An electric vehicles charging bay. Pexels Image
This article provides an analysis of Tesla’s margins, examining various segments in detail. It covers consolidated results, the automotive segment, energy and services, as well as the margin per vehicle.
Let’s take a look!
Investors interested in other key statistics of Tesla may find more resources on these pages:
- Tesla vs GM: vehicle profit and margin analysis,
- Tesla revenue by country: U.S., China, Norway, Netherlands, etc., and
- Tesla inventory breakdown analysis.
Please use the table of contents to navigate this page.
Table Of Contents
Definitions And Overview
O2. How Does Tesla Improve Its Profit Margins?
Consolidated Results
A1. Profit Margins
Automotive Segment
B1. Gross Margin
Energy And Services Segment
C1. Gross Margin
Profit Margin Per Car
D1. Revenue And Profit Per Vehicle
D2. Gross Margin Per Vehicle
Conclusion And Reference
S1. Conclusion
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
Definitions
To help readers understand the content better, the following terms and glossaries have been provided.
Adjusted EBITDA: Adjusted EBITDA, which stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization, refers to a financial performance measure that adds back certain items to EBITDA to provide a more accurate picture of a company’s operational profitability and cash flow.
The adjustments made to EBITDA typically include non-recurring, irregular, or one-time expenses or incomes that are not considered part of the regular operating activities of a company. These adjustments can include items such as stock-based compensation, litigation expenses, restructuring costs, and gains or losses from asset sales.
By making these adjustments, Adjusted EBITDA aims to provide a clearer view of a company’s underlying operational performance and its ability to generate cash flow from its core business activities, excluding the effects of financing decisions, capital structure, and tax environment.
Management, investors, and analysts commonly use this metric to compare profitability among companies and industries, as it eliminates the effects of financing and accounting decisions.
Revenue Per Vehicle: Tesla revenue per vehicle is calculated as total automotive revenue (inclusive of sales and leasing, as well as regulatory credit revenue) divided by total vehicle deliveries.
In the case of profit per car, the automotive revenue is replaced by the automotive gross profit.
How Does Tesla Improve Its Profit Margins?
Tesla has pursued several strategies to boost its margins:
- Vertical Integration: Tesla controls much of its supply chain and manufacturing process. This includes producing many components in-house, such as batteries, and owning its sales and service centers. This control can lead to cost savings and efficiencies, reducing reliance on external suppliers and mitigating risks related to price fluctuations and supply chain disruptions.
- Innovations in Manufacturing: The company continuously seeks to innovate in the manufacturing process. For instance, Tesla has introduced large-scale casting machines, known as Giga Presses, to produce larger parts of a car in a single piece, reducing production steps and costs and increasing the structural integrity of its vehicles. Additionally, Tesla aims for highly automated production lines to improve efficiency and reduce labour costs.
- Economies of Scale: As Tesla’s production volume increases, the company benefits from economies of scale. The cost per unit of production decreases as fixed costs are spread over larger units. This is particularly significant in the battery production segment, where Tesla has been investing heavily in Gigafactories to scale up production and reduce the cost of batteries, a major component cost of EVs.
- Software and Services Revenue: Tesla is not just a car manufacturer; it also generates revenue through software and services. This includes its Full Self-Driving (FSD) package, over-the-air (OTA) software updates that improve vehicle performance or add new features, and energy products and services. The margins on software are significantly higher than those on hardware, contributing positively to Tesla’s overall margins.
- Direct Sales Model: Tesla uses a direct sales model, selling vehicles directly to consumers rather than through franchised dealerships. This model eliminates the dealership markup, potentially increasing Tesla’s margins. It also allows Tesla to control the customer experience and pricing more directly.
- Continuous Improvement and Cost Reduction: Tesla operates on a principle of continuous improvement (referred to as ‘Kaizen’ in manufacturing circles), where it constantly seeks ways to reduce costs and improve efficiency in all aspects of its business, from manufacturing to logistics to procurement.
By focusing on these strategies, Tesla aims to boost its margins while scaling its production and expanding its product lineup. This approach helps the company sustain its growth and supports its mission to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy.
