Ford River Rouge Complex, Dearborn, MI. Source: Flickr
This article delves into an in-depth analysis of Ford Motor’s revenue breakdown, categorized by various sources such as new and used vehicle sales, services, leasing income, financing income, and insurance income.
You may find other key statistic of Ford Motor on these pages:
Revenue
- Ford revenue by segment: Ford Blue, Ford Pro, Ford Model-e, etc.,
- Ford revenue per car sold in North America, Europe, China, etc., and
- Ford revenue by country: U.S., Canada, U.K., Germany, And Mexico.
Profit Margin
- Ford profit margin by segment: Automotive, Ford Credit, etc.,
- Ford profit per vehicle, and
- Ford vs GM: vehicle profit and margin.
Other Statistics
Let’s get started!
Please use the table of contents to navigate this page.
Table Of Contents
Definitions And Overview
A2. Ford Business Overview
A3. How Does Ford Generate Revenue
Revenue By Type
B1. Revenue From Sales Of New Vehicles, Parts, And Accessories
B2. Revenue From Sales Of Used Vehicles And Services
B3. Revenue From Leasing, Financing, And Insurance Income
Percentage Of Revenue By Type
C1. Percentage Of Revenue From Sales Of New And Used Vehicles, Parts, And Accessories, And Services
C2. Percentage Of Revenue From Leasing, Financing, And Insurance Income
Growth Rates Of Revenue By Type
C3. YoY Growth Rates Of Revenue By Type
Automotive Revenue By Region (Legacy)
D1. Revenue From North And South America, Europe, And China
D2. Percentage Of Revenue From North And South America, Europe, And China
D3. YoY Growth Rates Of Revenue From North And South America, Europe, And China
Automotive Profit Margin By Region (Legacy)
D4. Adjusted EBIT From North And South America, Europe, And China
D5. Adjusted EBIT Margin From North And South America, Europe, And China
Conclusion And Reference
S1. Conclusion
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
Definitions
To help readers understand the content better, the following terms and glossaries have been provided.
Adjusted EBIT: Ford defines its adjusted EBIT as earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) excluding interest on debt (excl. Ford Credit Debt), taxes, and pre-tax special items.
Pre-tax special items include the following:
1. Pension and OPEB remeasurement gains and losses,
2. Gains and losses on investments in equity securities,
3. Personnel expenses, supplier- and dealer-related costs, and facility-related charges,
4. Other items that are not necessarily considered to be indicative of earnings from ongoing operating activities
This non-GAAP measure is useful to management and investors because it focuses on underlying operating results and trends and improves the comparability of period-over-period results.
Used Vehicle Sales: Ford sells used vehicles both at auction and through its consolidated dealerships.
Proceeds from the sale of used vehicles are recognized in Company excluding Ford Credit revenues upon transfer of control of the vehicle to the customer, and the related vehicle carrying value is recognized in Cost of sales.
Leasing Income: Ford Credit offers leasing plans to retail consumers through Ford and Lincoln brand dealers that originate the leases. Ford Credit records an operating lease upon purchase of a vehicle subject to a lease from the dealer.
The retail consumer makes lease payments representing the difference between Ford Credit’s purchase price of the vehicle and the contractual residual value of the vehicle plus lease fees, which Ford recognizes on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease agreement.
Depreciation and the gain or loss upon disposition of the vehicle is recorded in Ford Credit interest, operating, and other expenses.
Financing Income: Ford Credit originates and purchases finance installment contracts.
Financing income represents interest earned on the finance receivables (including sales-type and direct financing leases). Interest is recognized using the interest method and includes the amortization of certain direct origination costs.
Insurance Income: Income from insurance contracts is recognized evenly over the term of the agreement.
Insurance commission revenue is recognized on a net basis at the time of sale of the third party’s product or service to our customer.
Ford Business Overview
Ford’s revenue streams are diverse, spanning multiple segments:
- Automotive Segment: This is the core of Ford’s business, involving the design, manufacture, marketing, and servicing of cars, trucks, and SUVs. This segment includes the iconic Ford brand and the luxury Lincoln brand.
- Financial Services: Ford Credit provides automotive financing products to dealers and customers. This segment is a significant profit center, offering loans, leases, and insurance services.
How Does Ford Generate Revenue
Ford generates revenue from selling automobiles and related products and services. It designs, manufactures, markets, and services a broad range of cars, trucks, SUVs, electric vehicles, luxury vehicles, and commercial vehicles.
