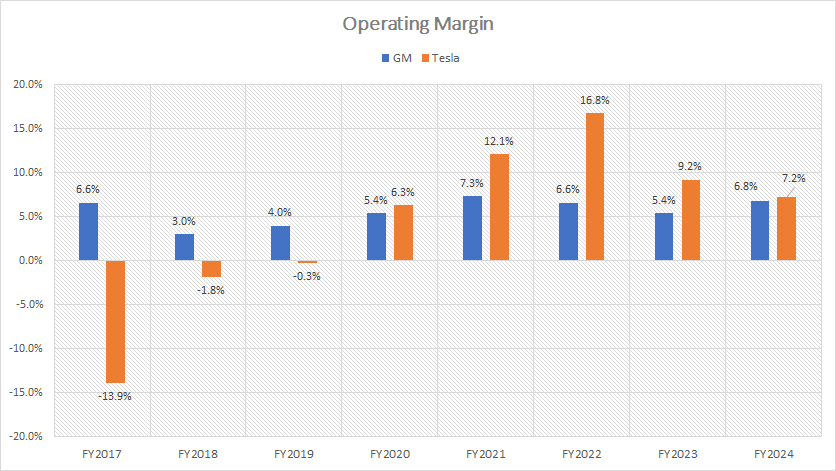
Operating Margin
gm-vs-tesla-in-operating-profit-margin
(click image to expand)
The definition of operating margin is available here: operating margin.
From an operational perspective, Tesla has historically operated more efficiently than General Motors (GM), as evidenced by Tesla’s higher operating margins. However, recent trends indicate a significant reduction in Tesla’s operating efficiency.
As of fiscal year 2024, Tesla’s operating margin had decreased to 7.2%, while GM’s operating margin had risen to 6.8%, bringing GM’s figure close to Tesla’s. This change reflects a narrowing gap in operational efficiency between the two companies.
Tesla’s reduced operating margin can be attributed to several factors, including increased production costs, competitive pressures, and the company’s strategy to produce and sell more affordable models like the Model 3 and Model Y. These factors have collectively impacted Tesla’s overall operating efficiency.
On the other hand, GM’s operating margin has improved due to the company’s focus on optimizing production processes and reducing operational costs. GM’s strategic shift towards higher-margin vehicles, such as trucks and SUVs, has also contributed to the enhanced operating margins. Additionally, GM’s investments in new technologies and manufacturing efficiencies have played a role in this positive trend.
Despite the recent convergence in operating margins, Tesla continues to lead over the longer term. Between 2022 and 2024, Tesla’s average operating margin was 11%, compared to GM’s average operating margin of 6% during the same period. This demonstrates Tesla’s historical advantage in operational efficiency.
The narrowing gap in operating margins between Tesla and GM underscores the dynamic and competitive nature of the automotive industry. Tesla’s focus on expanding its market presence through more affordable vehicles has led to a trade-off in operating margins, while GM’s emphasis on higher-margin segments and operational efficiencies has resulted in improved margins.
In summary, although Tesla has historically maintained higher operating margins than GM, recent trends indicate a convergence in operational efficiency. This shift reflects the evolving strategies and market dynamics within the automotive industry.
Summary
In summary, while Tesla has historically outperformed GM in several key metrics, recent trends indicate a more competitive landscape. Both companies have distinct strategies that reflect their unique strengths and market positions, with Tesla focusing on affordability and market expansion, and GM emphasizing higher-margin segments and operational efficiencies.
References and Credits
1. All financial figures presented were obtained and referenced from GM and Tesla’s annual reports published on the companies’ respective investor relations pages: GM SEC filings and Tesla SEC filings.
2. Pexels Images.
Disclosure
We may use the assistance of artificial intelligence (AI) tools to produce some of the text in this article. However, the data is directly obtained from original sources and meticulously cross-checked by our editors multiple times to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media. Additionally, providing a link back to this article from any website can help us create more content like this in the future.
Thank you for your support and engagement! Your involvement helps us continue to provide high-quality, reliable content.