
Research And Development. Source: Flickr Image
This article presents the research and development spending of social media companies such as Meta (NASDAQ: META), Twitter, Snapchat (NYSE: SNAP), and Pinterest (NYSE: PINS).
Apart from the R&D spending, we also look at several R&D-related ratios which include the R&D to revenue, R&D to costs and expenses, R&D to gross profit, and R&D attributed to share-based compensation.
Let’s take a look!
For other statistics related to social media companies, you may find more information on these pages:
- Margin comparison among Meta, Twitter, Snapchat, and Pinterest,
- Meta costs and expenses breakdown, and
- Average revenue comparison among Facebook, Twitter, Snapchat, and Pinterest.
Please use the table of contents to navigate this page.
Table Of Contents
Definitions And Overview
- Percentage Of R&D Attributed To Stock-Based Compensation (SBC) Expenses
- R&D To Revenue Ratio
- R&D To Gross Profit Ratio
- R&D To Total Costs And Expenses Ratio
- Non-Cash Expenses
O2. Who Is Winning The R&D Race? Meta, Twitter, Snap, Or Pinterest?
R&D Spending
A1. R&D Spending (Including Meta)
A2. R&D Spending (Excluding Meta)
Growth Rates
B1. Growth Rates Of R&D Spending
Ratios
C1. R&D Spending To Revenue Ratio
C2. R&D Spending To Costs And Expenses Ratio
C3. R&D Spending To Gross Profit Ratio
Stock-Based Compensation (SBC)
D1. Percentage Of R&D Spending Attributed To SBC Expenses
Conclusion And Reference
S1. Conclusion
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
Definitions Of Ratio
To help readers understand the content better, the following terms and glossaries have been provided.
Percentage Of R&D Attributed To Stock-Based Compensation (SBC) Expenses: The Percentage of R&D Attributed to Stock-Based Compensation (SBC) Expenses refers to the portion of a company’s total research and development (R&D) expenses that is accounted for by stock-based compensation provided to employees.
This includes stock options, shares, or other equity incentives awarded as part of the compensation package for employees involved in R&D activities.
It is typically expressed as a percentage and calculated using the formula:
\[\text{Percentage of R&D Attributed to SBC} = \left( \frac{\text{SBC Expense for R&D}}{\text{Total R&D Spending}} \right) \times 100\%\]
This metric helps stakeholders understand how much of the R&D budget is dedicated to compensating employees through equity rather than direct cash salaries.
R&D To Revenue Ratio: The R&D to revenue ratio is a financial metric measuring the proportion of a company’s revenue that is spent on research and development (R&D).
It is calculated by dividing the total R&D expenditures by the total revenue, usually expressed as a percentage. This ratio helps investors and analysts understand how much a company is investing in innovation and future growth relative to its sales.
The formula for the R&D to revenue ratio is:
\[\text{R&D to Revenue Ratio} = \left( \frac{\text{R&D Expenditures}}{\text{Total Revenue}} \right) \times 100\%\]
A higher R&D to revenue ratio indicates a stronger commitment to innovation and development, which can be crucial for long-term growth and competitiveness.
R&D To Gross Profit Ratio: The R&D to gross profit ratio is a financial metric measuring the proportion of a company’s gross profit that is spent on research and development (R&D).
This ratio helps investors and analysts evaluate how much of a company’s gross profit is being reinvested into innovation and future growth.
The formula for the R&D to gross profit ratio is:
\[\text{R&D to Gross Profit Ratio} = \left( \frac{\text{R&D Expenditures}}{\text{Gross Profit}} \right) \times 100\%\]
A higher R&D to gross profit ratio indicates a greater investment in innovation relative to the company’s profitability, which can be a sign of a commitment to long-term growth and competitiveness.
R&D To Total Costs And Expenses Ratio: The R&D to Total Costs and Expenses Ratio measures the proportion of a company’s costs of revenue and operating expenses that is attributed to research and development (R&D) activities.
This ratio provides insights into how much of the company’s resources are dedicated to innovation and developing new products or services.
It is typically calculated using the following formula:
\[\text{R&D to Total Costs and Expenses Ratio} = \left( \frac{\text{R&D Spending}}{\text{Costs Of Revenue + Operating Expenses}} \right) \times 100\%\]
This ratio is useful for comparing the R&D intensity of different companies or assessing changes in a company’s R&D investment over time.