In addition to vehicle sales, Ford generates revenue from financing services, extended service plans, and other aftermarket products. It also has a significant presence in mobility, including autonomous vehicle development and ride-sharing services.
Overall, Ford Motor is a diversified company with multiple revenue streams within the automotive industry.
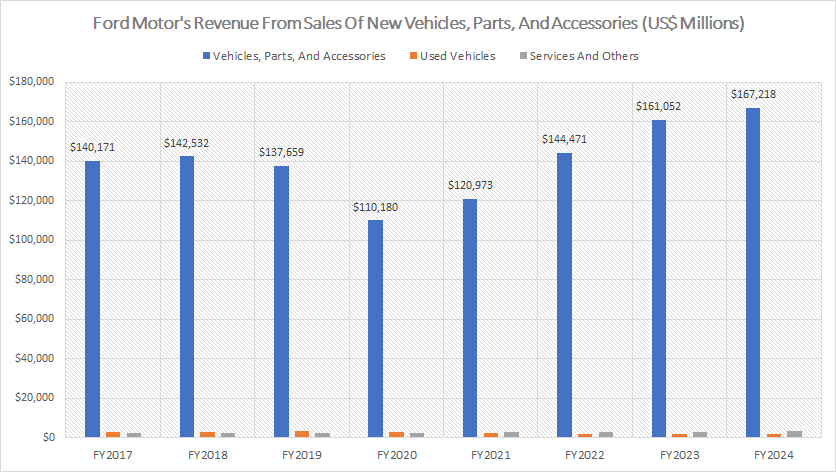
Revenue From Sales Of New Vehicles, Parts, And Accessories
Ford-Motor-revenue-from-sales-of-new-vehicles-parts-and-accessories
(click image to expand)
Ford’s primary revenue stream is derived from the sales of new vehicles, parts, and accessories, as depicted in the graph accompanying this article. This category constitutes the most significant portion of the company’s income, substantially surpassing all other revenue sources.
In fiscal year 2024, Ford generated $167.2 billion from the sales of new vehicles, parts, and accessories, marking a 4% increase from the $161.1 billion recorded in fiscal year 2023.
This growth continues a positive trend, as the revenue from this segment reached $144.5 billion in fiscal year 2022, up from $121 billion in the previous year.
While Ford does earn revenue from the sales of used vehicles and services, this income is relatively negligible when compared to the substantial earnings from new vehicle sales, parts, and accessories.
This disparity underscores the dominant role that new vehicle sales play in Ford’s financial success. The consistent growth in this segment highlights Ford’s strong market presence and customer demand for its new vehicles, parts, and accessories.
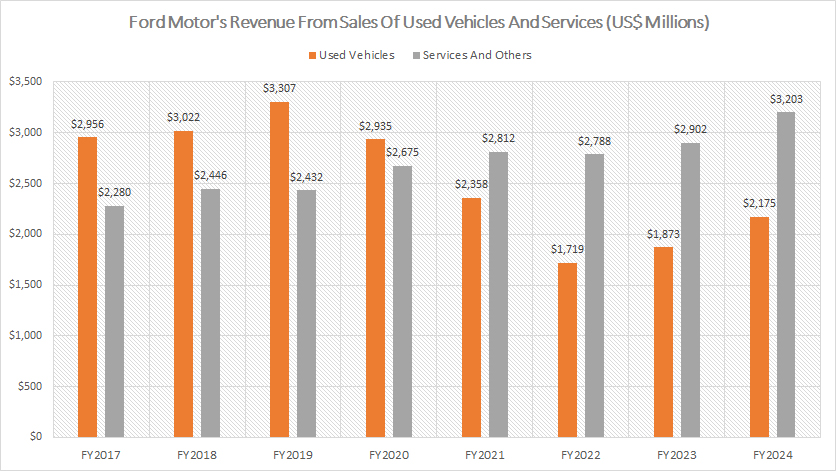
Revenue From Sales Of Used Vehicles And Services
Ford-Motor-revenue-from-sales-of-used-vehicles-and-services
(click image to expand)
The graph above provides a detailed breakdown of Ford’s income from the sales of used vehicles and services. The definition of Ford’s used vehicle sales is available here: used vehicle sales.
As illustrated, in fiscal year 2024, Ford’s revenue from used vehicle sales and services totaled $2.2 billion and $3.2 billion, respectively. These figures are significantly lower than the substantial revenue generated from the sales of new vehicles, parts, and accessories, which we saw in earlier paragraphs.
