Tesla vehicle. Pexels Image.
This article presents Tesla’s gross profit breakdown by segment. Apart from the consolidated gross profit breakdown, we also look at Tesla’s automotive gross profit breakdown.
Please note that the consolidated gross profit breakdown includes the profit from Tesla’s regulatory credits. On the other hand, the automotive gross profit breakdown excludes them.
Let’s move on!
For other key statistics of Tesla, you may find more resources on these pages:
Sales
Revenue
Energy
Profit Margin
- Profit margin breakdown: automotive, energy, and services,
- Gross profit and gross margin per car,
- Profit per employee,
R&D Comparison
Debt, Cash, and Liquidity
- Financial health: debt level, payment due, and liquidity,
- Cash flow and cash on hand analysis,
- Debt to equity, capital structure, and more,
- Liquidity check: current ratio, working capital, and quick ratio,
Comparison With Peers
- Marketing, advertising, and promotional spending,
- Tesla vs GM: profit margin comparison,
- Tesla vs Ford: vehicle profit and margin,
- Tesla vs BYD: profit margin comparison,
Other Statistics
- Interest expense and interest coverage ratio,
- Infrastructure expansion: supercharger stations, service fleets, and stores,
- Operating expenses breakdown analysis,
- Inventory breakdown analysis
Please use the table of contents to navigate this page.
Table Of Contents
Definitions And Overview
Consolidated Gross Profit Breakdown
A1. Automotive and Energy Gross Profit
A2. Automotive and Energy Gross Profit In Percentage
Automotive Gross Profit Breakdown
B1. Automotive Sales, Leasing, and Services Gross Profit
B2. Automotive Sales, Leasing, and Services Gross Profit In Percentage
Conclusion And Reference
S1. Insight
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
Definitions
To help readers understand the content better, the following terms and glossaries have been provided.
Regulatory Credits: Tesla’s regulatory credits are a form of government incentive designed to encourage the production of zero-emission vehicles (ZEVs).
Since Tesla exclusively manufactures electric vehicles, it earns these credits automatically and can sell them to other automakers that need them to comply with environmental regulations.
In the U.S., states like California require automakers to maintain a certain number of ZEV credits based on their total vehicle sales.
Companies that fall short must purchase credits from manufacturers with a surplus — like Tesla — allowing Tesla to generate revenue at a 100% profit margin.
Similar regulatory credit systems exist in China and the European Union, where Tesla also benefits from selling excess credits.
Tesla has historically relied on these credits to boost its profitability, though analysts debate whether this revenue stream is sustainable as more automakers transition to electric vehicles.
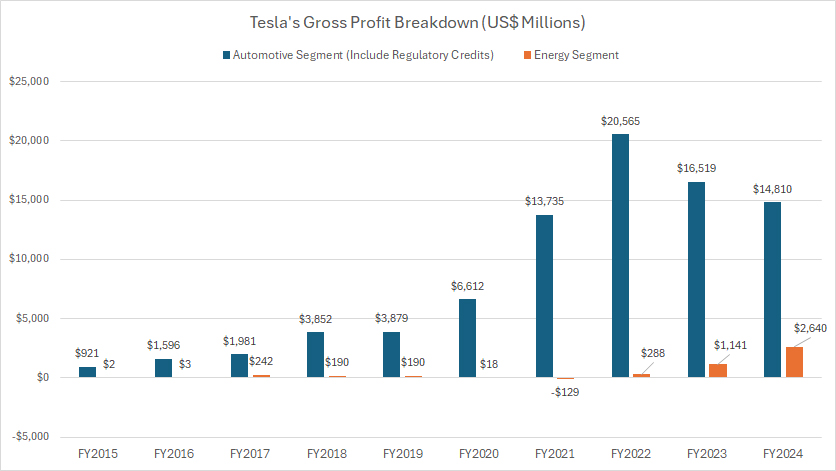
Automotive and Energy Gross Profit
Tesla-consolidated-gross-profit-breakdown
(click image to expand)
Tesla operates through two major segments: automotive and energy.
