A GM Cadillac Eldorado Brougham 1957. Flickr Image.
It’s interesting to see how Tesla’s (NASDAQ: TSLA) automotive business performs when compared with its bigger rival, General Motors (NYSE: GM). For your information, Tesla is relatively new to the automotive industry and is an all-electric vehicle player.
On the other hand, General Motors (GM) has already been in the trade for several decades and has only recently jumped on the electric vehicle bandwagon.
With both companies getting more ambitious in the electric vehicle space, it would be interesting to see how each measures up to one another in revenue and margins.
While both companies operate in the same industry, they have different approaches regarding how their products are distributed. In this aspect, Tesla adopts a retail-based business model, whereas GM’s business model is wholesale-based.
Theoretically, I would expect Tesla’s margin to be worse than that of GM, considering the extra expenses and costs required to operate its retail stores.
In this article, we compare Tesla and GM’s revenue and gross margins to see how the results stack up.
Let’s take a look!
Please use the table of contents to navigate this page.
Table Of Contents
Definitions And Overview
Overview
Segment Adjustment
B1. GM Financial
B2. Tesla Energy and Leasing Revenue
B3. Tesla Regulatory Credits
B4. Tesla Services Revenue
B5. Research & Development
Automotive Revenue Comparison
Gross Margin Comparison
Summary And Reference
S1. Summary
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
Definitions
To help readers understand the content better, the following terms and glossaries have been provided.
Automotive Revenue: Automotive revenue refers to the total income generated by companies involved in the automotive industry.
Automotive revenue can include sales from vehicles, parts, and accessories and income from services like maintenance and repairs.
Revenue can come from various segments, including manufacturing, wholesale, and retail sales. Overall, it reflects the financial performance of businesses in the automotive sector.
Gross Margin: Gross margin is a financial metric representing the difference between revenue and the cost of goods sold (COGS).
It is often expressed as a percentage of revenue and indicates how efficiently a company produces and sells its products.
A higher gross margin generally suggests that a company retains a larger portion of revenue after accounting for the direct costs of making its goods.
This metric is essential for assessing a company’s profitability and operational efficiency.
Apple-To-Apple Comparison
This article compares only the automotive sector of Tesla and GM. The definition of the automotive revenue is available here: automotive revenue.
Although Tesla and GM are both automobile companies, they have non-automotive businesses that contribute significantly to sales and revenues.
For example, Tesla gets a significant portion of sales in the energy sector.
On the other hand, General Motors derives a significant portion of its revenue not just from the automotive segment but also from its financial segment.
Therefore, we must make some adjustments for a similar comparison when measuring the automotive revenue and gross margin.
These adjustments include the exclusion of non-automotive portions.
GM Financial
For General Motors, GM Financial is the company’s captive finance arm.
The subsidiary provides loans and credit facilities to retail and commercial customers.
As a result, GM Financial derives most of its revenue from finance income and has no activities related to automobile manufacturing.
For this reason, the portion of revenue from GM Financial is excluded during the measurement of GM’s automotive revenue and gross margin.
Tesla Energy and Leasing Revenue
Similarly, Tesla’s energy is a business subsidiary that is unrelated to automobile manufacturing.
Aside from the energy sector, Tesla’s automotive leasing revenue is another revenue segment that needs to be adjusted so that the automotive revenue is in line with that of General Motors.
For your information, GM’s automotive leasing revenue is recognized as a type of finance income that belongs to GM Financial.
Therefore, Tesla’s energy and leasing revenue is stripped off during the measurement of the automotive revenue and gross margin to perform an apple-to-apple comparison.
Tesla Regulatory Credits
The same goes for Tesla’s automotive regulatory credits revenue, which needs to be adjusted as well.
As of fiscal 2023, General Motors has not broken down any sales from regulatory credits.
In this aspect, I assume that GM did not produce sufficient zero-emission vehicles to offset the emissions from fossil-fuel vehicles.
Therefore, I have excluded Tesla’s regulatory credits revenue for a similar comparison while measuring the automotive revenue and gross margin.
Tesla Services Revenue
GM wraps its services revenue under the automotive sector.
Therefore, to be in line with General Motors, I am also including Tesla’s services revenue as part of its automotive revenue.
For this reason, I am adding Tesla’s services revenue during the revenue and gross margin measurement for an apple-to-apple comparison.
Research and Development Costs
Similarly, GM put research and development expenses under the automotive segment, which is part of the gross margin measurement.
However, for Tesla, its R&D costs fall under the operating expenses which are outside of the gross margin measurement.
For a similar comparison, I need to add Tesla’s R&D costs into the automotive revenue to derive a gross margin identical to that of GM.
The problem for Tesla is that not all research and development expenses were spent in the automotive sector.
Some of Tesla’s R&D expenses may have been spent on the energy sector.
As such, I am adding a certain portion of Tesla’s R&D costs as part of the gross margin measurement.
This ratio is around 80%, consistent with the automotive revenue to total revenue ratio.