Non-Cash Expenses: Non-cash expenses are costs that appear on a company’s income statement but do not involve an actual outflow of cash during the accounting period.
These expenses are accounting entries that reflect the allocation of certain costs over time or other adjustments that do not require immediate cash payment. Common examples of non-cash expenses include:
- Depreciation: The allocation of the cost of tangible assets, such as machinery or equipment, over their useful lives.
- Amortization: The allocation of the cost of intangible assets, such as patents or trademarks, over their useful lives.
- Stock-based compensation: The value of shares or stock options given to employees as part of their compensation package.
- Impairment losses: Write-downs of the value of assets when their market value falls below their book value.
- Deferred taxes: Tax expenses that are recognized on the income statement but will be paid in future periods.
These non-cash expenses impact a company’s reported profitability but do not affect its cash flow directly.
Who Is Winning The R&D Race?
When it comes to R&D spending, Meta is clearly leading the pack. Meta Platforms (formerly Facebook) spent a staggering $38 billion on R&D in the twelve months ending Dec 31, 2023. This is significantly higher than other social media companies like Twitter, Snapchat, and Pinterest.
Twitter has been ramping up its R&D spending as well, but it still lags behind Meta. Snapchat and Pinterest also invest in R&D, but their spending is much lower compared to Meta.
It seems like Meta is really pushing the boundaries with its investments in areas like the metaverse and artificial intelligence.
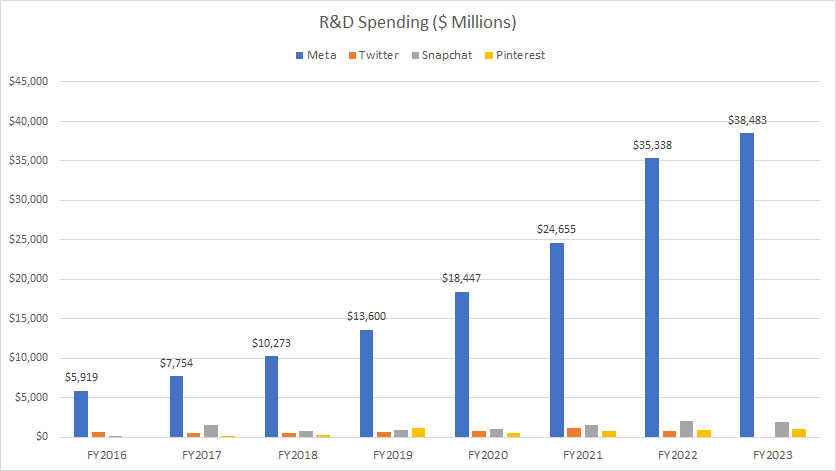
Research & Development Spending (Including Meta)
meta-twitter-snap-and-pinterest-research-and-development-spending
When we compare the R&D spending of all social media companies, Meta Platforms’ expenditure far exceeds that of its competitors, as illustrated in the chart above.
Other social media players, such as Twitter, Snap, and Pinterest, have R&D spending that pales in comparison to Meta. For instance, their R&D expenditures remain well below the $5 billion threshold.
In contrast, Meta’s R&D costs soared to a staggering $38.5 billion in fiscal year 2023, nearly 20 times higher than the nearest contender. Moreover, Meta’s research and development expenditures have been on the rise, growing 80% annually on average since fiscal year 2016.
In summary, Meta is deeply committed to R&D, investing substantial resources to maintain its competitive edge in the social media space.
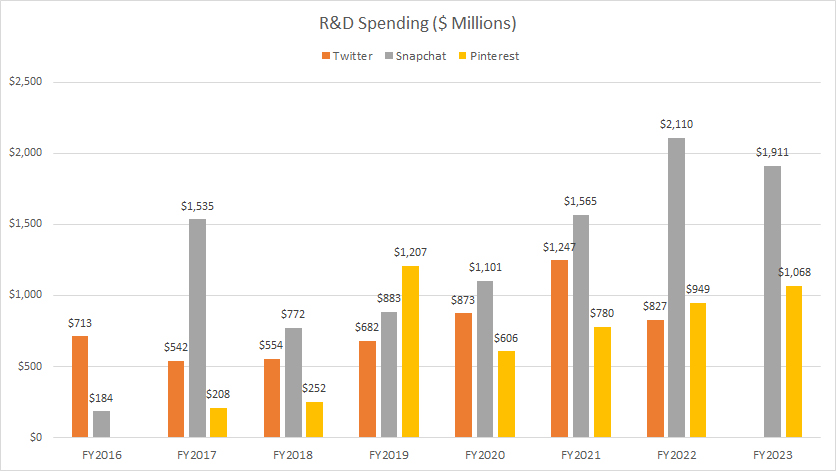
Research & Development Spending (Excluding Meta)
Twitter, Snap and Pinterest’s R&D spending
Without Meta included in the chart, we get a clearer picture of the R&D spending of smaller social media players such as Twitter, Snapchat, and Pinterest. These companies have relatively comparable R&D expenditures in monetary terms.
