Car on expressway. Pexels Image.
This article delivers a comprehensive analysis of GM’s revenue distribution across its various segments.
General Motors (GM) operates through several divisions, including GM North America (GMNA), GM International (GMI), GM Financial, Cruise, and Corporate.
The definitions of these divisions are available here: GM North America (GMNA), GM International (GMI), GM Financial, Cruise, and Corporate.
You may find key statistic of General Motors on these pages:
- GM revenue breakdown by category,
- GM wholesales worldwide and by segment, and
- GM global sales and market share.
Let’s take a look!
Please use the table of contents to navigate this page.
Table Of Contents
Definitions And Overview
O2. What drives GM’s high revenue from North America?
Automotive Segment
A1. GM North America (GMNA)
A2. GM International (GMI)
GM Financial
B1. GM Financial
Cruise And Corporate
Revenue In Percentage
D1. Percentage Of Revenue From GMNA
Summary And Reference
S1. Conclusion
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
Definitions
To help readers understand the content better, the following terms and glossaries have been provided.
GM North America (GMNA): General Motors’ GM North America (GMNA) is a key operating segment of General Motors (GM) encompassing the company’s automotive operations in the North American region, primarily the United States and Canada.
GMNA is responsible for the design, production, and sales of GM vehicles in these markets. It includes popular brands such as Chevrolet, GMC, Buick, and Cadillac. GMNA is a significant revenue generator for GM and plays a crucial role in the company’s overall financial performance2.
GM International (GMI): GM International (GMI) is a key operating segment of General Motors (GM) encompassing the company’s automotive operations outside of North America. This includes regions such as Asia-Pacific, Europe, South America, and the Middle East.
GMI is responsible for the design, production, and sales of GM vehicles in these international markets. It includes popular brands such as Chevrolet, Buick, Cadillac, and GMC. GMI plays a crucial role in GM’s global strategy, contributing to the company’s overall financial performance and market presence worldwide.
GM Financial: General Motors Financial Company, Inc., commonly known as GM Financial, is the wholly owned captive finance subsidiary of General Motors (GM). It was founded in 1992, originally as AmeriCredit Corporation, and was acquired by GM in October 2010. The company’s headquarters are located in Fort Worth, Texas, USA.
GM Financial provides a wide range of financial services to support GM’s automotive operations. These services include retail loan and lease programs, offering attractive financing and leasing options for customers purchasing GM vehicles.
In addition to consumer financing, GM Financial also offers commercial lending products, such as retail floorplan financing, construction loans, real estate loans, and insurance for car dealerships. This comprehensive suite of financial services is designed to facilitate the purchase and leasing process for both individual customers and dealerships.
Operating on a global scale, GM Financial has a presence in North America, Latin America, Europe, and Asia. Notably, the company operates a joint venture in China, further extending its reach in the international market.
Although GM’s core European operations, Opel and Vauxhall, were sold to PSA Groupe and BNP Paribas in 2017, GM Financial continues to provide financial services in the region.
GM Financial plays a crucial role in supporting GM’s automotive sales by providing flexible financing solutions. This support helps GM maintain a competitive edge in the market by making it easier for customers to purchase or lease GM vehicles.
GM Financial’s success is largely dependent on building strong, lasting relationships with auto dealers and customers, ensuring best-in-class customer service and promoting open, honest communication at all levels.
Cruise: Cruise LLC is a subsidiary of General Motors (GM) focusing on developing autonomous vehicle technology. Founded in 2013 by Kyle Vogt and Dan Kan, Cruise was acquired by GM in 2016. The company is headquartered in San Francisco, California, and has been a key player in GM’s efforts to advance self-driving car technology.
Cruise initially developed direct-to-consumer kits to retrofit vehicles with limited self-driving capabilities. Over time, the company shifted its focus to creating fully autonomous vehicles. Cruise’s technology has been integrated into GM’s Super Cruise system, which allows for hands-free driving on certain roads.
Despite facing challenges and suspending operations in 2023, Cruise resumed its activities in 2024. GM has since integrated Cruise’s technology into its advanced driver assistance systems for personal vehicles, continuing to work on both assisted-driving and autonomous driving technologies2.
What drives GM’s high revenue from North America?
Several factors drive GM’s significant revenue contribution from North America:
- Strong Market Presence
- GM has a well-established market presence in North America, particularly in the United States and Canada. The company’s brands, such as Chevrolet, GMC, Buick, and Cadillac, are household names with loyal customer bases. This strong brand recognition and loyalty translate into consistent vehicle sales.