In fiscal year 2023, Ford’s used car sales produced revenue of $1.9 billion, while services revenue came in at $2.9 billion. In fiscal year 2022, these revenue streams were $1.7 billion and $2.8 billion, respectively. Although these figures are relatively small compared to new vehicle sales, they have shown a steady increase post-pandemic, as depicted in the graph.
For instance, in fiscal year 2022, Ford’s sales of used vehicles generated $1.7 billion, marking the lowest level recorded over the past eight years. However, this revenue stream rebounded significantly, rising from $1.7 billion in 2022 to $2.2 billion in 2024, an increase of 29% in just two years. Despite this rebound, over the longer term from fiscal year 2017 to 2024, Ford’s revenue from used vehicle sales has declined by 27%, falling from $3 billion to $2.2 billion.
In contrast, Ford’s services revenue has remained resilient, even during the COVID-19 pandemic. From fiscal year 2017 to 2024, services revenue has consistently increased, rising from $2.3 billion in 2017 to $3.2 billion in 2024, marking an increase of 39% over the past eight years. This growth underscores the stability and importance of services as a revenue source for Ford.
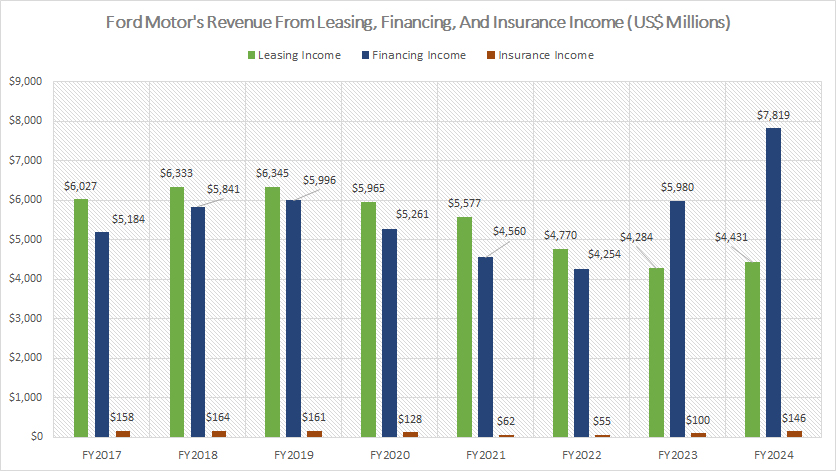
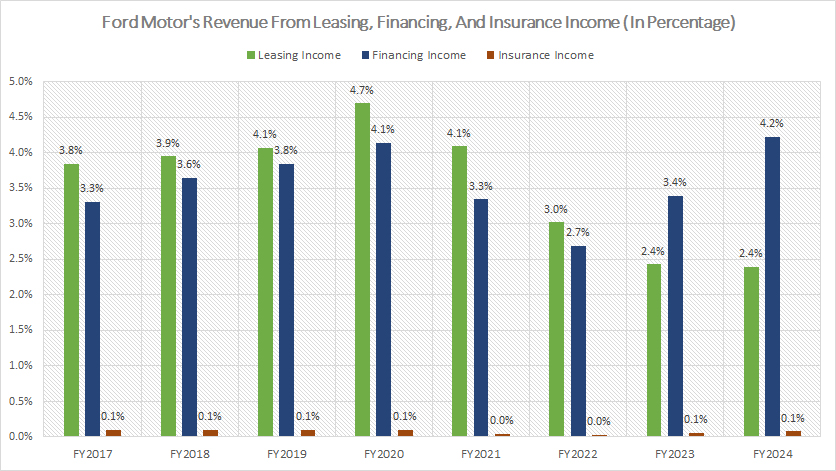
Revenue From Leasing, Financing, And Insurance Income
Ford-Motor-leasing-financing-and-insurance-income
(click image to expand)
Ford’s leasing, financing, and insurance income is derived primarily from Ford Credit, a wholly-owned subsidiary that provides vehicle-related lending and loan services. The definitions of these revenue streams are available here: leasing income, financing income, and insurance income.
In fiscal year 2024, Ford Motor earned $4.4 billion in leasing income, a slight increase from the $4.3 billion earned in fiscal year 2023. However, Ford’s leasing income has seen a significant decline over the years, dropping from $6 billion in 2017 to $4.4 billion in 2024 — a 28% decrease.
Conversely, Ford’s financing income experienced a remarkable recovery post-pandemic. As of fiscal year 2024, financing income rose to $7.8 billion, marking an 80% increase from the bottom level of $4.3 billion recorded in 2022.