Automotive Revenue
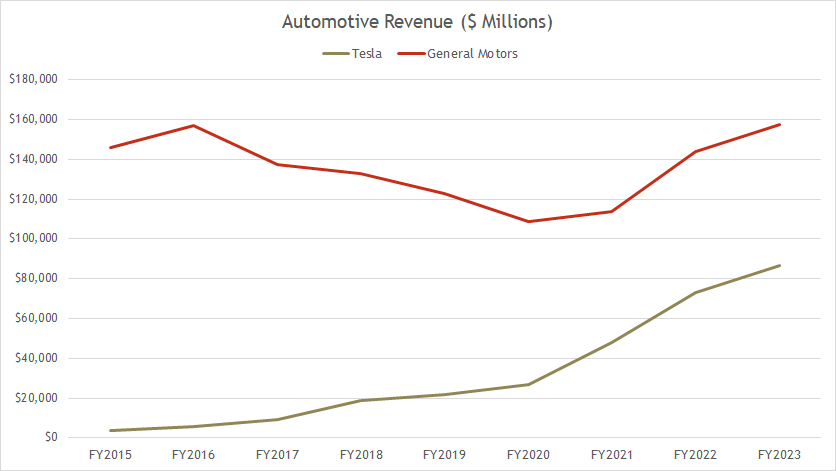
Automotive revenue comparison: Tesla vs GM
(click image to expand)
The above graph shows the comparison between Tesla’s adjusted automotive revenue and GM’s automotive revenue from fiscal 2015 to 2023 on a yearly basis. The definition of the automotive revenue is available here: automotive revenue.
As mentioned, Tesla’s automotive revenue has been adjusted to include and exclude a couple of items to be in line with that of General Motors.
That said, the chart above clearly shows that GM’s automotive revenue is much higher than Tesla’s.
As of fiscal year 2023, GM’s automotive revenue came in at nearly $160 billion versus Tesla’s $80 billion in the same period. As such, GM’s automotive revenue is about 2X higher than Tesla’s result.
While the gap was big in 2023, it was much bigger five years ago, reportedly at a 35X difference. In just five years, Tesla has nearly closed the gap with GM, illustrating the remarkable growth that Tesla has achieved in the automotive sector.
In contrast, GM’s automotive revenue has remained stagnant for so many year and has only been able to grow in recent periods.
Automotive Gross Margin
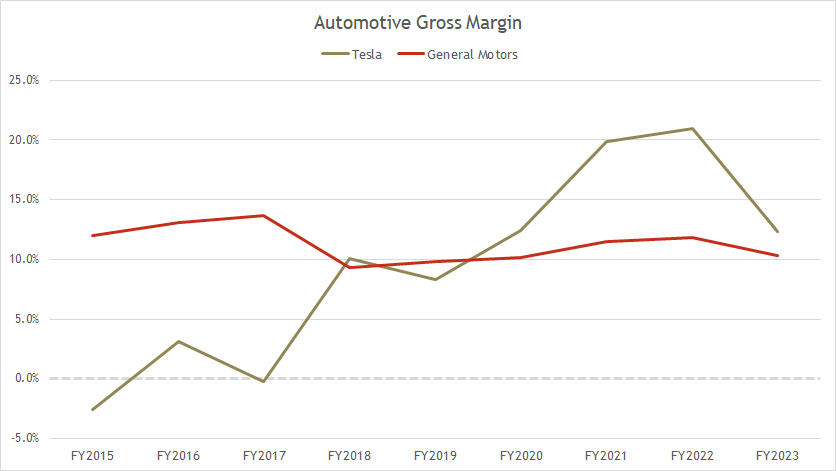
Automotive gross margin comparison: Tesla vs GM
(click image to expand)
As discussed in prior paragraphs, Tesla’s automotive gross margin is adjusted to include and exclude several items to align with GM’s results for an apple-to-apple comparison. The definition of the gross margin is available here: gross margin.
While the plots are zig-zagging in the chart, we can see that Tesla’s automotive gross margin has closely trailed General Motors’ gross margin.
During the post-pandemic periods which was after 2021, Tesla’s automotive gross margin significantly exceeded GM’s. Tesla’s automotive gross margin surpassed 20% consecutively in 2021 and 2022. However, Tesla’s automotive gross margin contracted in 2023.
As of 2023, Tesla’s automotive gross margin was around 12% versus GM’s result of 10%.
In most fiscal years, GM’s automotive gross margin has remained relatively stable, while Tesla’s results have been increasing. However, Tesla’s result dived significatly in 2023, primarily driven by rising cost and lower sales.
Conclusion
On an adjusted basis, Tesla’s automotive gross margin was slightly better than GM’s despite having a far smaller revenue than GM’s.
However, Tesla still has much work to do, considering that its automotive gross margin has significantly slumped in recent years.
Although Tesla operates a retail-based model instead of a wholesale-based model adopted by GM, Tesla can achieve a gross margin exceeding that of General Motors.
References and Credits
1. All financial figures presented were obtained and referenced from Tesla Investor Relations and GM Earning Releases.
2. Featured image was used under Creative Common Licenses and obtained from pcfishhk and Richard Wadd.
Disclosure
References and examples such as tables, charts, and diagrams are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant the total correctness of all content.
The content in this article is for informational purposes only and is neither a recommendation nor a piece of financial advice to purchase a stock.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media and provide a link to this article from any website so that more articles like this can be created.
Thank you!