Tesla supercharger stations at Southlake, Texas. Source: Flickr
To support the world’s transition from fossil fuels to clean energy, Tesla (NASDAQ: TSLA) has established a global network of infrastructure that is crucial to its operations and success.
This extensive network includes a variety of buildings and vehicles, such as supercharger stations, mobile service vehicles, and numerous stores and service locations that tirelessly serve Tesla’s mission.
These infrastructure assets are some of Tesla’s most valuable assets, playing a pivotal role in generating revenue and setting Tesla apart from its competitors.
Beyond their monetary value, these assets provide Tesla with significant competitive advantages by creating substantial barriers to entry for other companies.
Establishing such a network requires years of effort and a vast amount of resources, making it difficult for others to replicate.
Let’s take a look! You may find related statistic of Tesla on these pages:
- Tesla energy profit and margin,
- Tesla energy solar and storage deployments, and
- Will Tesla go out of business.
Please use the table of contents to navigate this page.
Table Of Contents
Definitions And Overview
O2. Are Tesla’s Superchargers free to use?
Network Of Infrastructure
A1. Supercharger Stations
A2. Mobile Service Fleet
A3. Stores and Service Locations
Growth Rates
B1. YoY Growth Rates Of Infrastructures
Summary And Reference
S1. Investor Takeaway
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
Definitions
To help readers understand the content better, the following terms and glossaries have been provided.
Superchargers: Tesla’s Superchargers are a network of high-speed charging stations designed to charge Tesla electric vehicles quickly. They are strategically located along popular highways and city centers, making long-distance travel more convenient and accessible for Tesla owners.
The Superchargers can deliver up to 170 miles of range in just 30 minutes of charging time, allowing drivers to quickly and easily recharge their vehicles while on the go. The stations are powered by renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, making them a more sustainable transportation option.
Mobile Service Fleet: Tesla’s mobile service fleet consists of technicians who travel to Tesla owners’ homes or workplaces to perform vehicle maintenance and repairs.
The service fleet is equipped with all the necessary tools and parts to address common issues and perform routine maintenance, such as tyre rotations or brake replacements. This service is designed to make it more convenient for Tesla owners to maintain their vehicles without taking them to a service center.
Stores And Service Locations: Tesla’s stores and service locations are physical locations where customers can purchase Tesla vehicles, receive information about Tesla products, and get support for their Tesla vehicles after purchase.
These locations are typically found in high-traffic areas, such as shopping malls or city centers, and are designed to provide customers with a unique and engaging experience. Tesla’s stores and service locations also offer maintenance and repair services for Tesla vehicles, test drives and product demonstrations.
The company aims to create a seamless and enjoyable customer experience at every stage of the vehicle ownership process, from purchase to maintenance and beyond.
Are Tesla’s Superchargers free to use?
No, Tesla’s Superchargers are not free. While some early Tesla models had unlimited free Supercharging, most new Tesla vehicles are now sold with a Supercharging fee.
The cost of Supercharging varies by location and electricity rates and can be viewed on the vehicle’s touchscreen or in the Tesla mobile app. However, Tesla occasionally offers free Supercharging as a promotion to incentivize purchases or to reward existing Tesla owners.
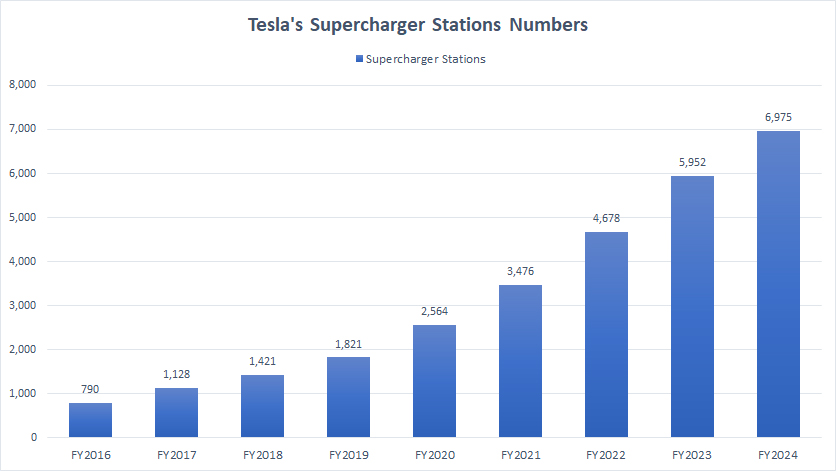
Supercharger Stations
Tesla’s supercharger stations
(click image to enlarge)
Average YoY Growth Rate From 2022 To 2024 => 26%
The definition of Tesla’s supercharger stations is available here: Superchargers.
