Piles Of Coal. Image source: Flickr Image.
This article examines Peabody Energy’s global and U.S. coal sales volumes, focusing on their U.S. thermal coal sales and seaborne coal sales.
Investors looking for other statistics of Peabody may find more resources on these pages:
- Peabody coal revenue and profit margin,
- Peabody coal price and profit per ton, and
- Peabody profit breakdown by segment.
Please use the table of contents to navigate this page.
Table Of Contents
Definitions And Overview
O2. Peabody’s Coal Shipment Overview
Consolidated Results
U.S. Results
B1. Total U.S. Thermal Coal Sales Volumes
Breakdown Of U.S. Results
C1. Powder River Basin And Other U.S. Results
Overseas Results
D1. Seaborne Coal Sales Volumes
Results By Percentage
E1. Percentage Of Global Coal Sales Volume
E2. Percentage Of U.S. Coal Sales Volume
Conclusion And Reference
S1. Conclusion
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
Definitions
To help readers understand the content better, the following terms and glossaries have been provided.
Seaborne Mining Operation: Peabody Energy’s seaborne mining operations primarily involve the extraction and export of coal to international markets. These operations are mainly located in Australia, where Peabody mines both thermal coal (used for power generation) and metallurgical coal (used in steel production).
Key mines in Australia include the Wambo Underground Mine, Wilpinjong Mine, Centurion Mine, Coppabella Mine, Metropolitan Mine, Middlemount Mine, and Moorvale Mine. These operations have significantly contributed to Peabody’s revenue, especially in the post-pandemic recovery period.
U.S. Mining Operation: Peabody Energy’s U.S. mining operations primarily involve coal mining and distribution across several states.
Their U.S. mines are located in Alabama, Colorado, Illinois, Indiana, New Mexico, and Wyoming. The company’s largest operation in the U.S. is the North Antelope Rochelle Mine in Wyoming (part of the Powder River Basin region), which produced over 62 million tons of coal in 2023.
Peabody Energy focuses on providing coal for electricity generation and steel production. They also market, broker, and trade coal through offices in the U.S. and other countries.
Powder River Basin: The Powder River Basin is a geologic structural basin located in southeast Montana and northeast Wyoming.
It is known for its extensive coal reserves and is the largest coal-producing region in the United States. The basin covers an area of about 120 miles east to west and 200 miles north to south. Major cities in the area include Gillette and Sheridan in Wyoming, and Miles City in Montana.
The Powder River Basin produces primarily thermal coal, which is used for power generation, and metallurgical coal (or coking coal), which is used for steelmaking. The region includes the Black Thunder Coal Mine, the most productive coal mine in the United States, and the North Antelope Rochelle Mine, the second most productive.
In addition to coal, the Powder River Basin has become a significant producer of natural gas, including conventional natural gas and coal-bed methane.
Tons Or Tonnes: The terms “tons” and “tonnes” are often used interchangeably, but they actually refer to different units of mass:
Tons: This is a unit of weight commonly used in the United States. One ton is equivalent to 2,000 pounds (approximately 907.185 kilograms).
Tonnes: This is a metric unit of weight used in most other countries. One tonne is equivalent to 1,000 kilograms (approximately 2,204.62 pounds).
So, while they both measure weight, the key difference is in their respective measurement systems and conversion factors.
Peabody’s Coal Shipment Overview
For your information, Peabody’s coal shipment volumes are divided into U.S. and seaborne segments.
Seaborne coal refers to coal that is mined and shipped outside of the United States to countries that need to import energy. Apart from the sales breakdown by region and country, Peabody’s coal sales are also divided by category and coal type.
Peabody mines and ships two types of coal: thermal and metallurgical coal.
Thermal coal is primarily used for power generation and is sold to utility companies. In contrast, metallurgical coal (or coking coal) is used for steelmaking and is sold primarily to steelmaking companies.
With this context, let’s proceed to look at the coal sales numbers.
