EV charging station. Flickr Image.
Tesla has established itself as a pioneer in the electric vehicle (EV) industry. Conversely, Ford only entered the battery EV market in 2020 with the launch of the all-electric MUSTANG MACH-E.
Additionally, Tesla is on track to deliver over 2 million EVs by 2025, whereas Ford sold fewer than 200,000 EVs in 2024.
While Ford may not be the first mover in the electric vehicle (EV) space, it remains a formidable player in the automobile industry, equipped with the necessary resources to compete with Tesla in the EV race.
For instance, Ford’s research and development spending in fiscal 2023 was nearly 300% higher than Tesla’s on a dollar-for-dollar basis.
This significant investment underscores Ford’s commitment to innovation and its determination to enhance its EV offerings, positioning the company as a strong contender in the rapidly evolving electric vehicle market.
Additionally, Ford’s flagship vehicle, the F-150 Lightning, an all-electric pickup truck that debuted in 2022, is making a significant impact on the company’s position in the EV race.
Will Ford overtake Tesla? The prospects look promising.
That said, this article offers a comparative analysis of Ford and Tesla across several key areas, including revenue per vehicle, vehicle profit, and margins.
Let’s get started!
Investors interested in other key statistics of Ford Motor and Tesla may find more resources on these pages:
- Tesla vs Ford and GM: marketing and advertising budget,
- Ford revenue streams: sales of new and used cars, services, and more, and
- Tesla expansion: Superchargers, service fleets, and locations.
Please use the table of contents to navigate this page.
Table Of Contents
Definitions And Overview
Revenue
A1. Revenue Per Car
Profit
B1. Profit Per Car
Margin
C1. Vehicle Margin
Consolidated Margin
D1. Operating Margin
Conclusion And Reference
S1. Conclusion
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
Definitions
To help readers understand the content better, the following terms and glossaries have been provided.
Revenue Per Car: Revenue Per Car is defined as automotive revenue excluding leasing, regulatory credits, non-automotive segments, etc., divided by vehicle sales.
Revenue Per Car = Automotive Revenue / Vehicle Sales
Vehicle sales represent vehicle wholesale in the case of Ford Motor and vehicle retail volume excluding leasing in the case of Tesla.
Profit Per Car: Profit Per Car is defined as automotive gross profit divided by vehicle sales
Profit Per Car = Automotive Gross Profit / Vehicle Sales
Vehicle sales represent vehicle wholesale in the case of Ford Motor and vehicle retail volume excluding leasing in the case of Tesla.
Vehicle Margin: Vehicle margin is defined as automotive gross profit as a ratio of automotive revenue.
Vehicle Margin = Automotive Gross Profit / Automotive Revenue
Automotive revenue represents car sales revenue excluding Ford Credit in the case of Ford Motor and leasing, regulatory credits, and energy in the case of Tesla.
Operating Margin: Operating margin is a financial metric that measures a company’s efficiency in generating profit from its operations.
It is expressed as a percentage and is calculated by dividing operating income (also known as operating profit) by net sales (revenue).
Operating Margin = Operating Income / Total Net Revenue
Essentially, operating margin shows what percentage of revenue is left over after paying for variable costs of production, such as wages and raw materials.
It’s a key indicator of a company’s financial health and its ability to manage its operations effectively. The higher the operating margin, the more profitable the company is considered to be.
