Microchips. Pexels Image.
This article presents an analysis of the revenue generated by Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited (TSMC) based on its various process nodes.
TSMC’s revenue by process node is derived from the sale of semiconductor wafers, categorized according to different generations of semiconductor manufacturing technologies.
Each process node represents a specific level of technological advancement and miniaturization in semiconductor fabrication. TSMC’s major process nodes include: 3nm technology, 5nm technology, 7nm technology, and older nodes.
The definitions of TSMC’s process nodes are available here: process nodes.
Let’s take a look! You may find related statistic of TSMC on these pages:
- TSMC revenue by country – U.S., China, Taiwan, Japan, etc.
- TSMC revenue from wafer sales and other products, and
- TSMC profit margin.
Please use the table of contents to navigate this page.
Table Of Contents
Definitions And Overview
O2. What is driving the significant growth in TSMC’s wafer revenue?
Process Node From 3nm To 10nm
A1. Revenue By Process Node: 3nm To 10nm
A2. Percentage Of Revenue By Process Node: 3nm To 10nm
Process Node From 16nm To 65nm
B1. Revenue By Process Node: 16nm To 65nm
B2. Percentage Of Revenue By Process Node: 16nm To 65nm
Process Node From 90nm And Above
C1. Revenue By Process Node: 90nm And Above
C2. Percentage Of Revenue By Process Node: 90nm And Above
Conclusion And Reference
S1. Conclusion
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
Definitions
To help readers understand the content better, the following terms and glossaries have been provided.
New Taiwan Dollar (TWD): The New Taiwan Dollar (TWD), abbreviated as NT$, is the official currency of Taiwan.
It is used in all forms of transactions within the country, from daily expenses to business dealings. The New Taiwan Dollar is issued by the Central Bank of the Republic of China (Taiwan) and is subdivided into 100 cents.
Its symbol is NT$, and it is known for its stability and wide acceptance in the region. The exchange rate of TWD to USD is NT$1,000 to US$30.30.
Wafer Revenue: TSMC’s wafer revenue refers to the income generated by Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) from the production and sale of semiconductor wafers.
These wafers are the foundational materials used to fabricate integrated circuits (ICs) and computer chips. TSMC manufactures these wafers using advanced semiconductor processes and sells them to various electronics manufacturers and fabless companies, which design the chips but outsource the manufacturing process.
TSMC’s wafer revenue is a significant component of the company’s overall revenue, driven by the demand for high-performance computing (HPC) products, smartphones, automotive applications, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and other digital consumer electronics.
The company’s ability to offer cutting-edge process technologies, such as 5nm, 4nm, and 3nm nodes, ensures that its wafers meet the evolving needs of its customers, contributing to sustained revenue growth.
Process Nodes: Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC)’s process nodes refer to the different generations of semiconductor manufacturing technologies developed by the company.
These nodes are typically named with a number followed by the abbreviation for nanometer (nm), such as 7nm, 5nm, and 3nm. Each process node represents a new level of miniaturization and technological advancement in semiconductor fabrication.
Key Process Nodes
- 7nm Technology: Introduced in 2018, TSMC’s 7nm FinFET (N7) technology marked a significant advancement in semiconductor manufacturing. It offered improved performance, power efficiency, and logic density compared to previous nodes.
- 5nm Technology: Launched in 2020, TSMC’s 5nm FinFET (N5) technology further enhanced performance and power efficiency. It enabled higher transistor density, allowing for more powerful and energy-efficient chips.
- 3nm Technology: In 2022, TSMC began high-volume production of its 3nm FinFET (N3) technology. This node introduced the FinFlex technology, which allows chip designers to optimize performance, power consumption, and area (PPA) by mixing and matching different standard cells within a chip.
- 2nm Technology: Currently under development, TSMC’s 2nm (N2) technology will feature the company’s first generation of nanosheet transistor technology. This node aims to deliver significant improvements in performance and power efficiency.
Evolution of Process Nodes
Process nodes have evolved over time, with each new generation offering smaller transistor sizes, higher performance, and better power efficiency.