Since 2017, Ford’s financing income has grown by 50%, climbing from $5 billion in 2017 to $7.8 billion in 2024. Financing income has now become one of the largest revenue sources for Ford Credit, reflecting its strategic importance.
On the other hand, Ford Motor’s insurance income remains relatively insignificant. In fiscal year 2024, insurance income contributed only $146 million, the lowest among all revenue streams. This negligible contribution underscores the minor role of insurance income in Ford’s overall revenue portfolio.
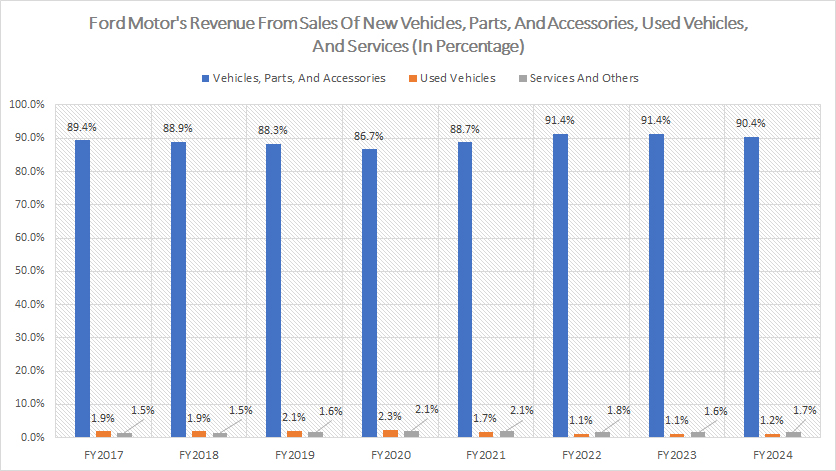
Percentage Of Revenue From Sales Of New And Used Vehicles, Parts, And Accessories, And Services
Ford-Motor-revenue-share-from-sales-of-new-vehicles-parts-and-accessories
(click image to expand)
Ford derives a significant portion of revenue from new car sales, parts and accessories. The definition of Ford’s used vehicle sales is available here: used vehicle sales
Over the years, Ford’s revenue from the sales of new vehicles, parts, and accessories has consistently accounted for nearly 90% of the company’s total income. This predominant revenue source underscores the critical importance of this segment to Ford’s financial health and overall business strategy.
In fiscal year 2024, this revenue stream made up 90.4% of Ford’s total revenue, highlighting its significance and central role in driving the company’s financial performance.
In stark contrast, other revenue sources, such as those from used car sales and services, constitute only a small fraction of the total income.
For instance, in fiscal year 2024, revenue from used car sales and services represented just 1.2% and 1.7% of Ford’s total revenue, respectively. This disparity emphasizes the dominant role that new vehicle sales, parts, and accessories play in Ford’s overall revenue portfolio.
The graph illustrates this clear difference in revenue contributions, reinforcing the necessity for Ford to maintain its strong market position in new vehicle sales and continuously innovate within this segment to ensure sustained growth and profitability.
Percentage Of Revenue From Leasing, Financing, And Insurance Income
Ford-Motor-leasing-financing-and-insurance-income-in-percentage
(click image to expand)
Ford’s leasing, financing, and insurance income is derived primarily from Ford Credit, a wholly-owned subsidiary that provides vehicle-related lending and loan services. The definitions of these revenue streams are available here: leasing income, financing income, and insurance income.
In fiscal year 2024, Ford Motor’s leasing income accounted for a modest 2.4% of the total revenue, maintaining a similar level to the previous fiscal year 2023.
However, over the longer term from fiscal year 2017 to 2024, the revenue share of Ford’s leasing income has significantly declined, falling from 3.8% in 2017 to just 2.4% in the latest result.
Conversely, the company’s financing income represented a more substantial 4.2% of the total revenue, up from 3.4% in fiscal year 2023.
Despite the significant increase in financing income in recent periods, its share of the total revenue has remained relatively stable compared to pre-pandemic levels.
This stability indicates that other revenue sources have been growing at a much faster pace, contributing to the overall diversification of Ford’s income streams.
On the other hand, Ford’s insurance business contributed a minimal 0.1% to the overall revenue in fiscal year 2024, underscoring its relatively minor role in the company’s financial portfolio.
This negligible contribution highlights the limited impact of the insurance segment compared to more dominant revenue sources like new vehicle sales, parts, and accessories.