Peabody’s Global Coal Sales Volumes
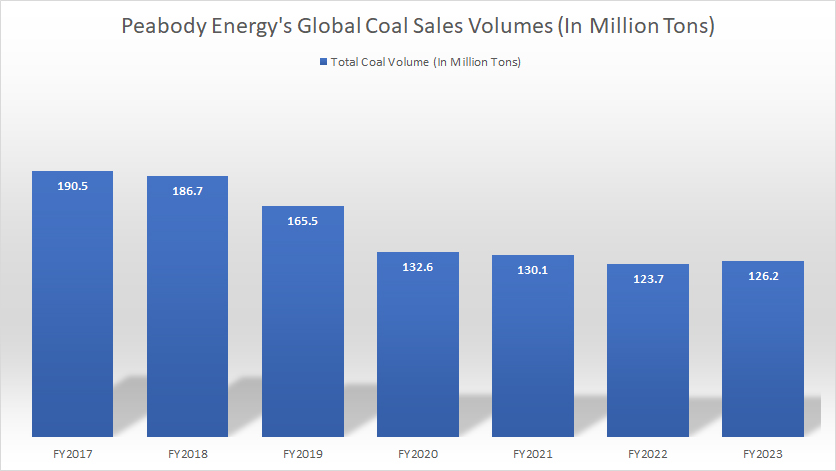
Peabody global coal sales volumes by year
(click image to enlarge)
The definition of tons and tonnes is available here: tons or tonnes.
On a consolidated basis, Peabody’s global coal sales volume reached 126.2 million tons in fiscal year 2023, up 2% over 2022. Although Peabody’s worldwide coal sales volumes increased in 2023, they have declined significantly over the long term, down 34% between fiscal year 2017 and 2023, or roughly 5% on average per year.
The most significant decline occurred in fiscal 2020 when the company shipped only 133 million tons of coal, compared to 166 million tons in the prior year, representing a 19% year-over-year decrease.
Several factors are driving the decline in Peabody’s global coal shipment volumes. The most significant factor is the shift to renewable energy. There is a global trend towards renewable energy sources, which has reduced the demand for coal. Many countries are investing in cleaner energy alternatives like wind, solar, and hydroelectric power.
In addition, stringent environmental regulations for coal usage have been implemented all around the world. These regulations and policies aim to reduce carbon emissions, leading to a decrease in coal consumption.
Furthermore, Peabody has shifted its focus from volume to value, prioritizing profitability over production. This has led to cuts in U.S. thermal coal production and increased attention to metallurgical coal operations.
Peabody’s U.S. Thermal Coal Sales Volumes
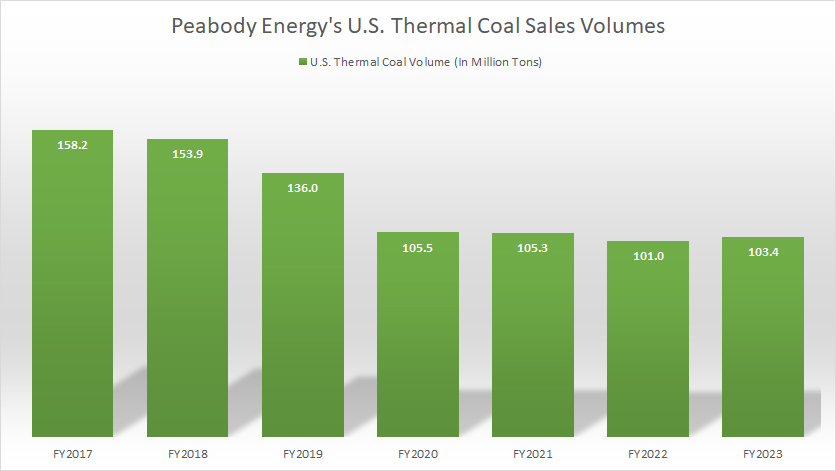
Peabody U.S. thermal coal sales volumes by year
(click image to enlarge)
The definition of tons and tonnes is available here: tons or tonnes. You can find more information about Peabody’s U.S. mining operations here: U.S. mining operations.