Initially, process nodes were named based on their gate lengths and half-pitch, but this is no longer the case. Today, the numbers used to signify each new node are chosen by companies and do not necessarily correspond to specific physical dimensions.
Importance of Process Nodes
Advancements in process nodes are crucial for the semiconductor industry as they enable the development of more powerful and energy-efficient chips.
These improvements drive innovation in various fields, including consumer electronics, automotive, artificial intelligence, and data centers.
Nanometer: A nanometer (nm) is a unit of measurement in the metric system, equal to one billionth of a meter. To put it in perspective, a nanometer is about 80,000 times smaller than the diameter of a human hair.
This incredibly small scale is commonly used in science and engineering, particularly in fields like nanotechnology, semiconductor manufacturing, and materials science.
Applications of Nanometers
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: In the semiconductor industry, process nodes are often defined in nanometers (e.g., 7nm, 5nm). These nodes indicate the size of transistors and other critical features on a chip, with smaller nodes allowing for more powerful and efficient electronic devices.
Scale Comparison
- 1 meter (m) = 1,000,000,000 nanometers (nm)
- 1 millimeter (mm) = 1,000,000 nanometers (nm)
- 1 micrometer (µm) = 1,000 nanometers (nm)
The nanometer scale is essential for many cutting-edge technologies and scientific research, enabling precise manipulation and measurement at the atomic and molecular levels.
Percentage Of Revenue By Process Node: Percentage of revenue by process node is calculated based on the ratio of the revenue from a certain process node to wafer revenue.
TSMC’s wafer revenue is generated through the sales of silicon wafer. You may find more information about this revenue stream here: wafer revenue.
What is driving the significant growth in TSMC’s wafer revenue?
Several factors are driving the significant growth in TSMC’s wafer revenue:
- Advanced Process Technologies: TSMC’s adoption of advanced process technologies, such as the 5nm, 4nm, and 3nm nodes, has been a major growth driver. These advanced processes are used in high-performance computing (HPC) products, flagship smartphones, and AI chips, which are in high demand.
- AI Deployment: The increasing deployment of AI technologies, both in data centers and edge devices, has led to higher wafer consumption per unit. AI chips require advanced manufacturing processes, which TSMC is well-equipped to provide.
- Supply Chain Recovery: The recovery of supply chains, particularly in the automotive and industrial sectors, has contributed to increased demand for semiconductor wafers. As these industries restock and ramp up production, TSMC benefits from the higher demand.
- Cloud AI Infrastructure: The expansion of cloud AI infrastructure has driven the need for more powerful and efficient chips, which TSMC produces. This trend is expected to continue, further boosting wafer revenue.
- Geopolitical Factors: TSMC’s strategic investments in new fabrication plants, such as the one in Phoenix, Arizona, supported by the U.S. Chips Act, help mitigate geopolitical risks and bring production closer to key customers in North America. This proximity to major markets enhances TSMC’s competitive edge.
- Diverse Customer Base: TSMC’s extensive customer base, including major players in the tech industry, ensures a steady stream of orders for its semiconductor wafers. The company’s reputation for quality and reliability makes it a preferred supplier.
- Market Leadership: TSMC’s position as a leader in the semiconductor industry, with a significant market share, allows it to capitalize on industry-wide growth trends. The company’s strong technological edge and customer base contribute to its revenue growth.
These factors collectively contribute to TSMC’s robust wafer revenue growth, positioning the company as a key player in the global semiconductor market.