Snap Inc.’s R&D spending has been on a roll, emerging as one of the fastest-growing companies, with R&D far exceeding that of other social media platforms. Snap’s R&D expenditures topped $1.9 billion as of the end of fiscal year 2023, significantly outpacing its peers.
On the other hand, Pinterest’s R&D spending reached $1.1 billion in fiscal year 2023, about 40% below Snap’s amount. Twitter’s R&D costs totaled $827 million for the six months ended June 30, 2022, as data was only available up to Q2 2022 after the company was taken private in Q3 2022. On an annual basis, this figure might reach $1.6 billion.
For Snapchat, its R&D spending has more than doubled since fiscal year 2019, while Pinterest’s figures have surged by over 80% since fiscal year 2020.
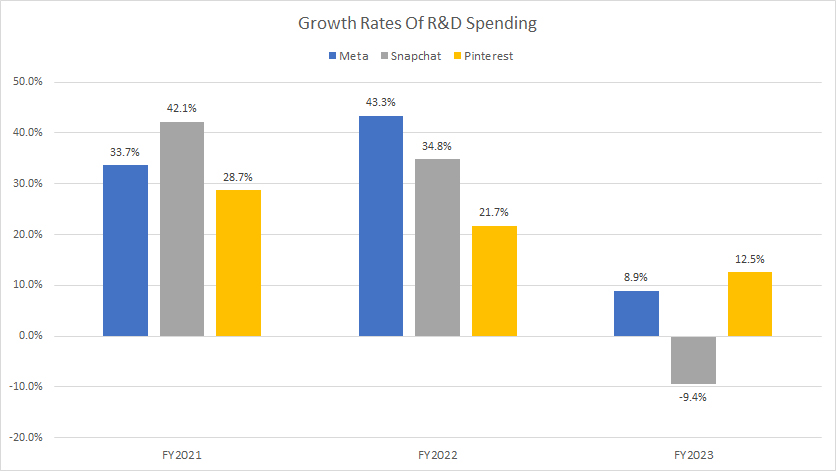
YoY Growth Rates Of R&D Spending
R&D spending growth rates
As the chart above illustrates, the year-over-year (YoY) growth rates of R&D spending for Meta, Snapchat, and Pinterest have significantly slowed over the last three years. In fiscal year 2023, the growth rate was the lowest compared to previous years.
In fiscal year 2023, Snapchat’s R&D spending declined compared to the previous year. Meta’s R&D spending growth slowed to single digits, at just 9%. Meanwhile, Pinterest’s R&D spending increased by only 12.5% in fiscal year 2023, marking the lowest growth rate recorded over the last three years.
On average, Meta’s R&D spending growth has amounted to 29% annually between fiscal years 2021 and 2023, the highest among Snap and Pinterest. Snapchat posted an average annual growth rate of 22.5% for its R&D expenses, while Pinterest came in at 21%, the lowest among the three social media players.
