Clean energy battery. Pexels Image.
This article provides a comparative analysis of the profitability and margins of Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited (TSMC) and Samsung Electronics.
TSMC (Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company) and Samsung are two leading players in the semiconductor industry. Both companies operate foundry business models, where they manufacture semiconductors for other companies.
TSMC focuses exclusively on this model, without designing its own chips. In contrast, Samsung runs a foundry business alongside its own semiconductor design and manufacturing, serving external clients and producing chips for its products.
Let’s look at the profit and margin!
You may find related statistic of TSMC on these pages:
- TSMC vs Intel: profit and margins comparison,
- TSMC vs Intel: R&D costs, and
- TSMC revenue breakdown: HPC, Smartphone, IoT, Automotive, etc..
Please use the table of contents to navigate this page.
Table Of Contents
Definitions And Overview
O2. Why is TSMC having much better profit margins than Samsung?
Profitability
A1. Gross Profit
Margins
B1. Gross Profit Margin
B2. Operating Profit Margin
B3. Net Profit Margin
Conclusion And Reference
S1. Conclusion
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
Definitions
To help readers understand the content better, the following terms and glossaries have been provided.
Currency Conversion: TSMC and Samsung presented their financial results in their native currencies, specifically the New Taiwan Dollar (TWD) for TSMC and the Korean Won (KRW) for Samsung.
The respective companies handled the conversion of these currencies to US dollars at the time of their earnings presentations, rather than the editors.
Gross Profit: Gross profit is a financial metric representing the difference between a company’s revenue and the cost of goods sold (COGS).
It measures how efficiently a company is producing and selling its goods. The formula for calculating gross profit is:
Gross Profit = Revenue − Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Gross profit is a key indicator of a company’s core profitability before accounting for overhead, taxes, and other operating expenses.
It is typically used to assess a company’s production efficiency and cost management. Higher gross profit margin indicates better efficiency in producing and selling products, while lower gross profit margin may suggest issues in cost control or pricing strategies.
Operating Profit: Operating profit, also known as operating income or operating earnings, is a measure of a company’s profitability from its core business operations, excluding any income or expenses not directly related to the primary business activities.
It is calculated by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit. Here’s a breakdown of the components:
- Gross Profit: Revenue minus the cost of goods sold (COGS).
- Operating Expenses: These include selling, general, and administrative expenses (SG&A), depreciation, and other expenses related to the core operations of the business.
The formula for calculating operating profit is:
Operating Profit = Gross Profit − Operating Expenses
Operating profit provides insight into a company’s efficiency in managing its core business activities and controlling costs. It is a key metric used by investors and analysts to evaluate a company’s financial health and operational performance.
Why is TSMC having much better profit margins than Samsung?
TSMC (Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company) consistently achieves better profit margins than Samsung due to several key factors:
-
Business Model:
- TSMC operates as a pure-play foundry, meaning it focuses exclusively on manufacturing semiconductor products for other companies based on their designs. This allows TSMC to concentrate on manufacturing efficiency and economies of scale.
- In contrast, Samsung designs and manufactures its own chips, which involves higher research and development (R&D) costs and capital expenditures.
-
Manufacturing Efficiency:
- TSMC is known for its cutting-edge manufacturing processes, including advanced technologies like 5-nanometer and 3-nanometer nodes. These technologies enable TSMC to produce smaller, more efficient, and powerful chips, which contribute to higher profit margins.
- Samsung also invests in advanced manufacturing technologies, but the dual focus on both foundry services and its own product lines can dilute its manufacturing efficiency.
-
Client Base:
- TSMC serves major clients such as Apple, Nvidia, and AMD, providing them with state-of-the-art semiconductor solutions. This strong client base ensures a steady demand for TSMC’s products and allows the company to maintain high utilization rates in its fabs, leading to better profit margins.
- Samsung, while also serving prominent clients, has to balance its foundry services with its internal demand for chips used in Samsung-branded products.
-
Cost Management
- TSMC’s focus on manufacturing efficiency and economies of scale allows it to manage costs effectively. By specializing in foundry services, TSMC can optimize its production processes and reduce overhead costs.