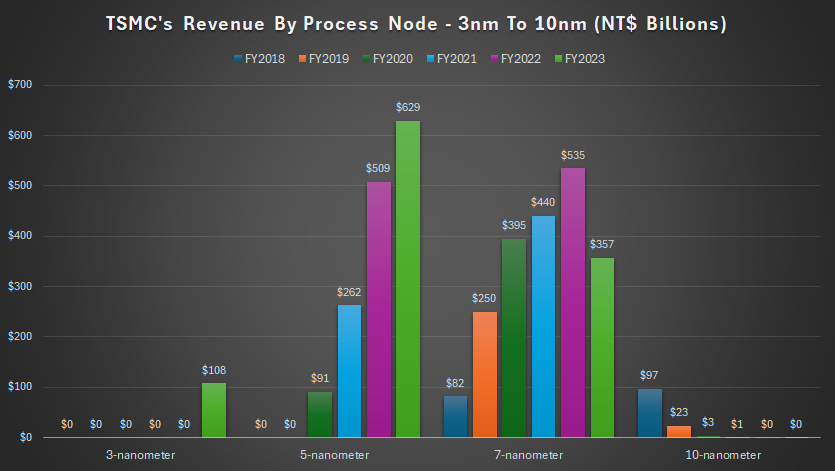
Revenue By Process Node: 3nm To 10nm
tsmc-revenue-by-node-3nm-to-10nm
(click image to expand)
The definitions of several of TSMC’s parameters are available here: wafer revenue, process nodes, and nanometer.
TSMC reports its financial statements primarily in New Taiwan Dollars (TWD). You can find more information about the currency exchange rates between TWD and the US dollar here: New Taiwan Dollar (TWD).
TSMC derives significant revenue from its advanced process nodes, with the 5nm technology being a major contributor, as depicted in the accompanying graph.
In fiscal year 2023, TSMC’s revenue from the 5nm process node reached an impressive NT$629 billion (US$19.2 billion), marking an increase of more than 20% from the NT$509 billion (US$15.5 billion) recorded in fiscal year 2022.
This growth underscores the strong demand for TSMC’s cutting-edge semiconductor manufacturing technology.
While the 7nm process node is an older technology, it still generates considerable revenue. In fiscal year 2023, TSMC’s revenue from the 7nm process node reached NT$357 billion (US$10.9 billion), a significant decrease from the NT$535 billion (US$16.3 billion) reported in fiscal year 2022.
This decline suggests that the 7nm process node may have peaked in fiscal year 2022 and is now experiencing a natural decline as customers transition to more advanced nodes.
TSMC began generating sales from its 3nm process node in fiscal year 2023. Before this year, TSMC did not derive any sales from the 3nm process node.
As customers start adopting this advanced technology, it is expected to become a significant revenue stream for the company in the coming years, showcasing TSMC’s ability to lead in semiconductor innovation.
The 10nm process node provided TSMC with NT$97 billion (US$3 billion) in revenue in fiscal year 2018. However, revenue from the 10nm process node has rapidly declined, generating no revenue in fiscal year 2023.
This decline highlights the industry’s shift towards more advanced nodes and the decreasing demand for older technologies.
The data indicates a clear shift in revenue from older nodes to more advanced ones. As customers continue to demand higher performance and energy efficiency, TSMC’s advanced nodes like 5nm and 3nm are becoming increasingly important.
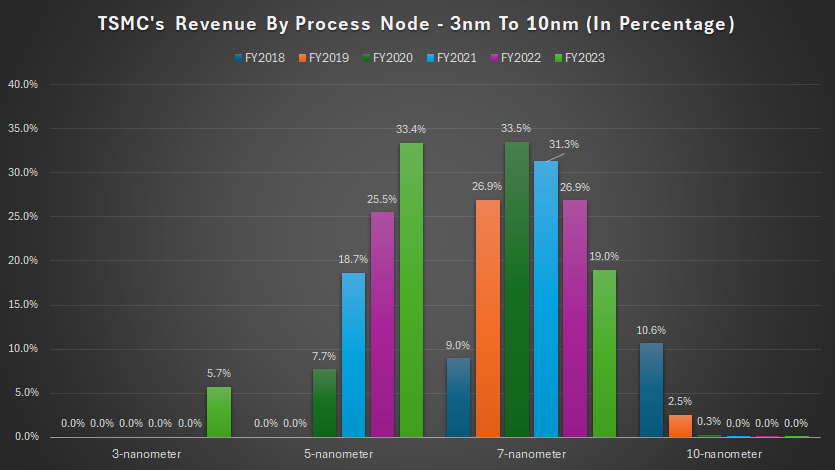
Percentage Of Revenue By Process Node: 3nm To 10nm
tsmc-revenue-by-node-3nm-to-10nm-in-percentage
(click image to expand)
The definitions of several of TSMC’s parameters are available here: wafer revenue, process nodes, and nanometer.
