Stock investment. Pixabay Image.
Ford and GM have long-standing histories, with Ford founded in 1903 and GM in 1908. They have established themselves as iconic brands globally, with a legacy of innovation and leadership in automotive manufacturing.
Both companies are committed to transitioning to electric vehicles (EVs). They have announced significant investments in EV development and have rolled out flagship electric models, such as the Ford Mustang Mach-E and the Chevrolet Bolt EV.
Despite the enthusiasm and dedication, both companies are still in the early stages of their transition, with the bulk of their sales still dominated by traditional fossil-fueled vehicles.
For example, Ford’s EV deliveries in 2023 comprised only 2% of the company’s total vehicle volumes. Similarly, GM’s EV sales in 2023 comprised only 3.3% of the company’s total vehicle volumes.
This article compares Ford and GM from the perspective of several metrics, including vehicle revenue, profit, and margin. Let’s take a look!
Investors interested in Ford and GM’s other statistics may find more resources on these pages:
- GM r&d spending vs Tesla,
- Ford sales and market share by region, and
- GM revenue breakdown and profit margin.
Please use the table of contents to navigate this page.
Table Of Contents
Definitions And Overview
Revenue
A1. Revenue Per Car
Profit
B1. Profit Per Car
Margin
C1. Vehicle Margin
Consolidated Margin
D1. Operating Profit Margin – GAAP
Conclusion And Reference
S1. Conclusion
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
Definitions
To help readers understand the content better, the following terms and glossaries have been provided.
Revenue Per Car: Revenue Per Car is defined as automotive revenue excluding leasing, regulatory credits, non-automotive segments, etc., divided by vehicle sales.
Revenue Per Car = Automotive Revenue / Vehicle Sales
Vehicle sales represent vehicle wholesale for both automakers.
Profit Per Car: Profit Per Car is defined as automotive gross profit divided by vehicle sales.
Profit Per Car = Automotive Gross Profit / Vehicle Sales
Vehicle sales represent vehicle wholesale for both automakers.
Vehicle Margin: Vehicle margin is defined as the ratio of automotive gross profit to automotive revenue.
Vehicle Margin = Automotive Gross Profit / Automotive Revenue
Automotive revenue represents car sales revenue excluding GM Financial in the case of General Motors and Ford Credit in the case of Ford Moyot.
Operating Margin: Operating margin is a financial metric that measures a company’s efficiency in generating profit from its operations.
It is expressed as a percentage and is calculated by dividing operating income (also known as operating profit) by net sales (revenue).
Operating Margin = Operating Income / Total Net Revenue
Essentially, operating margin shows what percentage of revenue is left over after paying for variable costs of production, such as wages and raw materials.
It’s a key indicator of a company’s financial health and its ability to manage its operations effectively. The higher the operating margin, the more profitable the company is considered to be.
Revenue Per Car
ford-vs-general-motors-in-revenue-per-car
(click image to expand)
The definition of revenue per car is available here: revenue per car.
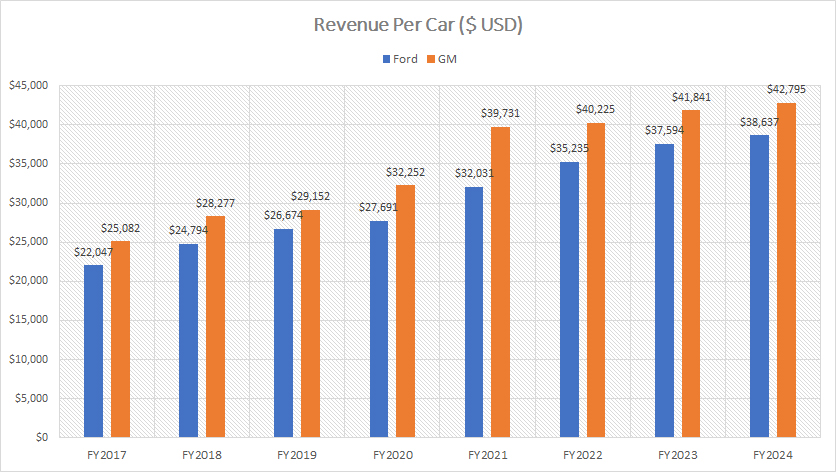
Overall, GM generates slightly higher revenue per vehicle versus Ford Motor, as shown in the chart above.