Tesla’s automotive gross profit includes the profit from sales of regulatory credits. You may find more information about Tesla’s regulatory credits here: regulatory credit.
Tesla’s automotive segment recorded a gross profit of $14.8 billion in fiscal year 2024, marking a decline from its 2022 peak of $20.6 billion.
However, over the longer horizon, from fiscal year 2015 to 2024, Tesla’s automotive gross profit has surged — expanding 15-fold over the decade.
It climbed from just under $1 billion to $14.8 billion in its latest financial results, reflecting the company’s substantial profitability growth.
On the other hand, its energy segment has seen remarkable growth in recent years, generating $2.6 billion in gross profit in fiscal year 2024 — a nearly tenfold increase since 2022.
This shift highlights the company’s evolving revenue dynamics, with energy operations gaining significant traction.
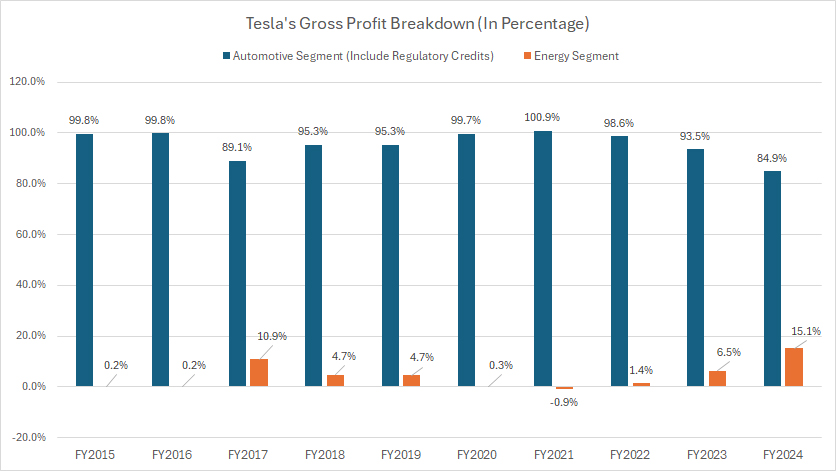
Automotive and Energy Gross Profit In Percentage
Tesla-consolidated-gross-profit-breakdown-in-percentage
(click image to expand)
Tesla operates through two major segments: automotive and energy.
Tesla’s automotive gross profit includes the profit from sales of regulatory credits. You may find more information about Tesla’s regulatory credits here: regulatory credit.
Tesla’s automotive segment remains the dominant source of its gross profit, as reflected in the data above.
In fiscal year 2024, automotive gross profit accounted for 85% of the total, while the energy segment contributed 15%.
Looking at the longer timeframe from 2015 to 2024, the automotive segment’s profit share has declined from 100% to 85%, while the energy segment has expanded from 0% to 15%.
A notable shift occurred in 2017, when the energy segment’s profit share jumped to 11%, largely due to Tesla’s acquisition of Solar Power, which temporarily boosted its energy-related earnings.
Subsequently, the ratio has significantly declined, but recovered recently due to the improving business prospect of the energy segment.
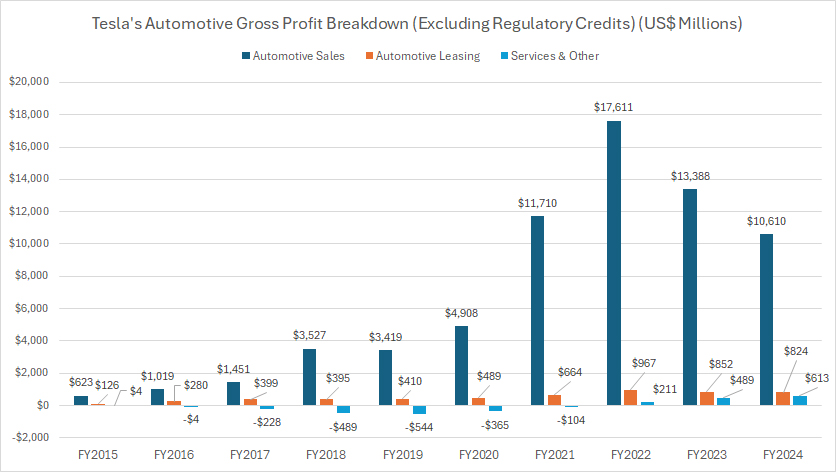
Automotive Sales, Leasing, and Services Gross Profit
Tesla-automotive-gross-profit-breakdown
(click image to expand)
Tesla’s automotive segment consists of automotive sales, automotive leasing, and services.