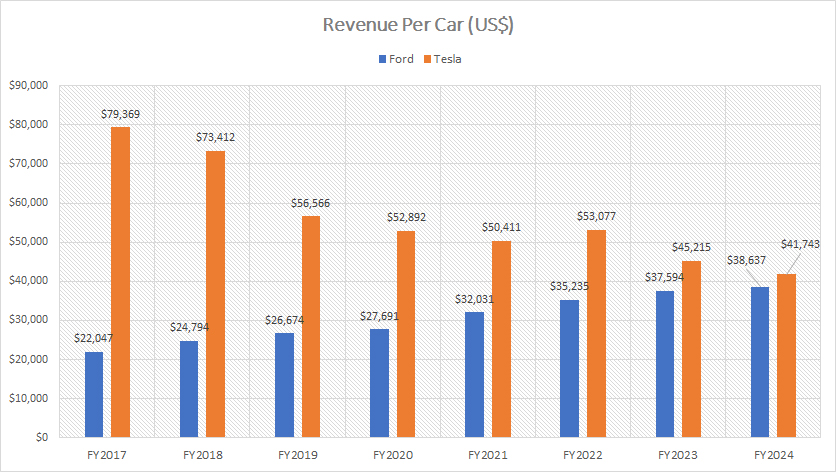
Revenue Per Car
ford-vs-tesla-in-revenue-per-car
(click image to expand)
The definition of revenue per car is available here: revenue per car.
Tesla earns slightly higher revenue per car than Ford, as depicted in the chart above.
In fiscal year 2024, Tesla’s revenue per car declined to $41,700, which is only 8% higher than Ford’s revenue per car of $38,600 in the same period. This represents a roughly $3,000 difference between Ford and Tesla.
Over the longer term, from fiscal year 2017 to 2024, Tesla’s revenue per car has significantly declined. It dropped from nearly $80,000 per car to slightly above $40,000 per car. This substantial decrease indicates a shift in Tesla’s pricing strategy or changes in its product mix over the years.
Conversely, Ford’s revenue per vehicle has been on an upward trajectory. As of fiscal year 2024, Ford’s revenue per vehicle topped nearly $39,000, marking the highest figure ever reported since 2017. This rise highlights Ford’s successful efforts to increase the value derived from each vehicle sold.
Between fiscal year 2017 and 2024, Ford’s revenue per vehicle has risen impressively from $22,000 to $39,000. This significant increase underscores Ford’s ability to enhance its pricing power and optimize its product offerings, leading to higher revenue per vehicle.
Essentially, while Tesla still earns slightly more revenue per car, the gap between Tesla and Ford has narrowed over the years. Ford’s continuous improvement in revenue per vehicle reflects its strategic focus on increasing profitability and competitiveness in the market.
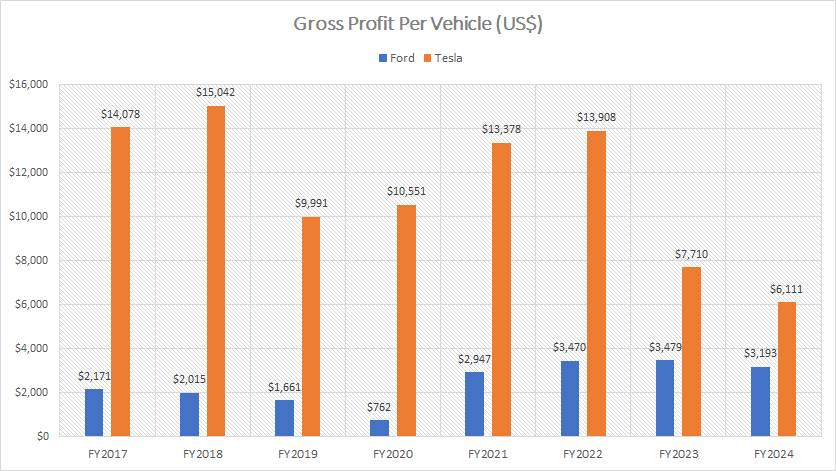
Profit Per Car
ford-vs-tesla-in-profit-per-vehicle
(click image to expand)
The definition of profit per car is available here: profit per car. Profit per car for both companies is evaluated based on the automotive gross profit.
While Tesla’s revenue per car is only 8% higher than Ford’s, its vehicle profit is nearly double that of Ford Motor, as shown in the accompanying graph.
In fiscal year 2024, Tesla’s profit per vehicle totaled $6,100, compared to Ford’s $3,200, resulting in a $2,900 difference or a 90% higher profit per vehicle.