TSMC reports its financial statements primarily in New Taiwan Dollars (TWD). You can find more information about the currency exchange rates between TWD and the US dollar here: New Taiwan Dollar (TWD).
The percentage of revenue is calculated based on the ratio of revenue from certain process node to wafer revenue. For more information, you may refer to this section: percentage of revenue by process node.
In fiscal year 2023, TSMC’s revenue from the 5nm process node accounted for 33% of the total within the wafer product segment, making it the highest among all process nodes.
Since its launch in 2020, the 5nm process node’s revenue contribution has rapidly increased, starting at 7.7% in fiscal year 2020 and climbing to 33% by 2023.
This growth underscores the high demand for TSMC’s advanced 5nm technology, which offers enhanced performance and energy efficiency, making it suitable for applications such as high-performance computing, mobile devices, and AI.
The 7nm process node, while older, still contributes significantly to TSMC’s revenue. In fiscal year 2023, it accounted for about 19% of the total wafer revenue.
However, the revenue contribution of the 7nm process node has declined from its peak of 33.5% in fiscal year 2020. This decrease reflects the industry’s shift towards more advanced nodes, such as 5nm and 3nm.
TSMC’s 3nm process node is relatively new, with revenue generation starting in fiscal year 2023. In this year, the 3nm process node contributed approximately 5.7% of the total wafer revenue.
As adoption of this advanced technology grows, it is expected to become a significant revenue stream for TSMC in the coming years.
The revenue contribution from TSMC’s 10nm process node peaked at 10.6% in fiscal year 2018. Since then, it has rapidly declined, reaching 0% in fiscal year 2023.
This decline highlights the obsolescence of older nodes as the semiconductor industry increasingly adopts newer, more efficient technologies.
In short, TSMC’s 5nm process node has become the largest revenue driver due to its advanced capabilities and widespread adoption. The introduction of the 3nm process node marks the next phase of technological advancement, positioning TSMC for future growth.
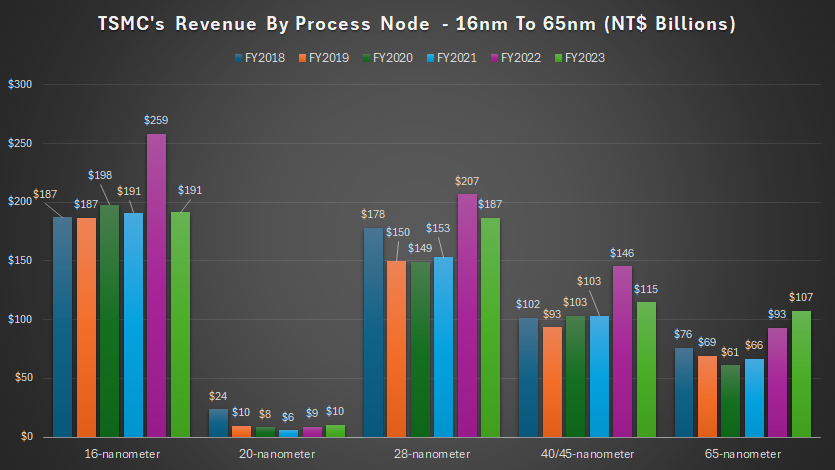
Revenue By Process Node: 16nm To 65nm
tsmc-revenue-by-node-16nm-to-65nm
(click image to expand)
The definitions of several of TSMC’s parameters are available here: wafer revenue, process nodes, and nanometer.
TSMC reports its financial statements primarily in New Taiwan Dollars (TWD). You can find more information about the currency exchange rates between TWD and the US dollar here: New Taiwan Dollar (TWD).