- Diverse Product Lineup
- GM offers a diverse lineup of vehicles, including cars, trucks, SUVs, and electric vehicles (EVs). This wide range of products caters to various consumer preferences and needs, helping GM capture a larger market share and generate substantial revenue.
- High Vehicle Sales Volume
- The North American market is one of the largest automotive markets globally, and GM consistently achieves high vehicle sales volumes in this region. For example, GM’s Chevrolet Silverado and GMC Sierra are among the best-selling trucks in the U.S., contributing significantly to the company’s revenue.
- Strong Supply Chain
- GM’s extensive supply chain in North America ensures efficient production and distribution of vehicles. The company’s strong relationships with suppliers and dealers enable it to maintain steady production levels and meet consumer demand effectively.
- Strategic Investments
- GM invests significantly in R&D and advanced technologies, including electric and autonomous vehicles. These investments help GM stay competitive in the evolving automotive industry, attract tech-savvy consumers, and generate additional revenue streams.
- Strategic Focus on North America
- GM North America (GMNA) is a major revenue generator for the company, focusing on the design, production, and sale of vehicles in the U.S. and Canada. This strategic focus allows GM to leverage its strengths in the region and maximize revenue opportunities.
These factors collectively drive GM’s significant revenue contribution from North America, highlighting the importance of the region to the company’s overall success.
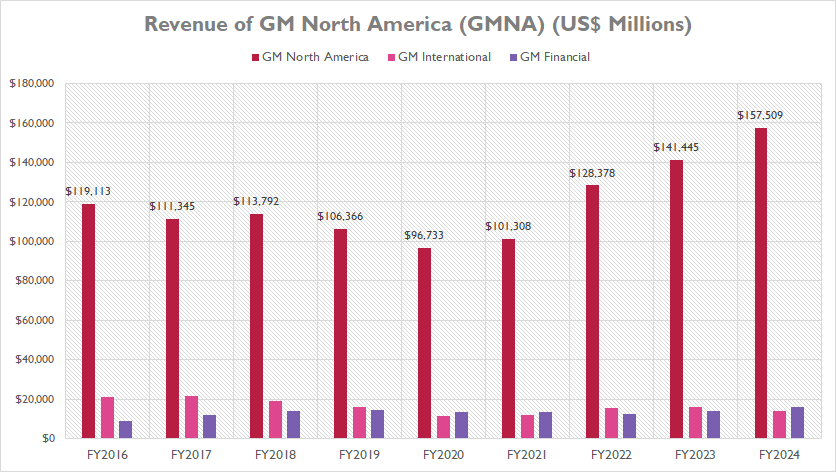
GM North America (GMNA)
GM-North-America-revenue
(click image to expand)
The definitions of GM’s operating segments are available here: GM North America (GMNA), GM International (GMI), and GM Financial.
GM derives the majority of its revenue from the GM North America (GMNA) segment, as illustrated in the graph above. When compared to the revenue generated by other segments such as GM International (GMI) and GM Financial, the revenue from GMNA is significantly higher.
In fiscal year 2024, GM’s revenue from GMNA reached an impressive $157.5 billion, representing an 11% increase from the $141.4 billion reported in fiscal year 2023. In the same period, GM’s revenue from GMI and GM Financial was less than $20 billion each, highlighting the dominant contribution of GMNA to the company’s overall financial performance.
A notable trend is the significant revenue growth of GMNA in the post-pandemic period, as depicted in the accompanying graph. GMNA’s revenue reportedly hit a low of $96.7 billion in fiscal year 2020. However, since then, GMNA’s revenue has shown a remarkable recovery, rising from $96.7 billion to $157.5 billion in just four years, reflecting a 63% increase.
On a longer-term basis, from fiscal year 2016 to 2024, GMNA’s revenue has climbed by 32%, increasing from $119.1 billion to $157.5 billion over nearly a decade. This sustained growth underscores GMNA’s critical role in driving GM’s overall financial success.
In summary, GMNA’s substantial revenue contribution highlights its importance to GM’s overall financial health and growth prospects. The segment’s impressive recovery and long-term growth trajectory demonstrate GM’s ability to capitalize on market opportunities and maintain a competitive edge in the North American automotive industry.