For example, GM took in revenue per vehicle totaling nearly $43,000 in fiscal year 2024, while Ford Motor earned just $38,600 in revenue per car in the same period.
On average, GM’s revenue per vehicle came in at $41,600 from fiscal year 2022 to 2024, while Ford’s figure amounted to $37,200 during the same period, which was slightly below General Motors.
A significant trend is the increasing revenue per vehicle for both automakers, as depicted in the chart above. For example, GM’s revenue per car has risen from $25,000 in 2017 to a record figure of $42,800 as of 2024. Ford’s figure has experienced a similar growth, rising from $22,000 in 2017 to $38,600 as of 2024.
The growing revenue per car for both automakers has been driven by several reasons. One of which is the increase in production and sale of SUVs and trucks for GM and Ford. SUVs and trucks generally have higher selling price and margins compared to smaller cars.
GM and Ford’s SUV and truck sales statistics are available here: GM SUV and truck sales and Ford SUV and truck sales.
The other reason is due to economic factors. For example, there has been inflation and disruptions to supply chains, which tends to drive up prices of raw materials and labor costs. Therefore, the global supply chain disruptions and inflationary pressures have led to an increase in vehicle prices, contributing to higher revenue per car for GM and Ford.
Profit Per Car
ford-vs-general-motors-in-profit-per-car
(click image to expand)
Profit per car for both automakers is evaluated based on the automotive gross profit. The definition of profit per car is available here: profit per car.
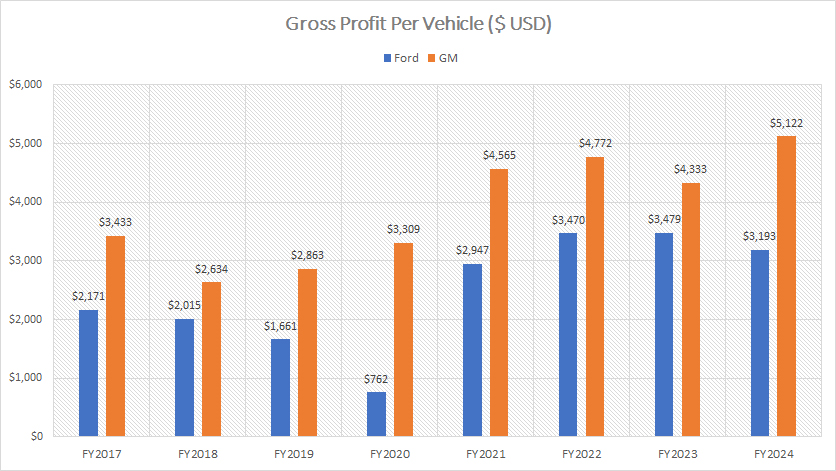
Given GM’s slightly higher revenue per vehicle, as discussed previously, it’s no surprise that GM also achieves higher profit per vehicle, as illustrated in the chart above.
In fiscal year 2024, GM’s profit per vehicle reached an impressive $5,100. In contrast, Ford’s profit per vehicle stood at $3,200, which is nearly $2,000 or 37% lower than GM’s.
Looking at a broader timeframe, from fiscal year 2022 to 2024, GM consistently earned an average profit of $4,700 per vehicle. During the same period, Ford’s average profit per vehicle was $3,400.
This significant difference underscores GM’s ability to capitalize on its revenue streams more effectively, resulting in higher profitability per unit sold.
Vehicle Margin
ford-vs-general-motors-in-vehicle-margin
(click image to expand)
Vehicle margin for both automakers is evaluated based on the automotive gross margin. The definition of the vehicle margin is available here: vehicle margin.
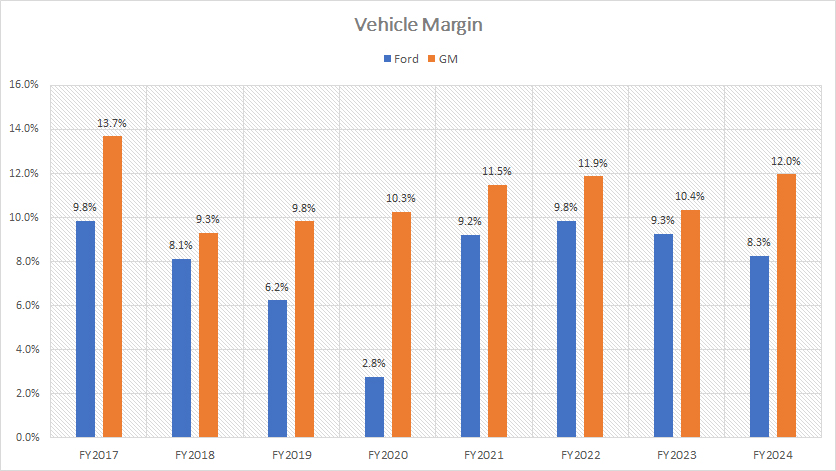
It’s no surprise that GM achieves a much higher vehicle margin compared to Ford, as illustrated in the chart above. This is primarily because GM generates significantly higher revenue and profit per vehicle than Ford.