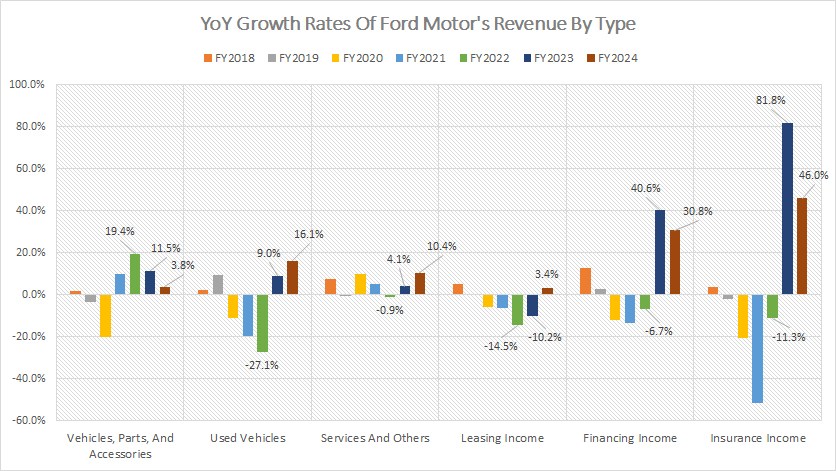
YoY Growth Rates Of Revenue By Type
Ford-Motor-yoy-growth-rates-of-revenue-by-type
(click image to expand)
Ford derives a significant portion of revenue from new car sales, parts and accessories. The definition of Ford’s used vehicle sales is available here: used vehicle sales
Among all revenue streams, Ford’s insurance income has exhibited the most significant growth, despite its relatively low absolute figures. On average, Ford’s insurance income has increased by 39% annually from fiscal year 2022 to 2024.
Conversely, Ford’s financing income has also shown robust growth, with an average annual increase of 21.5% between fiscal years 2022 and 2024, making it one of the fastest-growing revenue streams.
Ford’s sales of new vehicles, parts, and accessories have grown at an average annual rate of 12% over the past three years, making it the third-fastest growing income source.
Services revenue has experienced a modest average annual growth rate of 4.5%, while revenue from used vehicle sales has declined by an average of 1% annually from fiscal years 2022 to 2024.
In contrast, Ford’s leasing income has faced the most significant decline among all revenue streams, with an average annual decrease of 7% over the past three years.
This decline highlights the shifting dynamics within Ford’s revenue portfolio and emphasizes the company’s need to adapt to changing market conditions and consumer preferences.
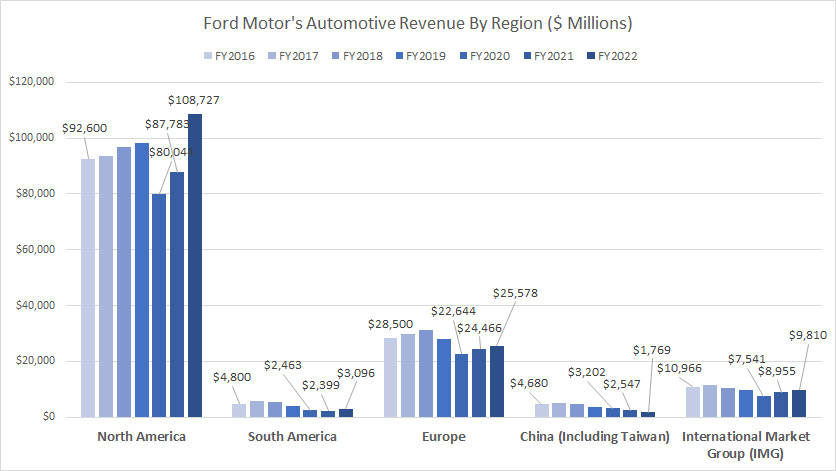
North And South America, Europe, And China Revenue
Ford-Motor-automotive-revenue-by-region
(click image to expand)
Starting in fiscal year 2023, Ford Motor Company has transitioned from breaking down its automotive revenue by region to reorganizing its segments into new divisions: Ford Blue, Ford Model e, Ford Pro, and Ford Next. For detailed revenue information by these new segments, please visit Ford revenue by segment.
Before 2023, Ford categorized its automotive revenue by region, including North America, South America, Europe, China (including Taiwan), and the International Market Group (IMG), which encompasses the Asia Pacific, Middle East, and Africa regions.
- North America: North America was Ford’s largest market, with revenue reaching over $100 billion in 2022, up from $88 billion in 2021. This marked a significant increase in revenue since 2020, highlighting the region’s vital importance to Ford’s overall financial performance.
- Europe: Europe was Ford’s second-largest market, with annual sales amounting to $26 billion in 2022, compared to $24 billion in 2021. Although Ford’s sales in Europe have increased since 2020, the growth has been more modest compared to North America.