The automotive gross profit presented here EXCLUDES the profit from sales of regulatory credits. You may find more information about Tesla’s regulatory credits here: regulatory credit.
Within Tesla’s automotive segment, automotive sales remain the primary profit driver, as shown in the chart above.
In fiscal year 2024, automotive sales generated $10.6 billion in gross profit, while automotive leasing contributed $824 million. Meanwhile, Tesla’s services division, although smaller, added $613 million in gross profit.
A key observation is the substantial profit growth across all divisions within the segment.
Notably, Tesla’s services division has undergone a major transformation, shifting from an unprofitable unit to a highly profitable one in recent periods.
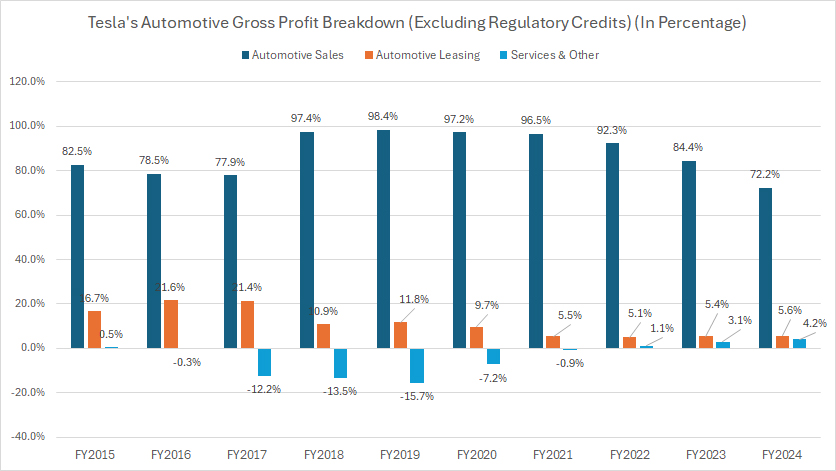
Automotive Sales, Leasing, and Services Gross Profit In Percentage
Tesla-automotive-gross-profit-breakdown-in-percentage
(click image to expand)
Tesla’s automotive segment consists of automotive sales, automotive leasing, and services.
The automotive gross profit presented here EXCLUDES the profit from sales of regulatory credits. You may find more information about Tesla’s regulatory credits here: regulatory credit.
In fiscal year 2024, Tesla’s automotive sales generated 72.2% of the company’s total gross profit, while automotive leasing contributed 5.6%, and services accounted for 4.2%.
Over the past decade, both automotive sales and leasing have experienced notable shifts in their gross profit contribution, while the services division has shown significant growth, becoming a more prominent part of Tesla’s profitability.
Insight
Tesla’s profit composition is evolving, with energy playing a larger role alongside traditional automotive sales.
While automotive remains dominant, increasing profitability across services and energy suggests strategic diversification beyond vehicle sales.
References and Credits
1. All financial figures presented were obtained and referenced from the company’s quarterly and annual reports published on the company’s investor relations page: Tesla Annual and Quarterly Results.
2. Pexels Images.
Disclosure
We may use artificial intelligence (AI) tools to assist us in writing some of the text in this article. However, the data is directly obtained from original sources and meticulously cross-checked by our editors multiple times to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media. Additionally, providing a link back to this article from any website can help us create more content like this in the future.
Thank you for your support and engagement! Your involvement helps us continue to provide high-quality, reliable content.