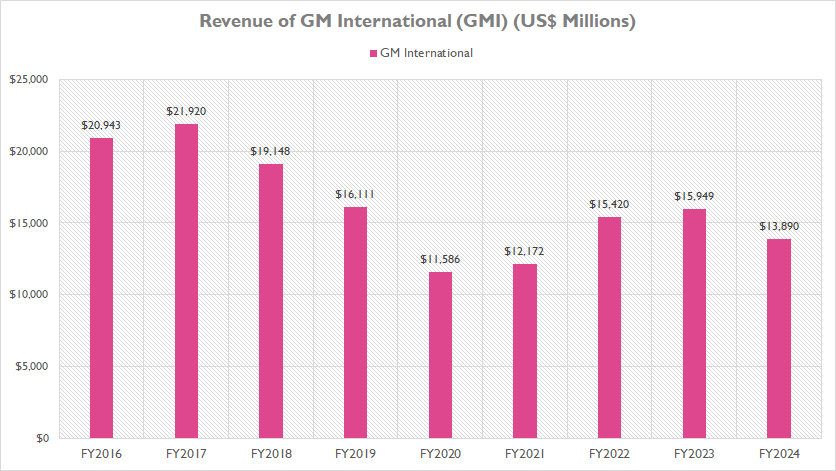
GM International (GMI)
GM-International-revenue
(click image to expand)
The definitions of GM’s operating segments are available here: GM North America (GMNA), GM International (GMI), and GM Financial.
The graph above presents a more detailed view of GM International (GMI)’s revenue. As illustrated, GMI’s revenue was significantly smaller than GMNA, amounting to only $13.9 billion in fiscal year 2024. This represents a 13% decline from the $15.9 billion reported in fiscal year 2023.
Moreover, GMI has not performed as well as GMNA in terms of revenue growth. From fiscal year 2016 to 2024, GMI’s revenue declined by over 50%, dropping from $20.9 billion to $13.9 billion over the nine-year period. This substantial decrease highlights the challenges faced by GMI in maintaining revenue growth in international markets.
However, it is important to note that GMI’s revenue has shown significant recovery post-pandemic. After reaching a low point at $11.6 billion in fiscal year 2020, GMI’s revenue has rebounded considerably, increasing by 20% to $13.9 billion in four years. This recovery indicates a positive trend in GMI’s performance, despite the long-term decline.
Several factors have contributed to GMI’s revenue challenges and subsequent recovery. Market dynamics in diverse and sometimes volatile international markets can impact revenue generation due to economic fluctuations, regulatory changes, and competitive pressures.
Additionally, GMI may have implemented strategic adjustments, such as cost-cutting measures, restructuring efforts, or targeted investments in growth areas, contributing to the post-pandemic recovery.
Enhancements in GMI’s product lineup, including the introduction of new models or technologies, may have driven increased sales and revenue in recent years. Improvements in operational efficiency, supply chain management, and production processes could have also played a role in stabilizing and growing GMI’s revenue post-pandemic.
Essentially, while GMI’s revenue has faced significant long-term challenges, the segment’s post-pandemic recovery reflects a resilient and adaptive approach. This recovery, though modest, highlights GMI’s efforts to navigate and overcome adverse market conditions, contributing to GM’s overall global presence.
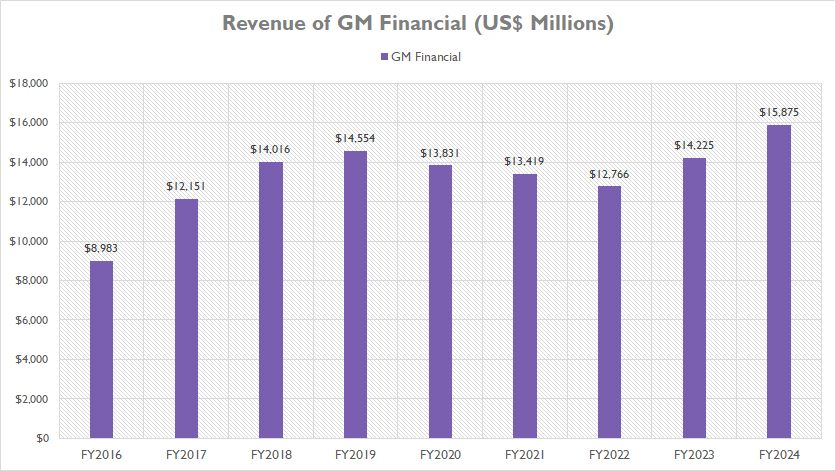
GM Financial
GM-Financial-revenue
(click image to expand)
The definitions of GM’s operating segments are available here: GM North America (GMNA), GM International (GMI), and GM Financial.