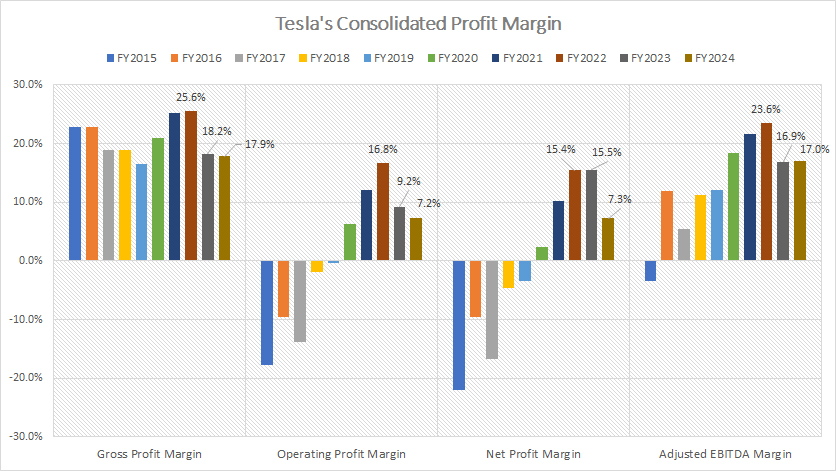
Consolidated Profit Margins
tesla-consolidateed-profit-margins
(click image to expand)
You may find more information about the adjusted EBITDA here: adjusted EBITDA.
From a consolidated profit margin perspective, Tesla has shown consistent profitability in most fiscal years. However, the company’s profitability has only emerged consistently in recent periods, particularly in terms of operating and net profit margins.
Between fiscal years 2022 and 2024, Tesla maintained an average gross profit margin of 21%. During the same timeframe, the company achieved an average operating profit margin of 11%, while its net profit margin averaged 13%.
Notably, Tesla’s adjusted EBITDA margin was considerably higher, averaging 19% over this period, highlighting the company’s ability to generate earnings before accounting for interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
A key observation is that Tesla’s profitability trajectory has been on a downward trend since 2022. This decline is significant, as it marks the period when Tesla reached its peak profit margins. The deteriorating margins may reflect increasing costs, competitive pressures, or other external factors impacting the business. Understanding these shifts is crucial for evaluating Tesla’s financial performance and future outlook.
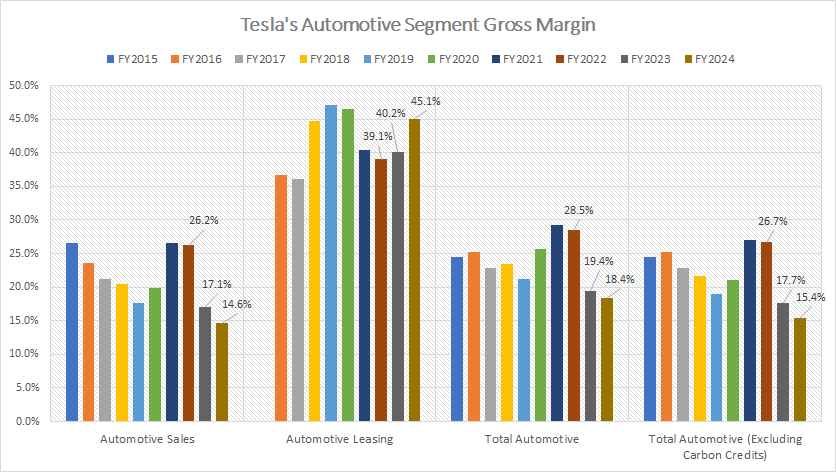
Automotive Segment Gross Margins
tesla-automotive-gross-margin
(click image to expand)
Tesla’s car sales and leasing revenue is available here: Tesla car sales revenue and leasing revenue.
Tesla has consistently delivered profitability within its automotive segment across most fiscal years. A notable standout is its leasing business, which has consistently achieved the highest profit margin within the segment, maintaining margins above 40%. This demonstrates the strong profitability of Tesla’s leasing operations.
In contrast, the gross margin for Tesla’s automotive sales was significantly lower, with the latest results showing a margin of just 15%. Over the period from fiscal year 2022 to 2024, Tesla’s automotive sales gross margin averaged 19%, while the leasing segment outperformed with an impressive average of 41% over the same timeframe.
When looking at the overall automotive segment, including revenue from automotive regulatory credits, Tesla achieved an average gross margin of 18%. However, it is important to highlight a significant downward trend since fiscal year 2022, when Tesla’s automotive segment gross margin peaked at 28.5%. This marked decline underscores a shift in profitability for the segment over recent years.
Excluding automotive regulatory credit revenue, Tesla’s gross margin within the automotive segment fell to 15%, roughly 3 percentage points lower than the margin achieved when regulatory credits are included. This distinction highlights the substantial impact of regulatory credits on Tesla’s overall profitability within the automotive segment.
The declining trend in gross margins may point to rising operational costs, competitive market dynamics, or shifts in pricing strategy, all of which warrant close examination for a comprehensive understanding of Tesla’s evolving financial landscape.