Tesla has built a comprehensive network of charging infrastructure known as Supercharger stations to dispel the perception that electric vehicles are limited by travel distance.
These Supercharger stations are designed to provide fast charging, enabling long-distance travel and encouraging the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Tesla’s Supercharger stations are equipped with industrial-grade high-speed chargers, specifically designed to recharge a Tesla electric vehicle significantly faster than other charging options.
Tesla’s Supercharger stations have dramatically increased since 2016. Over the past nine years, Tesla has more than quadrupled the number of Supercharger stations worldwide, growing from 790 stations in 2016 to nearly 7,000 stations by the end of fiscal year 2024, as shown in the accompanying chart.
Tesla’s consistent expansion underscores the importance of a robust Supercharging infrastructure for the broad adoption of electric vehicles. Expanding this unique asset requires significant upfront capital outlay.
The growth of Tesla’s Supercharger stations was particularly impressive in recent years. In 2024 alone, Tesla added more than 1,000 Supercharger stations.
Similarly, the number soared by 1,200 units in fiscal year 2023, marking the two best years of growth for the company’s Supercharger network. The continuous expansion of Tesla’s Supercharging infrastructure indicates healthy business prospects.
In summary, Tesla’s strategic investment in its Supercharging infrastructure plays a crucial role in encouraging the broad adoption of electric vehicles, providing a seamless and convenient charging experience, and securing a competitive edge in the market.
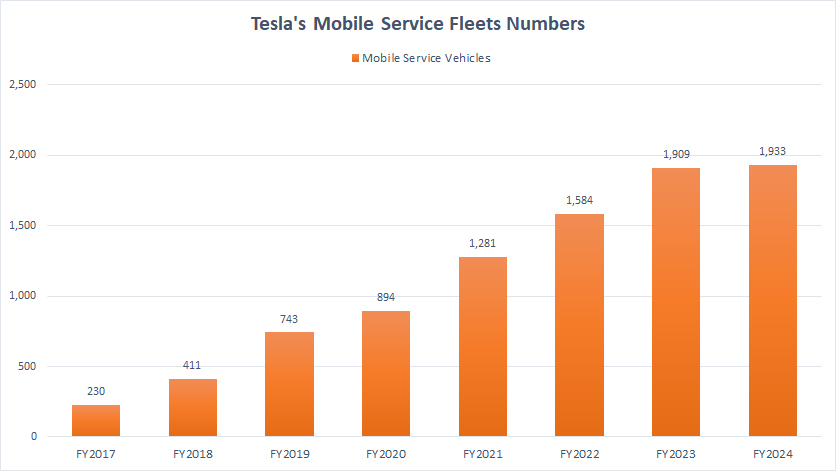
Mobile Service Fleet
Tesla’s mobile service fleet numbers
(click image to enlarge)
Average YoY Growth Rate From 2022 To 2024 => 15%
The definition of Tesla’s mobile service fleet is available here: mobile service fleet.
Tesla launched the mobile service fleet to provide the best car ownership experience for its customers. The biggest advantage of this fleet is that Tesla’s customers no longer need to visit service centers for vehicle maintenance.
In North America alone, the mobile service fleet completes a substantial number of service jobs, allowing customers to have their cars serviced without leaving their homes or offices.
Tesla claims that this service has achieved excellent customer satisfaction due to its convenience and lower costs compared to traditional service centers.
Tesla plans to continue increasing its service capacity, especially during the ramp-up period of the Model 3 and Model Y.
The chart above illustrates that Tesla’s mobile service fleet has grown tremendously, from only 230 vehicles in fiscal year 2017 to over 1,900 vehicles by the end of fiscal year 2024. This represents an average growth rate of roughly 15% over the past three years.
The extensive number of Tesla’s mobile service vehicles indicates a high barrier of entry for other electric vehicle (EV) companies, granting Tesla a distinctive competitive advantage.
In fiscal year 2021 alone, Tesla added nearly 400 mobile service vehicles, marking a growth of over 40% from 2020. In fiscal year 2023, Tesla added approximately 325 mobile service vehicles, a 20% increase from the previous year. By the end of fiscal year 2024, Tesla gained an additional 23 vehicles.