- Samsung, on the other hand, incurs higher costs due to its integrated business model, which includes both foundry services and its own semiconductor design and manufacturing.
-
R&D Investment:
- While both companies invest significantly in R&D, TSMC’s investments are primarily directed towards improving manufacturing processes and technologies. This targeted approach helps TSMC maintain its technological edge and achieve higher profit margins.
- Samsung’s R&D investments are spread across multiple business units, including consumer electronics and mobile communications, which can impact its overall profit margins.
These factors collectively contribute to TSMC’s superior profit margins compared to Samsung. TSMC’s focused business model, advanced manufacturing technologies, strong client base, effective cost management, and targeted R&D investments enable it to achieve higher profitability in the semiconductor industry.
Gross Profit
tsmc-vs-samsung-in-gross-profit
(click image to expand)
The definition of gross profit is available here: gross profit.
TSMC and Samsung report their financial results in their native currencies. The conversion of these currencies to USD was carried out by the respective companies, rather than the editors.
Samsung has consistently generated higher gross profits than TSMC, as depicted in the accompanying graph. In fiscal year 2024, Samsung’s gross profit reached $83.9 billion, while TSMC’s gross profit was $50.6 billion.
On average, between fiscal years 2022 and 2024, Samsung’s gross profit stood at $77 billion annually, whereas TSMC’s gross profit averaged $44 billion per year.
Despite Samsung’s significantly higher gross profits, they have largely remained stagnant over most fiscal years. In fact, they have declined over the long term. For instance, from fiscal year 2018 to 2024, Samsung’s gross profits declined by approximately 17%, dropping from $101.2 billion to $83.9 billion.
Conversely, during the same period, TSMC’s gross profit more than tripled, rising from $16.3 billion to $50.6 billion. This impressive growth highlights TSMC’s ability to increase profitability through effective cost management, strategic investments, and a focus on advanced manufacturing technologies.
While Samsung continues to lead in terms of gross profit, TSMC’s rapid growth trajectory signifies its potential to further close the gap. The stark contrast between the two companies’ profit trends underscores the dynamic and competitive nature of the semiconductor industry.
In summary, although Samsung consistently outperforms TSMC in gross profits, TSMC’s remarkable growth rate suggests it is well-positioned to enhance its profitability and strengthen its market presence in the years to come.
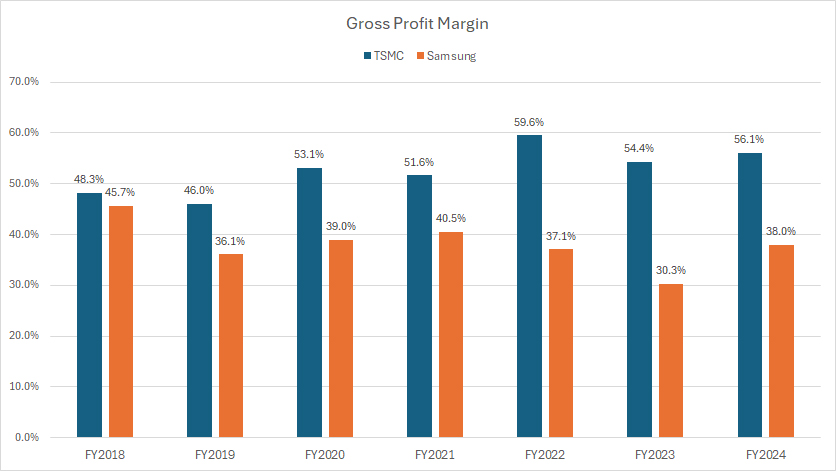
Gross Profit Margin
tsmc-vs-samsung-in-gross-profit-margin
(click image to expand)
The definition of gross profit is available here: gross profit.
TSMC and Samsung report their financial results in their native currencies. The conversion of these currencies to USD was carried out by the respective companies, rather than the editors.
Although Samsung generates significantly higher gross profits than TSMC, its gross profit margin is much lower in comparison, as shown in the chart above.
In fiscal year 2024, Samsung’s gross profit margin amounted to only 38%, while TSMC’s figure reached 56%, a considerably better result. On average, from fiscal year 2022 to 2024, TSMC’s gross profit margin landed at 57%, whereas Samsung’s gross profit margin was 35%.