Despite being an older technology, TSMC’s 16nm process node remains relevant and generates significant sales. In fiscal year 2023, TSMC derived approximately NT$191 billion (US$5.8 billion) in revenue from the 16nm process node, which is about 26% lower than the NT$259 billion (US$7.9 billion) recorded in fiscal year 2022.
However, over the past six years, revenue from the 16nm process node has been relatively stable, averaging around NT$200 billion (US$6.1 billion) annually since fiscal year 2018. This stability underscores the continued demand for 16nm technology in various applications.
The 28nm process node, being an even older technology, still contributes considerable revenue to TSMC. In fiscal year 2023, revenue from the 28nm process node reached NT$187 billion (US$5.7 billion), slightly down from the NT$207 billion (US$6.3 billion) reported in fiscal year 2022.
On average, TSMC’s revenue from the 28nm process node amounted to NT$170 billion (US$5.2 billion) annually between fiscal year 2018 and 2023. The sustained revenue from the 28nm process node indicates its continued relevance in the semiconductor industry.
TSMC generates roughly the same amount of revenue from the 40/45nm and 65nm process nodes. In fiscal year 2023, revenue from the 40/45nm process nodes totaled NT$115 billion (US$3.5 billion), while revenue from the 65nm process node amounted to NT$107 billion (US$3.3 billion).
On average, from fiscal year 2021 to 2023, TSMC’s revenue from the 40/45nm and 65nm process nodes has been NT$121 billion (US$3.7 billion) and NT$89 billion (US$2.7 billion), respectively.
These figures highlight the ongoing demand for older process nodes in various applications, particularly in industries where cutting-edge technology is not always required.
The 20nm process node provided TSMC with NT$24 billion (US$0.7 billion) in revenue in fiscal year 2018. Since then, revenue from the 20nm process node has rapidly declined, generating only NT$10 billion (US$0.3 billion) in fiscal year 2023.
This decline reflects the natural progression towards more advanced nodes as customers seek higher performance and efficiency.
TSMC’s revenue trends across various process nodes demonstrate the company’s ability to maintain a diverse product portfolio catering to different market needs.
While newer nodes like 5nm and 3nm are driving significant growth, older nodes such as 16nm, 28nm, 40/45nm, and 65nm continue to generate substantial revenue.
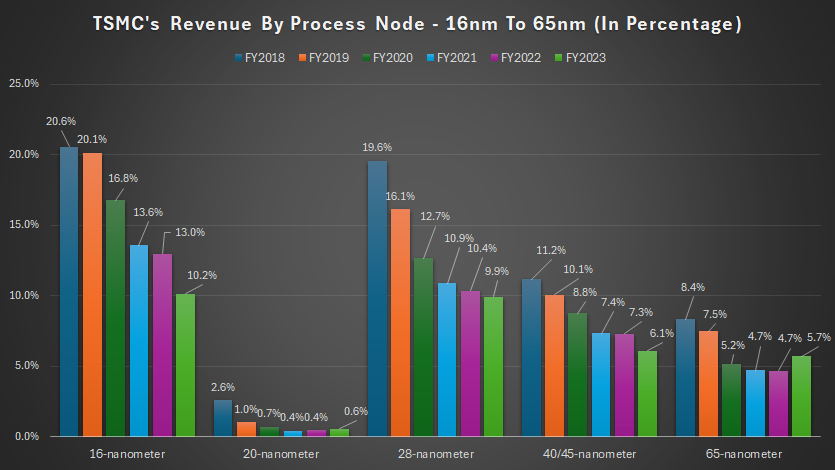
Percentage Of Revenue By Process Node: 16nm To 65nm
tsmc-revenue-by-node-16nm-to-65nm-in-percentage
(click image to expand)
The definitions of several of TSMC’s parameters are available here: wafer revenue, process nodes, and nanometer.
TSMC reports its financial statements primarily in New Taiwan Dollars (TWD). You can find more information about the currency exchange rates between TWD and the US dollar here: New Taiwan Dollar (TWD).
The percentage of revenue is calculated based on the ratio of revenue from certain process node to wafer revenue. For more information, you may refer to this section: percentage of revenue by process node.