In fiscal year 2024, GM’s vehicle margin reached an impressive 12.0%, while Ford’s vehicle margin was 8.3%. This substantial difference highlights GM’s efficiency in converting revenue into profit.
On average, between fiscal years 2022 and 2024, GM maintained an average vehicle margin of 11%, compared to Ford’s 9%. This consistent performance underscores GM’s ability to manage costs and maximize profitability more effectively than its competitor.
Essentially, GM’s ability to command higher prices for its vehicles, particularly in the SUV and truck segments, boosts its overall revenue per unit, and therefore the profit margin per car.
Operating Profit Margin – GAAP
ford-vs-general-motors-in-operating-profit-margin
(click image to expand)
The definition of the operating margin is available here: operating margin.
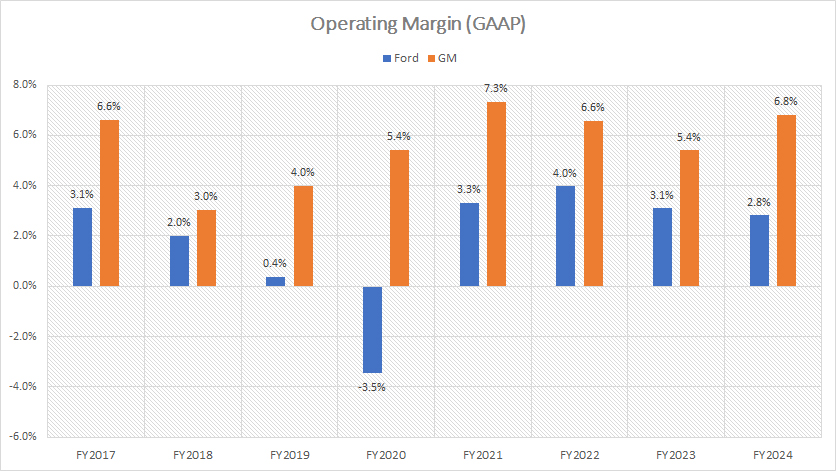
From an operational standpoint, GM demonstrates superior efficiency compared to Ford, as evidenced by GM’s significantly better operating profit margin shown in the chart above.
In fiscal year 2024, GM achieved an operating profit margin of 7%, while Ford’s operating profit margin was notably lower at 3%. This disparity underscores GM’s ability to manage its operations more effectively and turn a higher proportion of its revenue into profit.
Looking at the data over a broader period, from fiscal year 2022 to 2024, GM consistently maintained an average operating profit margin of 6%, in contrast to Ford’s average of 3%. This trend highlights GM’s operational prowess and strategic advantages in cost management and resource allocation.
Essentially, GM’s effective cost control measures and streamlined production processes enable it to reduce operational expenses, thereby enhancing profitability.
Summary
To recap, GM not only generates higher revenue and profit per vehicle but also operates more efficiently, resulting in a significantly higher profit margin per car and operating profit margin compared to Ford. This operational efficiency positions GM favorably in the competitive automotive industry, allowing it to capitalize on its strengths and drive sustainable growth.
References and Credits
1. All financial figures in this article are obtained and referenced from annual reports published on the company’s investor relations pages:
i) Ford Earnings Releases, and
ii) GM Investor Relation.
2. Pixabay Images.
Disclosure
We may use the assistance of artificial intelligence (AI) tools to produce some of the text in this article. However, the data is directly obtained from original sources and meticulously cross-checked by our editors multiple times to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media. Additionally, providing a link back to this article from any website can help us create more content like this in the future.
Thank you for your support and engagement! Your involvement helps us continue to provide high-quality, reliable content.