Looking over a longer timeframe, from fiscal year 2018 to 2024, Samsung’s gross profit margin has consistently remained lower, declining from 46% to 38% over the past seven years. This downward trend suggests challenges in maintaining profitability amidst varying market conditions and operational costs.
Conversely, TSMC’s gross profit margin has steadily climbed, increasing from 48% in fiscal year 2018 to 56% in the most recent results. This upward trajectory highlights TSMC’s ability to enhance operational efficiency, manage costs effectively, and capitalize on advancements in semiconductor manufacturing technologies.
The contrasting trends in gross profit margins between Samsung and TSMC underscore the differences in their business models and operational strategies. TSMC’s focus on being a pure-play foundry allows it to optimize production processes and achieve higher margins. In contrast, Samsung’s integrated approach, balancing foundry services with in-house chip design and manufacturing, appears to impact its overall margin performance.
In summary, TSMC produces much better profitability than Samsung. While Samsung leads in gross profit generation, TSMC’s superior gross profit margins demonstrate its operational prowess and strategic focus on efficiency and technological innovation. This distinction positions TSMC favorably in the competitive semiconductor landscape, showcasing its potential for sustained profitability and growth.
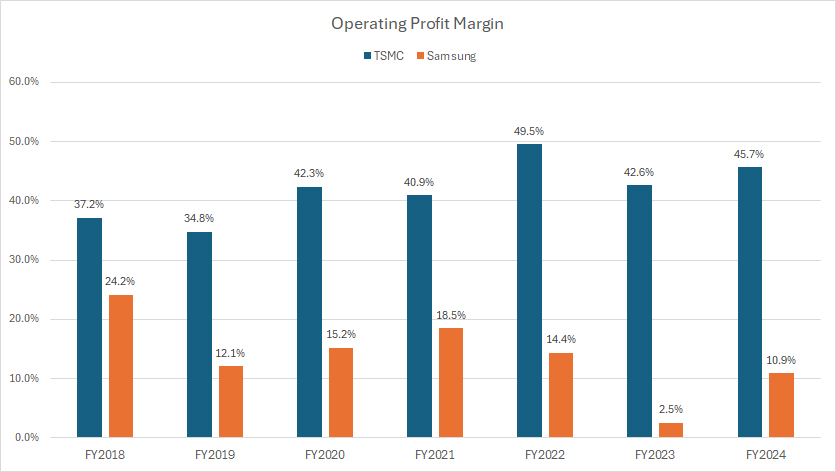
Operating Profit Margin
tsmc-vs-samsung-in-operating-profit-margin
(click image to expand)
The definition of operating profit is available here: operating profit.
TSMC and Samsung report their financial results in their native currencies. The conversion of these currencies to USD was carried out by the respective companies, rather than the editors.
From an operational perspective, TSMC operates much more efficiently than Samsung, as reflected by TSMC’s significantly higher operating margins shown in the graph above.
TSMC’s operating profit margin averaged an impressive 46% from fiscal year 2022 to 2024. During the same period, Samsung’s operating profit margin averaged only 9%, a much lower figure than TSMC’s result.
A notable trend is TSMC’s significant improvement in operational efficiency over the years. This is evidenced by the rising operating profit margin, which has increased from 37% in fiscal year 2018 to 46% in the latest result. This consistent growth showcases TSMC’s ability to optimize its operations, manage costs effectively, and enhance production efficiency, resulting in higher profitability.
In contrast, Samsung’s operating efficiency has deteriorated over the same period. The operating profit margin dropped from 24% in fiscal year 2018 to a low of 2.5% in 2023 before recovering to 11% in fiscal year 2024. This decline indicates challenges in maintaining operational efficiency amidst fluctuating market conditions and rising production costs.
TSMC’s superior operational performance can be attributed to its focused business model as a pure-play foundry, allowing it to streamline production processes and achieve economies of scale. Additionally, TSMC’s commitment to continuous improvement and investment in advanced manufacturing technologies has played a crucial role in enhancing its operational efficiency.