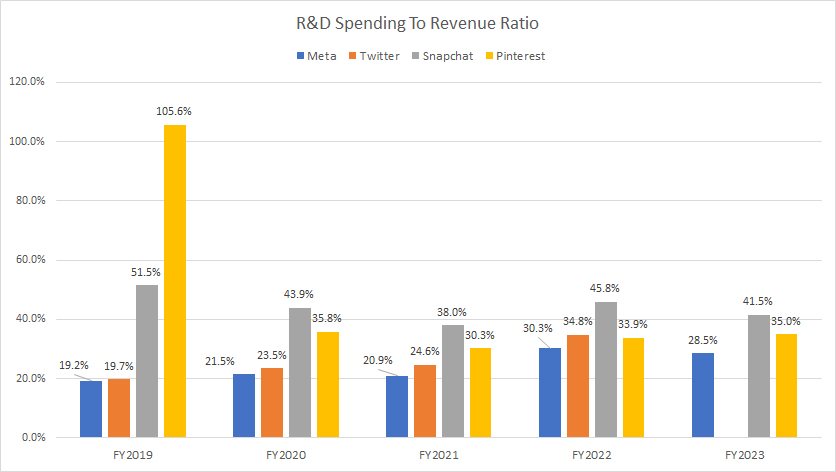
Research & Development Spending To Revenue Ratio
R&D spending to revenue ratio
You can find the definition of the R&D to revenue ratio here: R&D To Revenue Ratio.
Meta (formerly Facebook) has consistently recorded the lowest R&D-to-revenue ratio among social media players, as shown in the graph above. Over the past five years, Meta’s average R&D-to-revenue ratio has been 24%, significantly lower than Snapchat’s average of 44% and Pinterest’s average of 48%.
Meanwhile, Twitter’s R&D-to-revenue ratio averaged 22% between fiscal years 2017 and 2021, which is also significantly lower compared to Snap Inc. and Pinterest.
In fiscal year 2023, Snapchat’s R&D-to-revenue ratio declined to 41.5% from 46% the previous year. Meanwhile, Pinterest’s R&D-to-revenue ratio increased to 35% from 34% the previous year.
Meta’s R&D to revenue ratio is lower than Snap and Pinterest primarily because Meta has a much larger revenue base. Meta’s revenue is significantly higher compared to Snap and Pinterest, which means that even though Meta spends a substantial amount on R&D, the ratio appears lower when compared to the smaller revenue bases of Snap and Pinterest.
To put it into perspective, Meta’s revenue was $135 billion in fiscal year 2023. On the contrary, Snap and Pinterest generated only $4.6 billion and $3.1 billion in revenue, respectively, during the same period.
This doesn’t necessarily mean Meta is investing less in R&D in absolute terms; it just means the ratio is lower due to the larger revenue base.
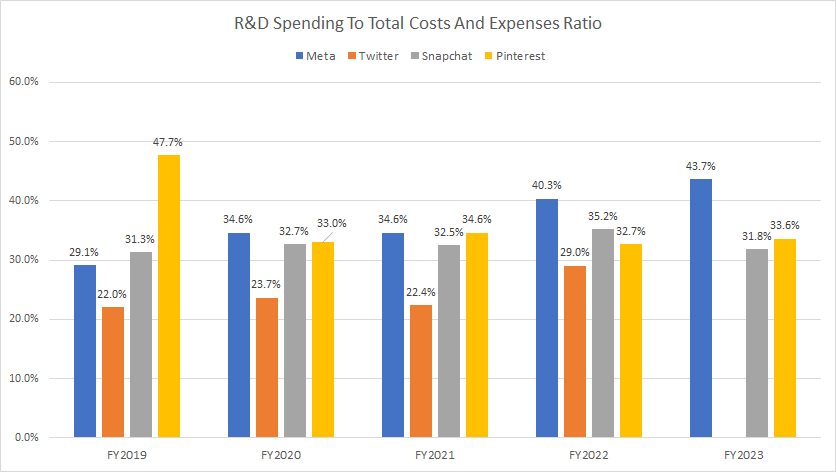
Research & Development Spending To Total Costs And Expenses Ratio
R&D spending to costs and expenses ratio
You can find the definition of the R&D to costs and expenses ratio here: R&D To Costs And Expenses Ratio.
R&D spending is an integral part of a company’s costs and expenses of doing business. Therefore, it’s valuable to determine how much of these costs and expenses are allocated to R&D activities.
The ratio of R&D spending to total costs and expenses measures the percentage of a company’s total costs that goes into research and development. Essentially, this ratio indicates how optimized a company’s costs and expenses are for R&D. A higher ratio signifies more optimized costs and expenses for R&D as a greater portion is being channeled into these activities.
According to the chart above, it’s interesting to see that Meta actually has the highest ratio of R&D spending to total costs and expenses among all social media companies, despite having the lowest R&D spending to revenue ratio.