Peabody’s U.S. thermal coal shipment volume reached 103.4 million tons in fiscal year 2023, up 2% over 2022. However, on a long-term basis, Peabody’s U.S. thermal coal sales have significantly declined since fiscal year 2017, reaching one of the record lows in fiscal year 2023.
A major factor driving the decline in Peabody’s U.S. thermal coal sales is the low price of natural gas, which has made it a more attractive option for power generation compared to coal.
Also, Peabody has shifted its focus from volume to value, prioritizing profitability over production. This has led to cuts in U.S. thermal coal production and increased attention to metallurgical coal operations.
In addition, there is a global trend towards renewable energy sources, reducing the demand for coal. Many countries are investing in cleaner energy alternatives like wind, solar, and hydroelectric power. The U.S. is no exception, and this shift has led to Peabody’s lower coal sales in the region.
Peabody’s Powder River Basin And Other U.S. Results
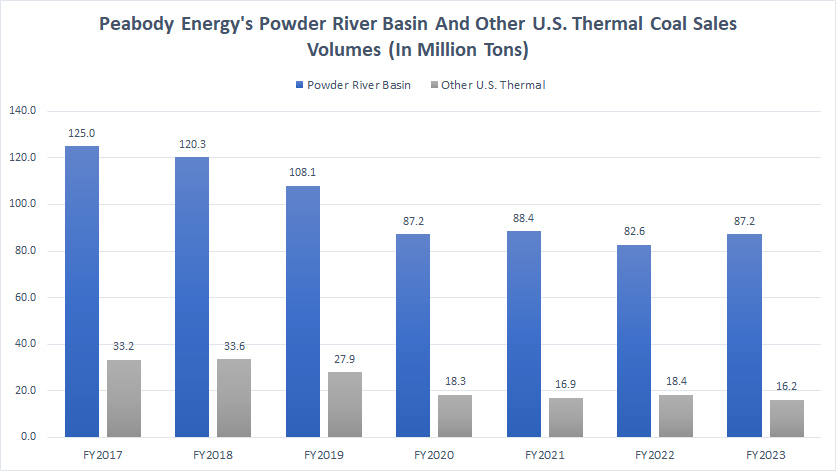
Peabody Powder River Basin thermal coal sales volumes by year
(click image to enlarge)
The definition of tons and tonnes is available here: tons or tonnes. You can find more information about Peabody’s U.S. mining operations here: U.S. mining operations.
Within the U.S., Peabody’s coal shipment volumes primarily come from the Powder River Basin mining operation, where thermal coal is mined. Peabody also has other mining operations in the Midwestern and Western U.S., but these represent only a small portion of its U.S. coal sales volumes, as shown in the chart above.
As of 2023, Peabody shipped 87.2 million tons of thermal coal from the Powder River Basin, while its other U.S. mining operations delivered 16.2 million tons of thermal coal. Therefore, Peabody’s coal sales volumes from the Powder River Basin alone were more than four times higher than those from the rest of its U.S. locations.
A significant trend is that Peabody’s coal shipment volumes from both regions in the U.S. have considerably decreased over the years, with a decline of more than 30% for the Powder River Basin mining operations since fiscal year 2017 and over 50% for other U.S. mining operations for the same period.