From fiscal year 2022 to 2024, Tesla’s profit per vehicle averaged $9,200, whereas Ford’s profit per vehicle averaged just $3,400. This highlights an even larger disparity in vehicle profit between the two companies.
A significant trend is that Ford’s profit per car has been relatively stable and has steadily risen, reaching a peak of $3,500 in 2023, the highest figure ever measured. However, this figure declined to $3,200 in fiscal year 2024.
Conversely, Tesla’s profit per car has decreased over time, reaching just $6,100 in fiscal year 2024, the lowest profit recorded since 2017. This decline may be attributed to various factors such as pricing adjustments or changes in the product mix.
Despite Tesla’s higher revenue per car, the downward trend in its profit per vehicle suggests potential challenges in maintaining profitability. On the other hand, Ford’s consistent improvement in profit per vehicle reflects its efforts to optimize costs and enhance operational efficiency.
Overall, while Tesla still outpaces Ford in terms of vehicle profit, the narrowing gap indicates that Ford is making strides in improving its profitability. Both companies continue to navigate the competitive automotive landscape, striving to balance revenue growth and cost management.
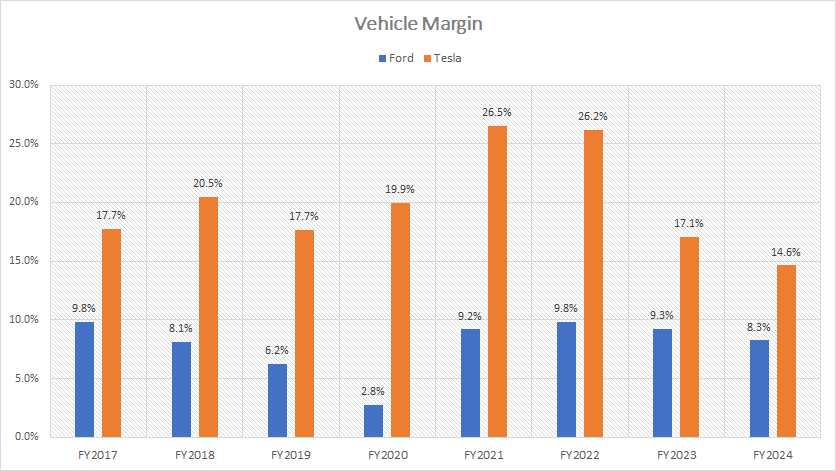
Vehicle Margin
ford-vs-tesla-in-vehicle-margin
(click image to expand)
The definition of vehicle margin is available here: vehicle margin. Vehicle margin for both companies is evaluated based on the automotive gross profit margin.
Tesla’s profitability per vehicle is significantly higher than Ford’s, as evidenced by the higher vehicle margins shown in the accompanying graph.
In fiscal year 2024, Tesla’s vehicle margin was 14.6%, nearly double Ford’s 8.3%. In fiscal year 2023, Tesla’s vehicle margin stood at 17.1%, compared to Ford’s 9.3%, marking a substantial difference between the two companies.
While Tesla has historically produced superior vehicle margins compared to Ford, its profitability has been on a downward trend. Tesla’s vehicle margins, once as high as 26%, have declined to approximately 15% in recent results. This decrease may be attributed to factors such as increased competition, rising production costs, and changes in market conditions.
On the flipped side, Ford’s vehicle margin has remained relatively stable, showing resilience over the years. Ford’s margin only saw a significant drop once over the past eight years, notably reaching a low of 3% in fiscal year 2020. However, Ford’s vehicle margin has since rebounded, demonstrating a remarkable recovery post-pandemic. As of fiscal year 2024, Ford’s vehicle margin stands at 8.3%.
Despite the downward trend in Tesla’s vehicle margin, the company continues to maintain a higher profitability per vehicle compared to Ford. This reflects Tesla’s strong brand positioning, technological innovation, and efficient production processes. On the other hand, Ford’s steady improvement in vehicle margins indicates its strategic efforts to optimize costs and enhance operational efficiency.