For example, Meta’s ratio of R&D spending to total costs and expenses have averaged 37% between fiscal year 2017 and 2023, the highest compared to Twitter, Snap, and Pinterest. The ratio reached a record level of 44% as of fiscal year 2023, also significantly above the level of Snap Inc. and Pinterest.
Additionally, Meta’s ratio of R&D to costs and expenses has significantly increased since fiscal year 2019, rising from 29% to 44% over five years. This trend highlights the company’s efforts to optimize its research and development activities.
Snap Inc. and Pinterest allocate nearly the same portion of their costs and expenses to R&D, with Pinterest’s spending being slightly higher.
For example, Snapchat’s R&D-to-total-costs-and-expenses ratio has averaged 33% since fiscal year 2019, while Pinterest’s ratio has amounted to 36% over the same period. Meanwhile, Twitter invested the least amount of costs and expenses in R&D, averaging only 22% between fiscal year 2017 and 2021.
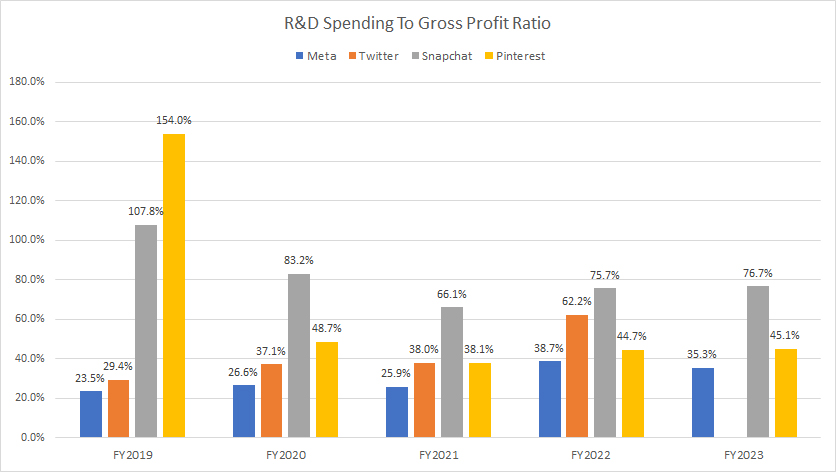
Research & Development Spending To Gross Profit Ratio
R&D spending to gross profit ratio
You can find the definition of the R&D to gross profit ratio here: R&D To Gross Profit Ratio.
Meta’s research and development expenditures account for a significantly lower portion of its gross profit compared to other social media players such as Twitter, Snapchat, and Pinterest, as illustrated in the chart above.
On average, Meta’s ratio of R&D to gross profit was only 30% over the past five years, compared to Snapchat’s average ratio of 73% and Pinterest’s average ratio of 43% over the past three years. Excluding the 2022 result, Twitter’s average ratio was 33% between fiscal years 2019 and 2021.
In fiscal year 2023, Snapchat’s research and development expenses accounted for nearly 77% of its gross profit, while Pinterest’s expenditure took up 45%. In contrast, Meta’s R&D spending made up just 35% of its gross profit in the same fiscal year, the lowest ratio among all compared social media players.
A major factor contributing to Meta’s lower ratio of R&D to gross profit is the company’s vast revenue and gross profit base. To put it into perspective, Meta’s gross profit was $109 billion in fiscal year 2023. In contrast, Snap and Pinterest generated gross profits of only $2.9 billion and $2.4 billion, respectively, during the same period.
Meta’s vast revenue and gross profit base has allowed it to maintain substantial R&D spending while keeping the ratio comparatively lower. This demonstrates Meta’s strong financial position, enabling it to invest heavily in innovation without heavily impacting its profitability ratios.
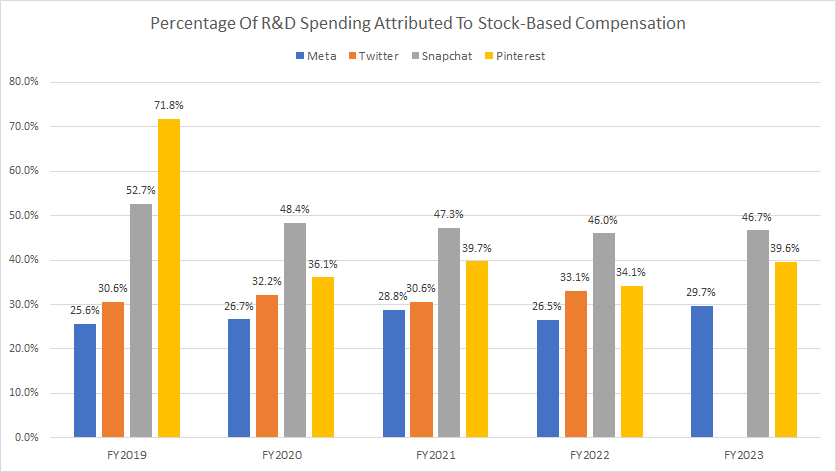
Percentage Of R&D Spending Attributed To SBC Expenses
sbc-to-research-and-development-spending-ratio
(click image to expand)
You can find the definition of the percentage of R&D attributed to SBC expenses here: percentage of R&D attributed to stock-based compensation (SBC) expenses.