Peabody’s Seaborne Coal Sales Volumes By Year
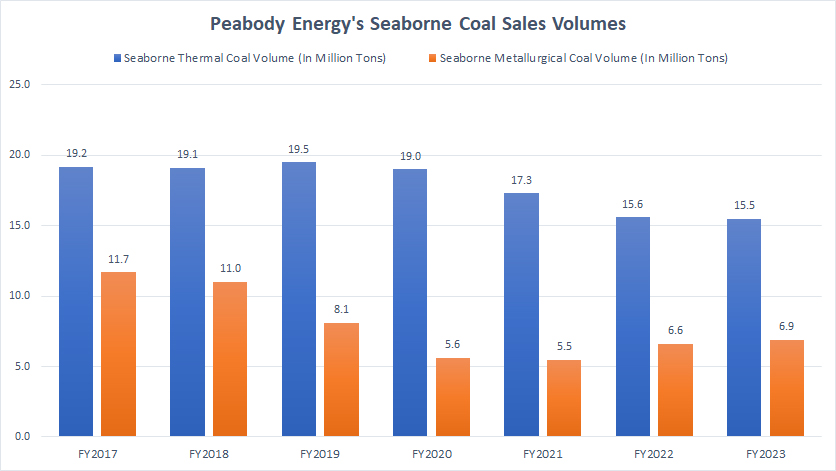
Peabody seaborne coal sales volumes by year
(click image to enlarge)
The definition of tons and tonnes is available here: tons or tonnes. You can find more information about Peabody’s seaborne mining operations here: seaborne mining operations.
Peabody’s seaborne coal sales volumes come from overseas mining operations, such as those in Australia. Peabody’s largest overseas mining operation is the Wilpinjong Mine in New South Wales, Australia, which spans an area equivalent to 5,500 football fields.
Peabody’s seaborne mining operations are divided into two segments: thermal and metallurgical coal. Metallurgical coal is used for steelmaking and is primarily sold to steelmaking companies, while thermal coal is sold mainly to utility companies for electricity generation.
As shown in the chart above, since fiscal year 2017, Peabody’s seaborne thermal coal shipments have significantly declined, reaching just 15.5 million tons in fiscal year 2023, the lowest level ever recorded since 2017. In contrast, Peabody’s seaborne metallurgical coal shipments reached a record figure of 6.9 million tons in fiscal year 2023, an increase of 5% over 2022 and 23% over 2020.
A key factor driving the decline in Peabody’s seaborne thermal coal shipment volumes is the global energy shift to renewable sources. There is a global trend towards renewable energy sources, which has reduced the demand for coal. Many countries are investing in cleaner energy alternatives like wind, solar, and hydroelectric power.
On the other hand, the primary factor driving the growth in Peabody’s overseas metallurgical coal sales is the continuous strong demand from the steel industry. For example, the global steel industry’s robust demand for metallurgical coal has driven up Peabody’s sales.
Also, Peabody has been expanding its metallurgical coal operations, including acquisitions of Tier 1 assets in Australia. This has increased its production capacity and market share.
Overall, Peabody’s overseas thermal coal sales have remained depressed even in the post-pandemic period, whereas metallurgical coal sales have significantly recovered post-pandemic, though they may not reach their pre-pandemic highs.
Peabody’s Percentage Of Global Coal Sales Volume
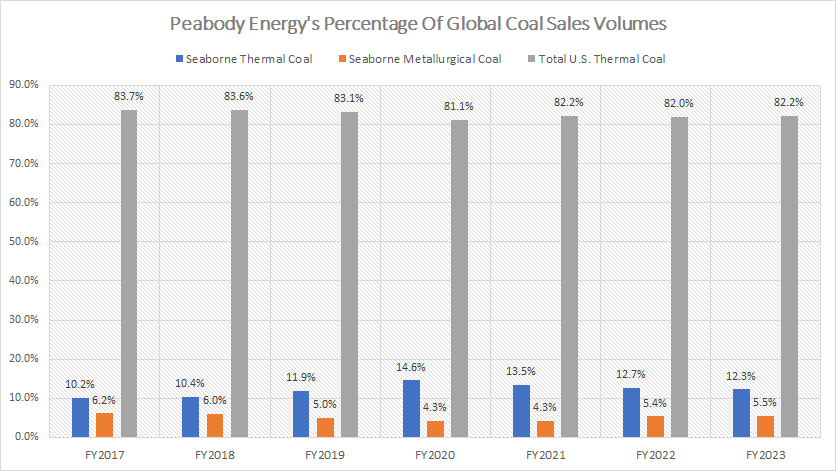
Peabody percentage of global coal sales volumes
(click image to enlarge)
From a percentage standpoint, Peabody’s U.S. thermal coal sales have accounted for the lion’s share of the company’s global coal volumes, as depicted in the chart above.