Essentially, while Tesla remains ahead in terms of vehicle margin, the narrowing gap between Tesla and Ford suggests that Ford is making significant strides in improving its profitability. Both companies continue to navigate the competitive automotive landscape, aiming to balance revenue growth and cost management.
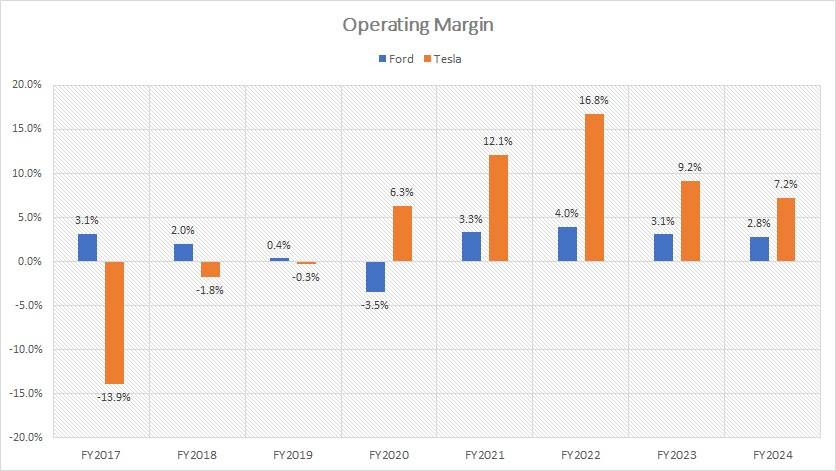
Operating Profit Margin
Ford vs Tesla in operating profit margin
(click image to enlarge)
The definition of operating margin is available here: operating margin.
From an operational perspective, Tesla operates much more efficiently than Ford Motor, as reflected by Tesla’s significantly higher operating margin shown in the chart above.
In fiscal year 2024, Tesla’s operating margin reached 7.2%, compared to Ford’s 2.8%. This means Tesla’s operating efficiency is more than twice that of Ford Motor.
On average, from fiscal year 2022 to 2024, Tesla’s operating margin was 11%, whereas Ford’s was just 3%, making Ford’s operating efficiency less than one-third of Tesla’s.
This substantial difference in operating margins underscores Tesla’s superior operational efficiency, which contributes to its higher profitability. Tesla’s ability to maintain higher margins indicates effective cost management, streamlined production processes, and a strong focus on innovation and technology.
Conversely, while Ford has made strides in improving its operational efficiency, it still lags behind Tesla. The lower operating margins suggest that Ford faces significantly higher operating expenses or less effective cost control measures, which impact its overall profitability.
Therefore, from an operational standpoint, Tesla is much more profitable than Ford Motor. This operational advantage allows Tesla to reinvest in research and development, expand its product offerings, and strengthen its market position in the electric vehicle industry.
Summary
In summary, Tesla continues to demonstrate superior operational efficiency and profitability compared to Ford. With higher vehicle margins and operating margins, Tesla is more adept at converting revenue into profit. Despite a decline in vehicle margins from its historical peak, Tesla still maintains a significant lead over Ford. This efficiency allows Tesla to reinvest in innovation, expand its product offerings, and strengthen its market position.
Ford, while lagging behind Tesla, has shown steady improvement in both vehicle and operating margins. The rebound in margins post-pandemic highlights Ford’s resilience and strategic efforts to optimize costs and enhance operational efficiency. Ford’s focus on increasing its revenue per vehicle has also contributed to its improved profitability.
References and Credits
1. All financial figures presented are obtained and referenced from Ford Motor and Tesla’s annual reports published on the respective investor relations pages:
i) Ford Earnings Releases, and
ii) Tesla SEC filings.
2. Flickr Images.
Disclosure
We may use the assistance of artificial intelligence (AI) tools to produce some of the text in this article. However, the data is directly obtained from original sources and meticulously cross-checked by our editors multiple times to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media. Additionally, providing a link back to this article from any website can help us create more content like this in the future.
Thank you for your support and engagement! Your involvement helps us continue to provide high-quality, reliable content.