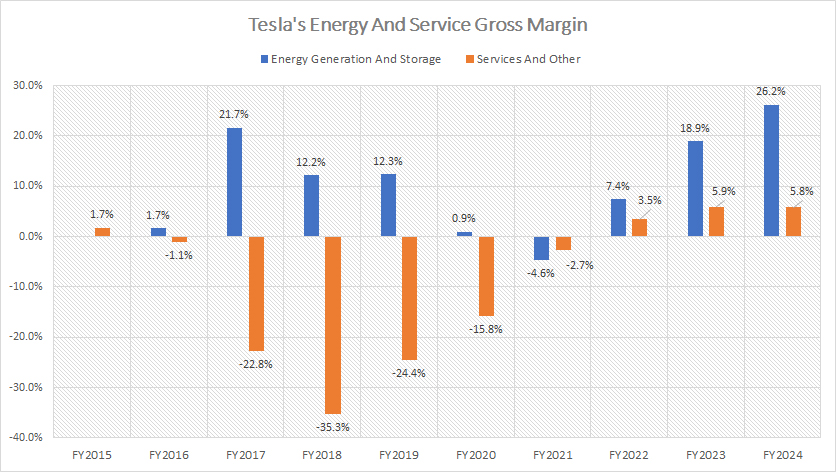
Energy And Services Gross Margin
tesla-energy-and-services-gross-margins
(click image to expand)
Tesla’s energy and services revenue is available here: Tesla energy generation and storage revenue and services revenue.
Tesla has recently turned its energy segment into a profitable venture, marking a notable shift in the company’s financial trajectory. Prior to fiscal year 2022, Tesla’s energy segment consistently operated at a loss, with its gross margin remaining in negative territory year after year. This pattern reflected the challenges of scaling the energy business and achieving cost efficiencies in a relatively nascent segment.
However, the turnaround has been remarkable. By fiscal year 2024, Tesla’s energy segment posted a record-breaking gross margin of 26%, the highest in the company’s history. This represents a significant improvement compared to the 19% gross margin recorded in 2023 and an even more modest 7% in 2022.
The consistent upward trajectory over these years underscores Tesla’s growing operational efficiency and market strength within the energy sector. Factors contributing to this growth likely include enhanced production processes, increased adoption of Tesla’s energy products such as Powerwalls and solar panels, and expanding economies of scale.
Similarly, Tesla’s services segment has shown a comparable shift toward profitability in recent periods. Before 2022, the services segment faced persistent losses, reflecting the challenges of managing operational costs in areas such as vehicle maintenance and charging infrastructure.
However, gross margins in the services segment have steadily risen, climbing from 3.5% in 2022 to nearly 6% in 2024. While this margin remains modest compared to other segments, the consistent improvement demonstrates Tesla’s ongoing efforts to optimize cost structures and enhance service delivery.
These shifts in profitability within the energy and services segments signal Tesla’s success in diversifying its revenue streams and fortifying its business model.
The company’s ability to turn previously loss-making divisions into profitable ones underscores its strategic focus on growth and operational excellence. Such achievements position Tesla as a multi-faceted player, extending its impact beyond automotive innovation into energy and service solutions.
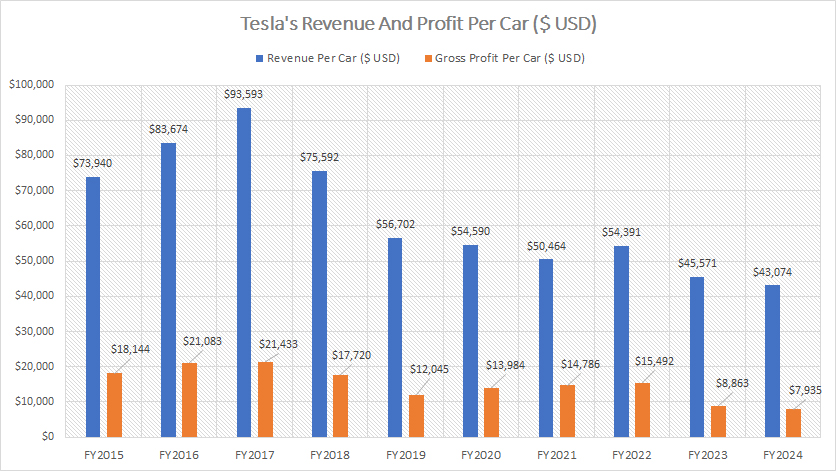
Revenue And Profit Per Vehicle
tesla-revenue-and-profit-per-vehicle
(click image to expand)
The formula for calculating Tesla’s revenue and profit per car is available here: revenue per vehicle.
As of fiscal year 2024, Tesla’s revenue per vehicle reached a new low of $43,000, marking a slight decline from the $45,600 recorded in the prior year. This figure represents a sharp and significant decrease compared to several years ago, when Tesla’s revenue per vehicle stood at over $70,000. Since 2018, Tesla’s revenue per car has fallen by more than 40%, reflecting a substantial shift in the company’s pricing strategy and product mix.