- South America: In South America, Ford’s automotive revenue was $3 billion in 2022, up from $2.4 billion in 2021. While this represents growth, the revenue from this region remains relatively low compared to other markets.
- China: Ford’s performance in China has been challenging, with automotive revenue declining significantly over the years. By 2022, revenue had decreased to just $1.8 billion, the lowest level ever reported in this region, indicating a stark contrast to its other markets.
- International Market Group (IMG): The IMG, which includes regions like the Asia Pacific, Middle East, and Africa, generated nearly $10 billion in revenue in fiscal year 2022. This segment has shown steady and substantial revenue contributions, emphasizing its importance within Ford’s global operations.
The strategic reorganization into the new divisions — Ford Blue, Ford Model e, Ford Pro, and Ford Next — reflects Ford’s commitment to evolving its business model to better align with emerging market trends and technologies, ensuring sustained growth and competitiveness in the global automotive industry.
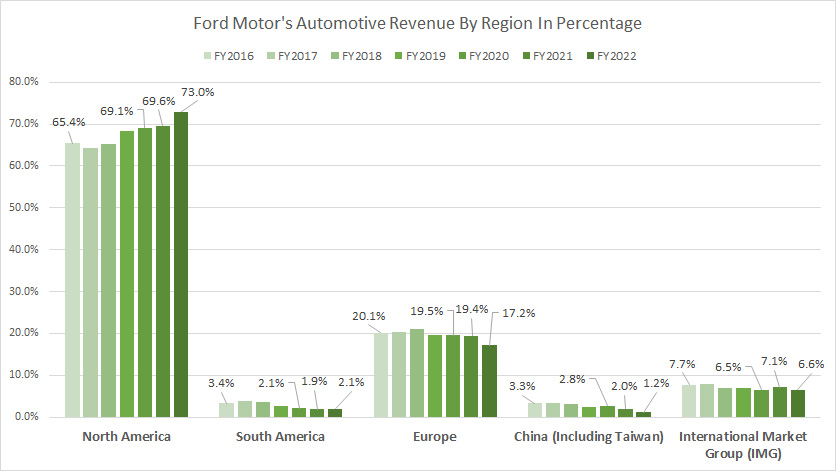
Percentage Of Revenue From North And South America, Europe, And China
Ford-Motor-automotive-revenue-by-region-in-percentage
(click image to expand)
Starting in fiscal year 2023, Ford Motor Company has transitioned from breaking down its automotive revenue by region to reorganizing its segments into new divisions: Ford Blue, Ford Model e, Ford Pro, and Ford Next. For detailed revenue information by these new segments, please visit Ford revenue by segment.
Prior to this change, Ford provided a regional breakdown of its automotive revenue. In fiscal year 2022, North America emerged as the largest contributor, accounting for 73% of Ford’s total automotive revenue. This marked a considerable rise from 65% in 2016, highlighting the growing importance of the North American market to the company.
Europe was Ford’s second-largest market, contributing approximately 17% to the automotive sector in 2022. While this region has seen a modest increase in revenue, it remains significantly behind North America in terms of contribution.
In fiscal year 2022, South America accounted for about 2% of Ford’s automotive revenue, reflecting a smaller but essential market segment. Similarly, sales in China comprised only 1.2% of total automotive revenue during the same period, underscoring the challenges Ford has faced in this region.
A noticeable trend is the decline in revenue contributions from most regions except North America. The North American market’s ratio has significantly increased from 65% in 2016 to 73% in 2022, illustrating its growing dominance in Ford’s overall revenue portfolio.
Additionally, the International Market Group (IMG), which includes regions like the Asia Pacific, Middle East, and Africa, contributed to Ford’s steady and substantial revenue, highlighting the company’s global reach.