On the other hand, Samsung’s integrated business model, which balances foundry services with its own semiconductor design and manufacturing, may contribute to higher operational complexities and costs, impacting its overall efficiency.
Overall, while TSMC demonstrates exceptional operational efficiency with consistently high operating margins, Samsung faces challenges in maintaining its profitability. TSMC’s strategic focus on manufacturing excellence and technological advancements positions it favorably in the competitive semiconductor landscape, highlighting its potential for sustained growth and profitability.
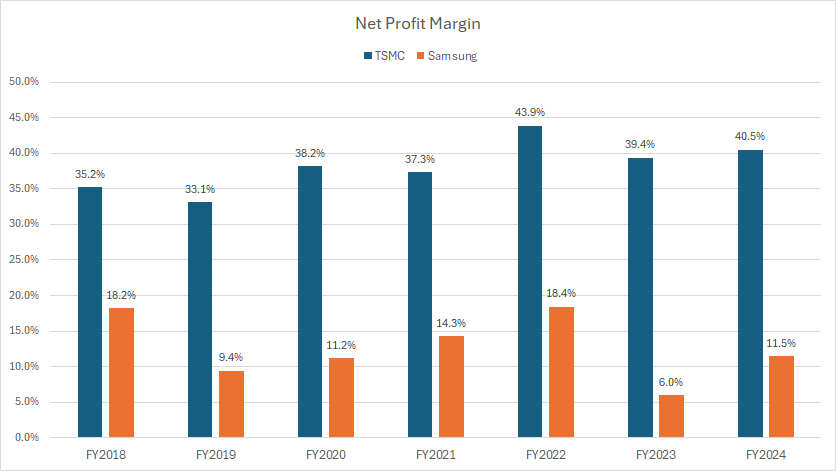
Net Profit Margin
tsmc-vs-samsung-in-net-profit-margin
(click image to expand)
The definition of operating profit is available here: operating profit.
TSMC and Samsung report their financial results in their native currencies. The conversion of these currencies to USD was carried out by the respective companies, rather than the editors.
In terms of net profit, TSMC is significantly more profitable than Samsung, as illustrated in the chart above. TSMC has consistently produced much higher net profit margins compared to Samsung.
TSMC’s net profit margins have not only been higher but have also demonstrated modest growth over time, increasing from 35% in fiscal year 2018 to 41% in fiscal year 2024. This steady improvement indicates TSMC’s effective cost management, strategic investments, and strong market position.
On the other hand, Samsung’s net profit margins have remained relatively flat over the same period. In fact, Samsung’s net profit margin has decreased slightly, falling from 18% in fiscal year 2018 to 12% in fiscal year 2024. This decline highlights Samsung’s challenges in maintaining profitability amidst competitive pressures and operational costs.
A particularly concerning trend for Samsung is the sharp drop in its net profit margin to a low of 6% in fiscal year 2023, marking a period of deteriorating profitability. Although Samsung managed to recover to a 12% net profit margin in fiscal year 2024, this still represents a significant decline from its earlier performance.
The stark contrast in net profit margins between TSMC and Samsung underscores TSMC’s superior operational efficiency and strategic focus. TSMC’s ability to maintain and grow its profit margins over time positions it favorably in the competitive semiconductor industry, enabling sustained profitability and growth.
In summary, while Samsung faces challenges in maintaining its net profit margins, TSMC’s consistent and growing profitability highlights its strong operational performance and strategic advantages in the semiconductor market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, TSMC’s superior profit and margin performance compared to Samsung highlights its strategic focus on operational efficiency, technological innovation, and effective cost management. While Samsung remains a formidable competitor, TSMC’s consistent growth in profitability and margins positions it favorably in the competitive semiconductor industry.
Credits and References
1. All financial figures presented were obtained and referenced from TSMC’s annual reports published on the company’s investor relations page: TSMC Annual Reports.
2. Pexels Images.
Disclosure
We may use the assistance of artificial intelligence (AI) tools to produce some of the text in this article. However, the data is directly obtained from original sources and meticulously cross-checked by our editors multiple times to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media. Additionally, providing a link back to this article from any website can help us create more content like this in the future.
Thank you for your support and engagement! Your involvement helps us continue to provide high-quality, reliable content.