GM Financial’s revenue is significantly smaller than GMNA’s, but it has surpassed GMI since fiscal year 2020, making it the second-largest revenue contributor after GMNA.
In fiscal year 2024, GM Financial’s revenue reached $15.9 billion, marking an increase of 12% from the $14.2 billion reported in fiscal year 2023. This growth highlights the segment’s expanding influence within GM’s overall financial structure.
From a long-term perspective, GM Financial’s revenue has climbed 77%, rising from $9 billion to $15.9 billion over the past nine years. This substantial growth underscores the segment’s critical role in enhancing GM’s revenue generation capabilities.
While revenue has increased over the long term, it remained relatively flat from fiscal year 2017 to 2022. However, post-2022, GM Financial has demonstrated significant revenue growth.
As seen, post-pandemic, GM Financial’s revenue accelerated from $12.8 billion in fiscal year 2022 to $15.9 billion in fiscal year 2024, representing an increase of 24% in just two years. This recent growth indicates the segment’s ability to adapt and thrive in changing market conditions.
Several factors have contributed to GM Financial’s revenue growth. GM Financial offers a wide range of financial products, including auto loans, leases, and insurance services. This diversification helps attract a broad customer base and generate consistent revenue streams.
Collaborations with dealerships and other financial institutions have enhanced GM Financial’s market reach and service offerings, contributing to increased revenue. The post-pandemic economic recovery has boosted consumer demand for vehicles and related financial services, positively impacting GM Financial’s revenue.
Investments in digital platforms and technology-driven solutions have streamlined GM Financial’s operations, improved customer experience, and supported revenue growth. Moreover, effective risk management practices have enabled GM Financial to maintain a stable revenue base while navigating economic uncertainties.
Overall, GM Financial’s substantial revenue growth over the long term, coupled with its recent acceleration post-2022, highlights its crucial role in GM’s financial ecosystem. The segment’s diverse offerings, strategic partnerships, and adaptive strategies position it as a key contributor to GM’s overall revenue generation.
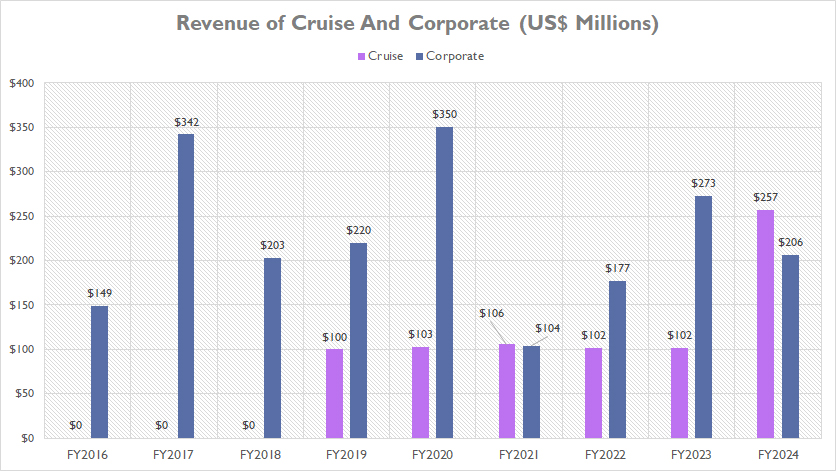
Cruise And Corporate
Cruise-and-Corporate-revenue
(click image to expand)
The definitions of GM’s operating segments are available here: Cruise.
GM’s revenue from the Cruise and Corporate segments is significantly small compared to other divisions, as illustrated in the chart above. Both segments generate less than $500 million each in most fiscal years.
In fiscal year 2024, Cruise generated just $257 million in revenue, while the Corporate segment produced $206 million. On average, from fiscal year 2022 to 2024, Cruise’s revenue totaled only $154 million annually, while the Corporate segment averaged $219 million per year.
Despite their smaller contributions, both segments play crucial roles within GM’s overall strategy. Cruise, for instance, focuses on developing autonomous vehicle technology, which has the potential to revolutionize the transportation industry. Although its current revenue is modest, the investments in autonomous driving technology could lead to substantial future gains as the market for self-driving vehicles matures.
The Corporate segment, while generating lower revenue, provides essential support services and strategic direction for GM’s global operations. This includes executive leadership, finance, legal and compliance, human resources, corporate communications, and more. These functions are vital for ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of the entire company.