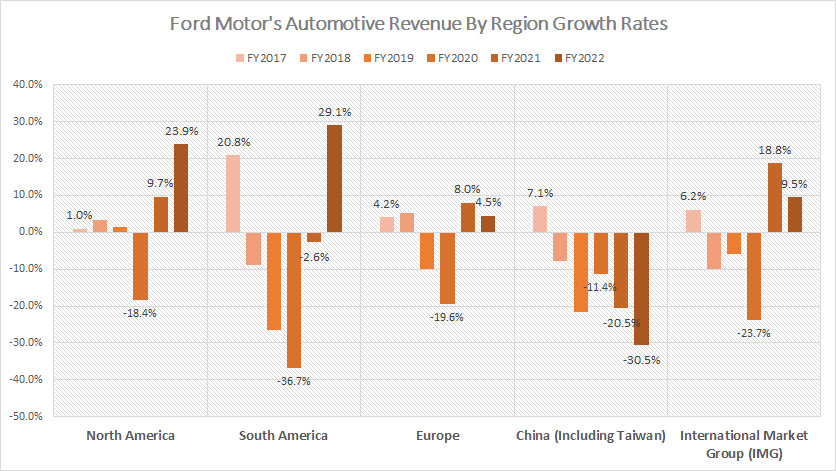
Growth Rates Of North And South America, Europe, And China Revenue
Ford-Motor-growth-rates-of-automotive-revenue-by-region
(click image to expand)
Starting in fiscal year 2023, Ford Motor Company has transitioned from breaking down its automotive revenue by region to reorganizing its segments into new divisions: Ford Blue, Ford Model e, Ford Pro, and Ford Next. For detailed revenue information by these new segments, please visit Ford revenue by segment.
Before this reorganization, Ford’s automotive revenue by region showed distinct trends. North America was the standout performer, with automotive revenue growing by an average of 5.1% annually between 2020 and 2022. This region’s increasing revenue contribution underscores the strategic importance of the North American market for Ford.
In contrast, Ford faced challenges in other regions:
- South America: Revenue growth declined by an average of 3.4% annually from 2020 to 2022.
- Europe: Revenue growth also experienced a downturn, with an average annual decrease of 2.3% during the same period.
- China: The most significant decline was seen in China, where revenue growth plummeted by an average of 20.8% annually between 2020 and 2022.
A noticeable trend is the significant recovery in Ford’s revenue growth in the post-COVID era across most regions, except for China. In 2022, Ford’s revenue in China decreased by over 30%, highlighting ongoing challenges in this market.
This reorganization into Ford Blue, Ford Model e, Ford Pro, and Ford Next represents a strategic shift aimed at aligning the company’s structure with evolving market trends and technological advancements. By focusing on these new divisions, Ford aims to enhance its competitiveness and drive growth in key areas.
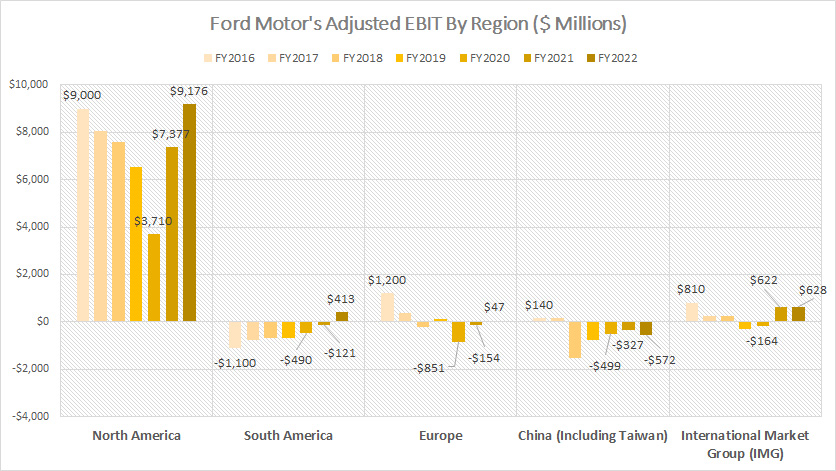
Adjusted EBIT From North And South America, Europe, And China
Ford-Motor-automotive-adjusted-EBIT-by-region
(click image to expand)
The definition of Ford’s adjusted EBIT is available here: adjusted EBIT. Starting in fiscal year 2023, Ford Motor Company has transitioned from breaking down its automotive revenue by region to reorganizing its segments into new divisions: Ford Blue, Ford Model e, Ford Pro, and Ford Next. For detailed profit margin information by these new segments, please visit Ford profit margin by segment.
Despite this shift, North America remains Ford’s major source of profit. In fiscal year 2022, Ford’s adjusted EBIT in North America reached $9.2 billion, a significant increase from $7.4 billion in 2021. This dramatic rise since 2020 reflects the region’s remarkable recovery in the post-COVID era and underscores North America’s critical role in Ford’s financial success.
In stark contrast, Ford has faced challenges and incurred losses in other regions, particularly in China. For example, Ford’s adjusted EBIT in China averaged -$466 million between 2020 and 2022. Similarly, in Europe, the adjusted EBIT averaged -$319 million during the same period. Despite turning a profit of $413 million in South America in 2022, Ford reported losses in this region for most other fiscal years.