A significant trend observed in TSMC’s revenue is the declining contributions from its older process nodes, specifically those ranging from 16nm to 65nm, over the last six years, as depicted in the chart above.
In fiscal year 2023, TSMC’s revenue contribution from the 16nm process node accounted for only 10% of the total within the wafer product segment, compared to 20.6% five years ago.
This decline reflects the industry’s shift towards more advanced nodes, which offer better performance and energy efficiency.
Similarly, the revenue contribution from TSMC’s 28nm process node accounted for only 10% of total revenue within the wafer product segment in fiscal year 2023, down from 20% in fiscal year 2018.
Despite its age, the 28nm process node still serves various applications, but its relative significance has diminished as newer technologies have emerged.
TSMC’s 40/45nm and 65nm process nodes each contributed only 6% of wafer revenue in fiscal year 2023, a significant drop from the 10% they each contributed five years ago.
These older nodes remain in use for specific applications, but their contributions have decreased as the demand for advanced nodes has increased.
The revenue contribution from TSMC’s 20nm process node has been relatively insignificant since fiscal year 2018. In that year, it contributed only 2.6% of wafer revenue.
This ratio decreased to less than 1% by fiscal year 2023, illustrating the rapid obsolescence of this node as customers transitioned to more advanced technologies.
The declining revenue contributions from TSMC’s older process nodes highlight the industry’s continuous push towards more advanced semiconductor technologies.
As customers demand higher performance, greater power efficiency, and increased functionality, TSMC has focused its efforts on developing and scaling newer nodes, such as 5nm and 3nm.
Revenue By Process Node: 90nm And Above
tsmc-revenue-by-node-90nm-and-above
(click image to expand)
The definitions of several of TSMC’s parameters are available here: wafer revenue, process nodes, and nanometer.
TSMC reports its financial statements primarily in New Taiwan Dollars (TWD). You can find more information about the currency exchange rates between TWD and the US dollar here: New Taiwan Dollar (TWD).
In fiscal year 2023, TSMC generated NT$87 billion (US$2.7 billion) in revenue from the 0.15/0.18 microns process node.
This node, although older, still contributes a modest portion to TSMC’s overall revenue. Its steady performance indicates ongoing demand for mature technologies in certain applications.
Similarly, TSMC made NT$47 billion (US$1.4 billion) in revenue from the 0.11/0.13 microns process node in fiscal year 2023.
This revenue highlights the continued relevance of these older nodes for specific use cases where advanced technology may not be necessary.
TSMC’s revenue from the 90nm process node was even smaller, totaling just NT$26 billion (US$0.8 billion) in fiscal year 2023.
Over the past three years, from fiscal year 2021 to 2023, TSMC earned an average annual revenue of NT$33 billion (US$1.0 billion) from this node.
While its contribution is limited, it remains a part of TSMC’s diverse product portfolio.
For process nodes 0.25 microns and above, TSMC’s revenue has averaged around NT$22 billion (US$0.7 billion) between fiscal years 2021 and 2023. In fiscal year 2023, TSMC generated just NT$18 billion (US$0.6 billion) from these older process nodes.
This consistent, albeit small, revenue stream indicates that there are still niche applications for these technologies. The revenue contributions from these much older process nodes are relatively small compared to TSMC’s more advanced technologies.
However, they play a vital role in TSMC’s overall business strategy by catering to niche markets and legacy systems that still require these mature technologies.
Maintaining a diverse range of process nodes allows TSMC to serve a broad array of customer needs, ensuring a stable revenue stream from different market segments.