The relatively small revenue figures from the Cruise and Corporate segments highlight GM’s strategic emphasis on its core automotive operations, particularly in the North American market. However, the ongoing investments in these segments underscore their long-term potential and the importance of innovation and effective management within GM’s overall business strategy.
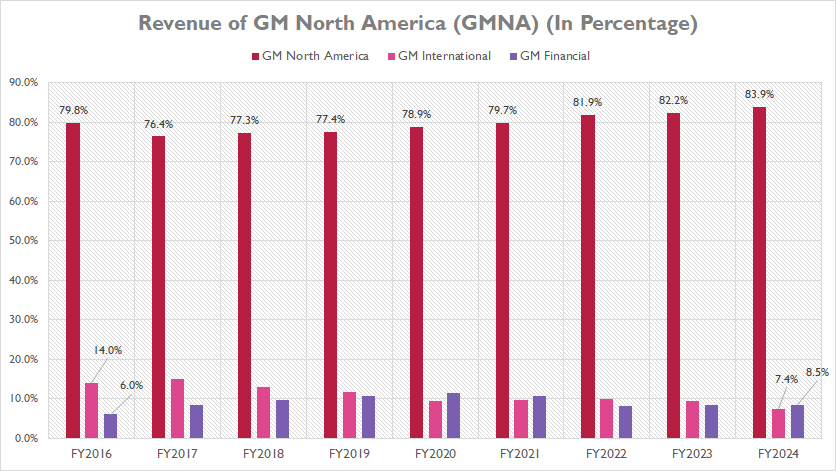
Percentage Of Revenue From GMNA
GM-North-America-revenue-in-percentage
(click image to expand)
The definitions of GM’s operating segments are available here: GM North America (GMNA), GM International (GMI), and GM Financial.
GM North America (GMNA) holds the lion’s share of General Motors’ total revenue, as highlighted in the accompanying chart. In fiscal year 2024, GMNA was responsible for a substantial 84% of the company’s revenue. This figure starkly contrasts with the contributions from GM International (GMI) and GM Financial, both of which accounted for less than 10% of the total revenue each for the same fiscal year.
Examining the long-term trends from fiscal year 2016 to 2024, GMNA’s revenue contribution has shown a slight but steady increase, moving from 80% to 84%. This consistent growth underscores the enduring significance of GMNA within the company’s financial ecosystem.
Conversely, during this same period, GMI’s revenue contribution has experienced a dramatic decline. In 2016, GMI contributed 14% to GM’s total revenue, but by 2024, this figure had plunged to 7%, representing a nearly 50% reduction over nine years. This sharp drop indicates a significant shift in GM’s revenue dynamics on the international front.
Meanwhile, GM Financial has seen a modest increase in its revenue share. Starting at 6% in 2016, it rose to 8.5% by 2024. This gradual rise highlights GM Financial’s growing role in the company’s revenue structure over the nearly decade-long period. The steady upward trend reflects the financial arm’s expanding influence and importance within General Motors’ overall business strategy.
Collectively, these shifts illustrate the evolving landscape of General Motors’ revenue sources, with GMNA’s dominance remaining unchallenged, GMI’s diminishing contribution, and the gradual ascendancy of GM Financial. This underscores the importance of strategic focus on bolstering both GMNA and GM Financial to sustain and enhance overall revenue performance.
Conclusion
In summary, GM North America (GMNA) continues to be the dominant segment, contributing a substantial 84% of the total revenue.
GM International (GMI) has experienced a dramatic decline in its revenue contribution. Meanwhile, GM Financial has seen a modest increase in its revenue share.
GM’s autonomous vehicle subsidiary, Cruise, has also been a part of the company’s revenue segments. However, its contribution remains relatively small compared to the other segments.
Overall, these shifts illustrate the evolving landscape of General Motors’ revenue sources. GMNA’s dominance remains unchallenged, GMI’s contribution is diminishing, and GM Financial is gradually ascending.
References and Credits
1. All data presented were obtained and referenced from GM’s annual reports published on the company’s investor relations page: General Motors Investor Relation.
2. Pexels Images.
Disclosure
We may use the assistance of artificial intelligence (AI) tools to produce some of the text in this article. However, the data is directly obtained from original sources and meticulously cross-checked by our editors multiple times to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media. Additionally, providing a link back to this article from any website can help us create more content like this in the future.
Thank you for your support and engagement! Your involvement helps us continue to provide high-quality, reliable content.