In fiscal year 2023, Peabody’s U.S. thermal coal sales made up 82% of the company’s global coal shipment volume, the largest share among all regions and countries. However, this ratio has slightly declined from the 84% recorded in fiscal year 2017.
In the same fiscal year, Peabody’s seaborne thermal coal contributed 12% of its worldwide coal volume, while seaborne metallurgical coal sales accounted for 5.5%, the lowest share among all regions and countries.
Over the past seven years, the sales contribution from Peabody’s seaborne thermal coal have slightly increased from 10% to 12%, while those of seaborne metallurgical coal have slightly decreased from 6.2% to 5.5%.
A noteworthy trend is that the sales contributions from coal sales for all regions and countries have remained relatively stable over the years, despite major changes in sales volume over the past seven years.
Peabody’s Percentage Of U.S. Coal Sales Volume
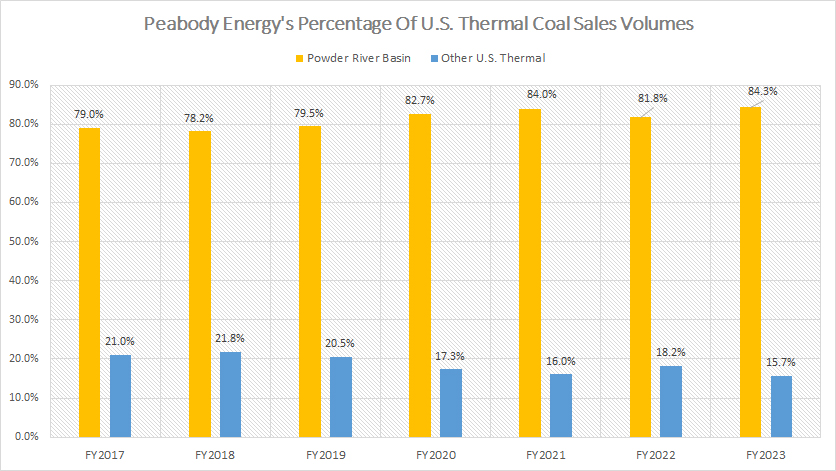
Peabody percentage of U.S. coal sales volumes
(click image to enlarge)
Within the U.S., Peabody’s Powder River Basin has contributed the lion’s share of the total volume, reaching 84% of the total in fiscal year 2023.
The remaining 16% is made up by other U.S. mining operations, primarily located in the Western and Midwestern regions.
A significant trend is that the sales contributions from the Powder River Basin have considerably grown over the last seven years, rising from 79% in fiscal year 2017 to 84% in fiscal year 2023, the highest ratio ever recorded since 2017.
On the other hand, other U.S. thermal coal sales have declined from 21% to 16% over the last seven years, reflecting a shift in production and market focus towards the Powder River Basin.
The lion’s share of Peabody’s coal shipments from the Powder River Basin highlights the dominant role of this region in the company’s overall coal production.
This region has consistently been the primary source of Peabody’s U.S. coal volume, underscoring its critical importance to the company’s operations.
Conclusion
Overall, while Peabody’s U.S. thermal coal sales have remained a significant portion of its global coal volumes, there has been a notable decline in sales volumes over the years. Overseas, seaborne thermal coal sales have remained depressed, while metallurgical coal sales have shown a recovery post-pandemic, though not reaching pre-pandemic highs.
References and Credits
1. All financial figures presented were obtained and referenced from Peabody’s annual reports published on the company’s investor relations page: Peabody Investor Center.
2. Flickr Images.
Disclosure
References and examples such as tables, charts, and diagrams are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant the full correctness of all content.
The content in this article is for informational purposes only and is neither a recommendation nor a piece of financial advice to purchase a stock.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media and also provide a link back to this article from any website so that more articles like this one can be created in the future.
Thank you!