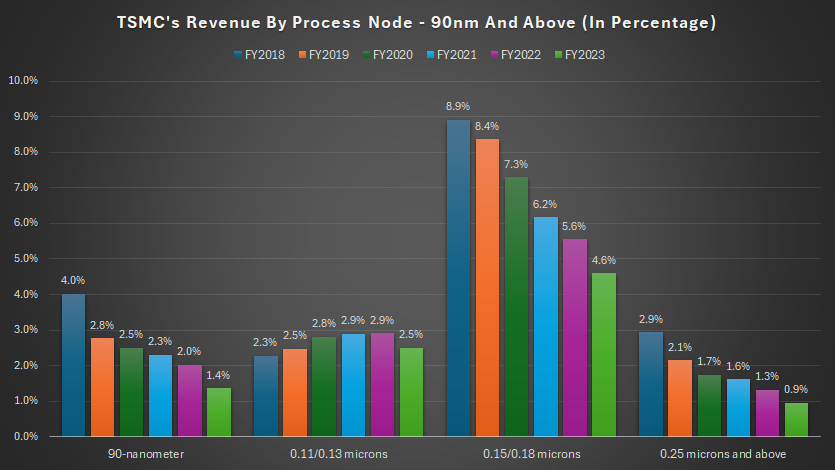
Percentage Of Revenue By Process Node: 90nm And Above
tsmc-revenue-by-node-90nm-and-above-in-percentage
(click image to expand)
The definitions of several of TSMC’s parameters are available here: wafer revenue, process nodes, and nanometer.
TSMC reports its financial statements primarily in New Taiwan Dollars (TWD). You can find more information about the currency exchange rates between TWD and the US dollar here: New Taiwan Dollar (TWD).
The percentage of revenue is calculated based on the ratio of revenue from certain process node to wafer revenue. For more information, you may refer to this section: percentage of revenue by process node.
From a percentage standpoint, the process nodes ranging from 90nm to 0.25 microns and above contribute less than 5% of TSMC’s total wafer revenue.
These older nodes, while still relevant for specific applications, represent a small fraction of the company’s overall revenue.
In fiscal year 2023, the revenue contribution from the 0.15/0.18 microns process node represented just 4.6% of TSMC’s total wafer revenue.
This is a significant decrease compared to the 8.9% recorded five years ago. The decline illustrates the industry’s shift towards more advanced process nodes, reducing the reliance on older technologies.
Similarly, TSMC’s 0.11/0.13 microns process node contributed only 2.5% of wafer revenue in fiscal year 2023. Although small, this percentage has been relatively consistent over the past six years.
The steady contribution underscores the ongoing demand for these mature nodes in specific niche applications where cutting-edge technology is not required.
TSMC’s 90nm process node contributed less than 1% of wafer revenue in fiscal year 2023. Unlike the relatively stable contribution from the 0.11/0.13 microns process node, the revenue percentage from the 90nm node has significantly declined since fiscal year 2018.
This decline indicates the gradual obsolescence of the 90nm technology as the industry adopts more advanced nodes.
The revenue contribution from the 0.25 microns and above process nodes also fell below 1% of wafer revenue in fiscal year 2023.
Similar to the 90nm node, the ratio for the 0.25 microns and above nodes has considerably declined over the past five years, reflecting the diminishing demand for these older technologies.
The diminishing revenue contributions from older process nodes highlight the semiconductor industry’s rapid evolution towards more advanced technologies.
TSMC’s ability to stay ahead in this competitive landscape depends on its continued innovation and development of cutting-edge process nodes.
While these mature nodes still play a role in specific markets, TSMC’s growth and success are driven by the adoption and advancement of newer, more efficient technologies.
Conclusion
In summary, the shift in revenue contributions from older to more advanced nodes underscores TSMC’s focus on innovation and meeting market demands for high-performance and energy-efficient semiconductor technologies.
While older nodes continue to generate some revenue, advanced nodes like 5nm and 3nm are driving significant growth and establishing TSMC’s leadership in the semiconductor industry.
Credits and References
1. All financial figures presented were obtained and referenced from TSMC’s annual reports published on the company’s investor relations page: TSMC Annual Reports.
2. Pexels Images.
Disclosure
We may utilize the assistance of artificial intelligence (AI) tools to produce some of the text in this article. However, the data is directly obtained from original sources and meticulously cross-checked by our editors multiple times to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media. Additionally, providing a link back to this article from any website can help us create more content like this in the future.
Thank you for your support and engagement! Your involvement helps us continue to provide high-quality, reliable content.