The primary driver of this decline is Tesla’s strategic focus on mass-market electric vehicles (EVs), particularly the introduction of the Model 3 and Model Y. These models are designed to make EVs more accessible and affordable for a broader consumer base, effectively lowering the average revenue per vehicle. While this move aligns with Tesla’s mission to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy, it has had a noticeable impact on its financial metrics.
As revenue per vehicle declines, Tesla’s profit per car has experienced a parallel downward trajectory. By 2024, Tesla’s gross profit per vehicle had reached $7,900, representing an 11% decrease from $8,900 in the prior year. This figure is a stark contrast to historical levels, where gross profit per car exceeded $20,000. The drop of more than 50% underscores the financial implications of Tesla’s push toward affordability and higher production volumes.
The decline in gross profit per car is, once again, tied to the shift toward mass-market models, which inherently come with lower price points and, consequently, slimmer profit margins. By prioritizing affordability, Tesla has successfully expanded its market reach but has faced trade-offs in terms of profitability on a per-unit basis. This dynamic highlights the ongoing balancing act between achieving scale and maintaining profitability — a challenge that Tesla navigates as it continues to lead the EV revolution.
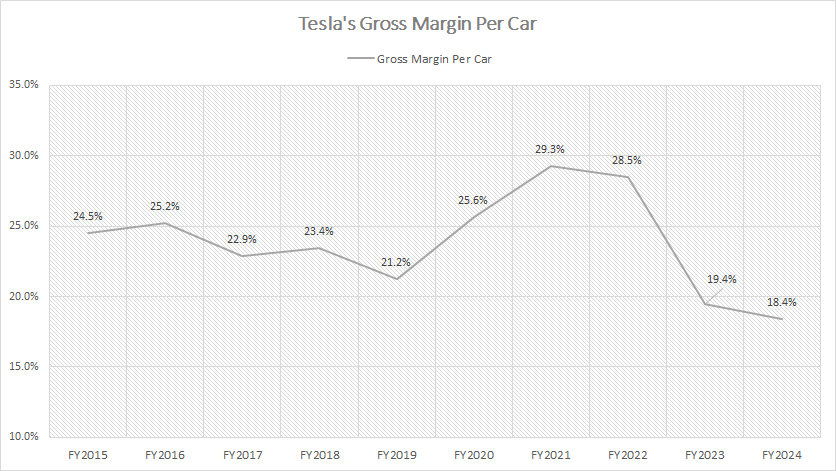
Gross Margin Per Vehicle
Tesla’s vehicle margin
(click image to expand)
Tesla’s vehicle margin shown in the chart above is evaluated based on the gross margin per car sold.
That said, Tesla’s vehicle gross margin stood at 18% as of fiscal year 2024, representing a slight decline from the 19% achieved in 2023. However, this figure marks a dramatic decrease compared to the 28.5% gross margin recorded in 2022 — a peak that underscores the earlier strength of Tesla’s vehicle profitability.
The erosion in vehicle gross margin is noteworthy and points to several underlying factors. First, the expansion of Tesla’s production capacity and the shift towards higher volumes of more affordable mass-market models, such as the Model 3 and Model Y, have played a pivotal role. These models, while essential for broadening Tesla’s customer base and solidifying its position as a market leader in electric vehicles (EVs), inherently come with lower margins compared to premium models like the Model S and Model X.
Additionally, the competitive landscape of the EV market has intensified in recent years. With more automakers entering the space and driving innovation, Tesla faces growing pressure to remain price-competitive while still delivering high-quality products. This competition has likely contributed to margin compression, as Tesla balances customer affordability with profitability goals.
Furthermore, rising raw material costs — particularly for essential components like lithium, cobalt, and nickel used in EV batteries — have likely weighed on Tesla’s margins. Global supply chain disruptions, inflationary pressures, and geopolitical uncertainties have compounded these challenges, making it increasingly difficult to maintain historically high profitability levels.
While this downward trend in margins may raise concerns, it also reflects Tesla’s commitment to making EVs more accessible to the masses, a cornerstone of its long-term mission to accelerate the adoption of sustainable energy.
Conclusion
In summary, Tesla’s ability to balance affordability, profitability, and diversification will be critical in determining its long-term financial success. While recent declines in key metrics like gross margins and profit per vehicle may concern investors, they also reflect Tesla’s broader commitment to scaling sustainable energy solutions globally — a strategy that could pay off significantly in the long run.
References and Credits
1. All financial figures presented were obtained and referenced from Tesla’s quarterly and annual reports published on the company’s investor relations page: Tesla Press Releases.
2. Pexels Images.
Disclosure
We may use the assistance of artificial intelligence (AI) tools to produce some of the text in this article. However, the data is directly obtained from original sources and meticulously cross-checked by our editors multiple times to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media. Additionally, providing a link back to this article from any website can help us create more content like this in the future.
Thank you for your support and engagement! Your involvement helps us continue to provide high-quality, reliable content.