This continuous expansion demonstrates Tesla’s improving business prospects and commitment to enhancing customer experience. The convenience and efficiency of the mobile service fleet not only improve customer satisfaction but also reduce the operational strain on physical service centers.
In summary, Tesla’s strategic investment in its mobile service fleet underscores its commitment to providing exceptional customer service and maintaining a competitive edge in the EV market.
By eliminating the need for customers to visit service centers, Tesla offers unparalleled convenience and cost savings, contributing to the overall satisfaction and loyalty of its customers.
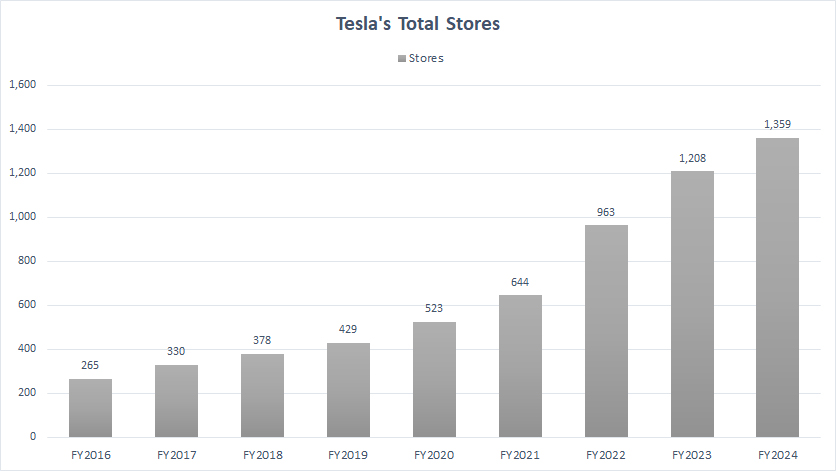
Stores and Service Locations
Tesla’s new stores and service locations numbers
(click image to enlarge)
Average YoY Growth Rate From 2022 To 2024 => 29%
The definition of Tesla’s stores and service locations is available here: stores and service locations.
Tesla strategically opens its stores and service locations in highly visible, premium outlets in major metropolitan markets. These stores are exclusively owned and operated by Tesla, with no involvement from third-party vendors.
This approach enables Tesla to maintain better control of inventory, manage warranty services and pricing, strengthen the Tesla brand, and gather faster customer feedback.
According to Tesla, opening new stores and service centers in new geographic areas boosts demand for its products. As a result, Tesla has rapidly increased its retail footprint by establishing more stores and service outlets.
These facilities are often combined with sales personnel in service centers, referred to as “Service Plus” locations. Despite the importance of opening new stores and service locations, the average year-over-year growth rate was only 29% between fiscal year 2022 and 2024.
In recent years, Tesla may have slowed down the opening of new stores and service locations as the services provided by these stores can overlap with those offered by the mobile service fleet.
Additionally, maintaining new stores and service locations requires significant working capital and resources. Tesla has been conservative in managing expenses and costs and has switched to online booking for most of its products.
As a result, Tesla’s new store and service location openings have remained relatively flat in recent years. However, Tesla still operates over 1,300 stores and service locations globally as of the end of fiscal year 2024.
In fiscal year 2024, Tesla grew its store and service locations by 12.5% year-over-year, which amounted to about 150 new store and service location openings.
While the growth in new store and service location openings has slowed, Tesla’s extensive network of over 1,300 locations continues to play a vital role in its business strategy.
The company’s focus on cost management and online booking further optimizes operational efficiency and resource allocation.
In summary, Tesla’s stores and service locations contribute significantly to its business model by driving demand, enhancing customer experience, and maintaining brand integrity.