It’s a common practice for tech companies like Facebook, Twitter, Snap, and Pinterest to reward their employees with company stocks. Therefore, it’s worthwhile to explore the percentage of R&D spending that comes from stock-based compensation.
As shown in the chart above, Snap Inc. leads the pack with 48% of its R&D expenditures paid by stock-based compensation on average over the past five years, the highest ratio among all companies compared. In fiscal year 2023, around 47% of Snap Inc.’s R&D spending was expensed through stock-based compensation.
On the other hand, only about 27.5% of Meta’s R&D expenditure came from stock-based compensation, the lowest ratio among Snap, Pinterest, and Twitter. In fiscal year 2023, Meta’s ratio increased slightly to 30% from 26.5% the previous year.
Pinterest’s R&D expenditures attributed to SBC were at 44% on average over the last five years, also a much higher ratio than Meta’s and Twitter’s. In fiscal year 2023, Pinterest’s SBC to R&D ratio was 40%.
While some of these tech giants have been less inclined to use stock-based compensation as a form of reward for employees, the percentage remains very high for most companies. Stock-based compensation is a non-cash expense and will only dilute the shares outstanding after they are vested to employees. Therefore, the company that awards the most stocks to employees as part of its R&D cost will see its shares outstanding increase the most.
However, the advantages of using stock-based compensation (SBC) to expense R&D spending likely outweigh the disadvantages. For instance, SBC incentivizes performance by aligning employees’ interests with the company’s success. Employees are motivated to perform better as their compensation is directly tied to the company’s stock performance.
Moreover, SBC attracts talent. Offering stock options and equity incentives helps attract top talent, especially in a competitive industry like technology. Talented individuals are often drawn to companies that offer potential for significant financial rewards through stock ownership.
Besides, SBC saves cash for cash-strapped companies like Twitter, Snap, and Pinterest. In this regard, SBC is a non-cash expense, which helps manage cash flow and conserve cash for other critical operations. This can be particularly beneficial for companies that are rapidly growing and need to reinvest their cash into R&D and other areas.
In short, these reasons make stock-based compensation an attractive option for tech giants like Meta, Twitter, Snapchat, and Pinterest looking to drive innovation and growth while managing costs effectively.
Conclusion
Meta’s R&D spending, while substantial, accounts for a smaller portion of its revenue and gross profit due to its vast revenue and gross profit base. In contrast, Twitter, Snap Inc., and Pinterest dedicate a larger share of their revenue and gross profits to R&D.
Relative to costs and expenses, Meta leads the pack when it comes to allocating resources to research and development. In this regard, a significant portion of Meta’s costs and expenses is dedicated to R&D compared to Twitter, Snap, and Pinterest.
Twitter, Snap Inc., and Pinterest have also shown significant R&D investments, with Snap and Pinterest’s stock-based compensation expenses averaging the highest ratios. This approach helps conserve cash and incentivize employees.
References and Credits
1. All financial figures presented in this article were obtained from and referenced in the annual reports available on the respective companies’ investor relations pages:
a) Facebook Investor Relations
b) Pinterest Investor Relations
c) Twitter Investor Relations
d) Snap Investor Relations
2. Flickr Images.
Disclosure
References and examples such as tables, charts, and diagrams are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant the total correctness of all content.
The content in this article is for informational purposes only and is neither a recommendation nor a piece of financial advice to purchase a stock.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media and providing a link to it from any website so that more articles like this can be created.
Thank you!

Very good analysis
Thanks, I will share this web link to our invest study group.
you are so good.
Nurofusion BE user. MASKUN