Despite operating in China for over a decade, Ford continues to struggle with penetrating the Chinese market effectively. This challenge is evident in the consistent losses reported in the region. Conversely, North America remains the most profitable region for Ford, consistently generating substantial profits over the years.
This regional performance highlights the critical importance of North America to Ford’s overall profitability and the ongoing challenges the company faces in other global markets. As Ford continues to navigate these regional dynamics, the reorganization into new divisions aims to better align its structure with evolving market trends and technological advancements, positioning the company for sustained growth and competitiveness in the global automotive industry.
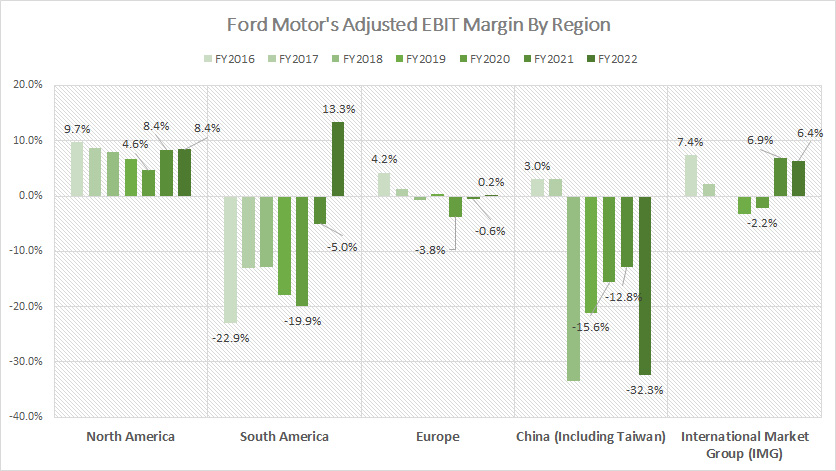
Adjusted EBIT Margin From North And South America, Europe, And China
Ford-Motor-automotive-adjusted-EBIT-margin-by-region
(click image to expand)
The definition of Ford’s adjusted EBIT is available here: adjusted EBIT. Starting in fiscal year 2023, Ford Motor Company has transitioned from breaking down its automotive revenue by region to reorganizing its segments into new divisions: Ford Blue, Ford Model e, Ford Pro, and Ford Next. For detailed profit margin information by these new segments, please visit Ford profit margin by segment.
North America has consistently been a significant profit center for Ford Motor Company, underlining the region’s importance to the company’s overall financial health. Although the adjusted EBIT in North America dropped to just 4% in 2020, it averaged 7.2% between fiscal years 2020 and 2022. This rebound underscores the region’s strong recovery in the post-pandemic era.
In fiscal year 2022, Ford achieved an adjusted EBIT margin of 13.3% in South America, marking the first profit in this region since 2016. This positive shift reflects improved market conditions and strategic adjustments.
Conversely, Ford’s adjusted EBIT margin has struggled in other regions:
- Europe: The adjusted EBIT margin averaged -1.4% since 2020, indicating ongoing challenges in achieving profitability.
- China: The situation is even more dire, with an average adjusted EBIT margin of -20.3% between 2020 and 2022, the worst among all regions. This underscores the significant difficulties Ford faces in penetrating the Chinese market.
In summary, North America remains Ford Motor’s most profitable region, consistently generating stable and substantial profits. The company’s performance in other regions, particularly Europe and China, highlights the varying challenges and opportunities across its global operations.
This regional disparity emphasizes the critical role of North America in Ford’s financial strategy and the necessity for targeted efforts to improve profitability in other key markets.
Conclusion
Overall, Ford’s revenue streams are dominated by the sales of new vehicles, parts, and accessories, while other segments like used vehicle sales, services, leasing, financing, and insurance play relatively smaller but important roles in the company’s financial portfolio.
The steady growth in financing and insurance income, coupled with the resilience of services revenue, highlights Ford’s diversified revenue base and its strategic focus on maintaining a strong market presence across different segments.
Credits and References
1. All financial figures presented were obtained and referenced from Ford Motor’s quarterly and annual reports published on the company’s investor relations page: Ford shareholders page.
2. Flickr Images.
Disclosure
We may use the assistance of artificial intelligence (AI) tools to produce some of the text in this article. However, the data is directly obtained from original sources and meticulously cross-checked by our editors multiple times to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media. Additionally, providing a link back to this article from any website can help us create more content like this in the future.
Thank you for your support and engagement! Your involvement helps us continue to provide high-quality, reliable content.