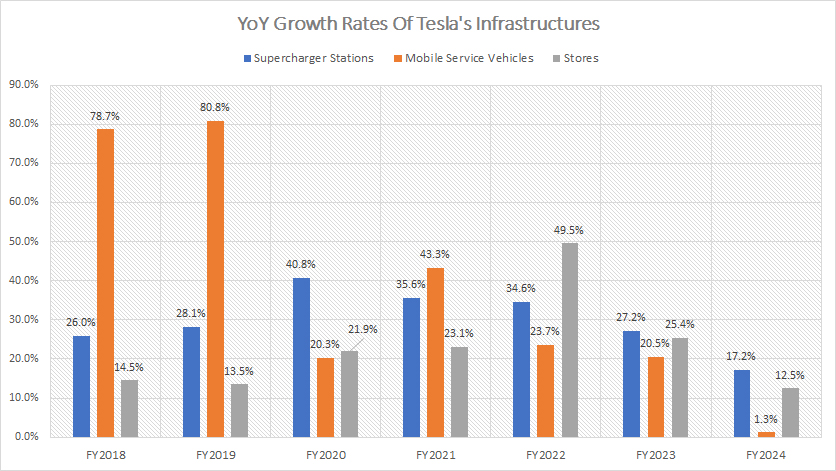
YoY Growth Rates Of Infrastructures
tesla-infrastructures-yoy-growth-rates
(click image to expand)
As depicted in the chart above, the growth of Tesla’s infrastructure, including its Supercharger stations, mobile service fleets, and new store openings, has significantly slowed in fiscal year 2024.
In fiscal year 2024, the number of Tesla’s Supercharger stations grew by only 17% year-over-year. This represents a slowdown compared to the more aggressive expansion rates seen in previous years.
Despite this deceleration, Tesla’s Supercharger network remains one of the largest and most advanced charging infrastructures globally, providing fast and convenient charging options for Tesla owners.
The growth of Tesla’s mobile service fleet has also decelerated. In fiscal year 2024, the mobile service fleet increased by only 1.3% over fiscal year 2023
While the growth rate has slowed, the mobile service fleet continues to play a crucial role in offering convenient and efficient service options for Tesla customers, allowing them to have their vehicles serviced without visiting a service center.
Tesla’s store locations saw a 12.5% year-over-year increase in fiscal year 2024. Although this growth rate is modest compared to previous years, Tesla’s retail and service network continues to expand strategically.
The company focuses on opening stores and service centers in high-visibility, premium outlets in major metropolitan markets. These locations enhance brand presence, provide comprehensive customer service, and drive demand for Tesla’s products.
Despite the recent slowdown in infrastructure growth, Tesla’s commitment to enhancing its Supercharger network, mobile service fleet, and store locations remains strong.
These assets are essential for supporting the broad adoption of electric vehicles and maintaining a competitive edge in the market. The strategic expansion of these infrastructures will continue to play a vital role in Tesla’s long-term business prospects.
Investor Takeaway
In conclusion, Tesla operates a vast and extensive network of Supercharger stations worldwide. This infrastructure allows Tesla drivers to travel long distances with convenient and fast charging options.
Alongside this, Tesla has significantly expanded its mobile service fleet, which provides on-the-go maintenance and repair services, ensuring customer convenience and satisfaction.
Tesla’s mobile service fleet is easier to maintain and requires less capital to operate compared to new store and service locations.
The mobile service fleet can cover a larger geographic area than fixed service centers, providing greater flexibility and cost savings for customers. As a result, the mobile service fleet likely offers a higher return on invested capital.
Given these advantages, Tesla has shifted some of its focus towards the mobile service fleet and online ordering, potentially closing some physical stores.
This strategic move allows Tesla to streamline operations and reduce costs while still providing excellent service to its customers.
Despite the shift towards mobile services, Tesla’s physical stores and service locations still hold significant value. They provide a premium shopping experience and serve as key touchpoints for customer engagement.
These locations help boost brand visibility and offer comprehensive support and services that enhance the overall Tesla ownership experience.
In summary, Tesla’s infrastructure, including Supercharger stations, mobile service fleets, stores, and service locations, is crucial for the company’s operations and growth.
While the mobile service fleet offers cost efficiency and flexibility, physical stores and service locations provide valuable customer engagement and support. Together, these assets form a robust foundation for Tesla’s continued success.
References and Credits
1. All data presented were obtained and referenced from Tesla’s update letters published on the company’s investor relations page: Tesla Press Releases.
2. Tesla supercharger detailed info: Tesla charging infrastructure.
3. Flickr Images.
Disclosure
We may utilize the assistance of artificial intelligence (AI) tools to produce some of the text in this article. However, the data is directly obtained from original sources and meticulously cross-checked by our editors multiple times to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media. Additionally, providing a link back to this article from any website can help us create more content like this in the future.
Thank you for your support and engagement! Your involvement helps us continue to provide high-quality, reliable content.