Cybertruck production line. Source: Tesla Update Letter.
This article explores Tesla’s interest expense and interest coverage ratio, providing insights into its financial performance.
We analyze Tesla’s interest expense to observe changes in its debt-related expenses over time.
Additionally, we examine the interest coverage ratio, also known as the times interest earned ratio, to assess Tesla’s ability to meet its debt obligations effectively.
Let’s dive in!
For other key statistics of Tesla, you may find more resources on these pages:
Sales
Revenue
- Revenue streams and profit margin breakdown,
- Revenue by country: U.S., China, Norway, Netherlands, etc.,
- Revenue per employee and revenue per car
Energy
Profit Margin
- Profit margin breakdown: automotive, energy, and services,
- Profit per employee,
- Tesla vs BYD: profit margin comparison
R&D Budget
- Tesla vs GM,
- Tesla vs Ford,
- Tesla vs Chinese EV,
- Tesla vs BYD
Debt, Cash, and Liquidity
- Financial health: debt level, payment due, and liquidity,
- Cash flow and cash on hand analysis,
- Debt Ratios: debt to equity, capital structure, and more,
- Liquidity check: current ratio, working capital, and quick ratio
Comparison With Peers
- Marketing, advertising, and promotional spending,
- Tesla vs GM: profit margin comparison,
- Tesla vs Ford: vehicle profit and margin
Other Statistics
- Infrastructure expansion: supercharger stations, service fleets, and stores,
- Operating expenses breakdown analysis,
- Inventory breakdown analysis
Please use the table of contents to navigate this page.
Table Of Contents
Definitions And Overview
Debt Expense
A1. Interest Expense
Income
Interest Coverage
C1. Interest Coverage With Respect To Operating Income & EBITDA
Conclusion And Reference
S1. Insight
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
Definitions
To help readers understand the content better, the following terms and glossaries have been provided.
Interest Coverage Ratio: The interest coverage ratio (also called times interest earned ratio) is a financial metric that measures a company’s ability to pay interest on its outstanding debt. It is calculated by dividing a company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) by interest expenses.
The resulting ratio indicates how many times a company’s profits can cover its interest payments. A higher interest coverage ratio means a company can better meet its interest obligations and is considered less risky to lenders and investors.
EBITDA: EBITDA stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization. It is a financial metric to evaluate a company’s operating performance and cash flow.
EBITDA helps to determine a company’s profitability by looking at its revenue minus all of the expenses that are directly related to its operations, such as cost of goods sold, salaries, and overhead costs, but excluding non-operating expenses such as interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
Investors and analysts often use this metric to compare the financial performance of different companies in the same industry.
Interest Expense
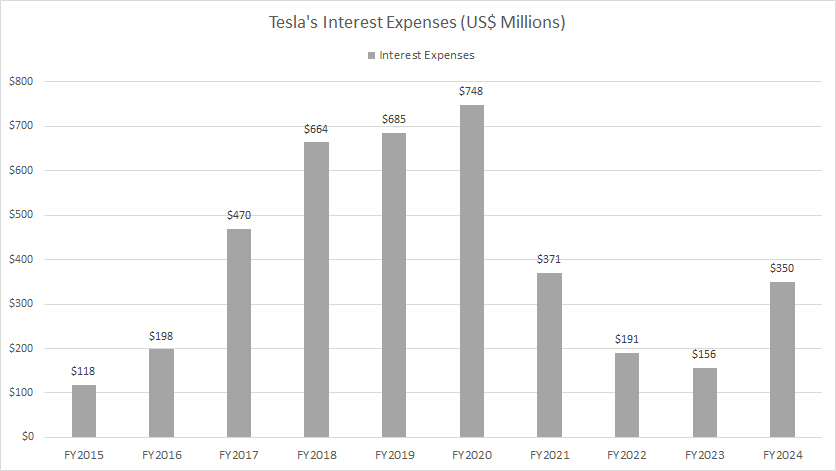
Tesla interest expense
Tesla reported interest expenses of $191 million, $156 million, and $350 million for the fiscal years ending December 31, 2022, 2023, and 2024, respectively.
Notably, Tesla achieved a significant reduction in interest expenses, which had peaked at $748 million in fiscal year 2020. By fiscal year 2024, interest expenses had declined by over 50% compared to the 2020 peak.
This substantial decrease in interest expenses over recent years can be attributed to Tesla’s proactive approach of aggressively reducing its debt, as detailed in the article: Tesla debt.
Operating Income & EBITDA
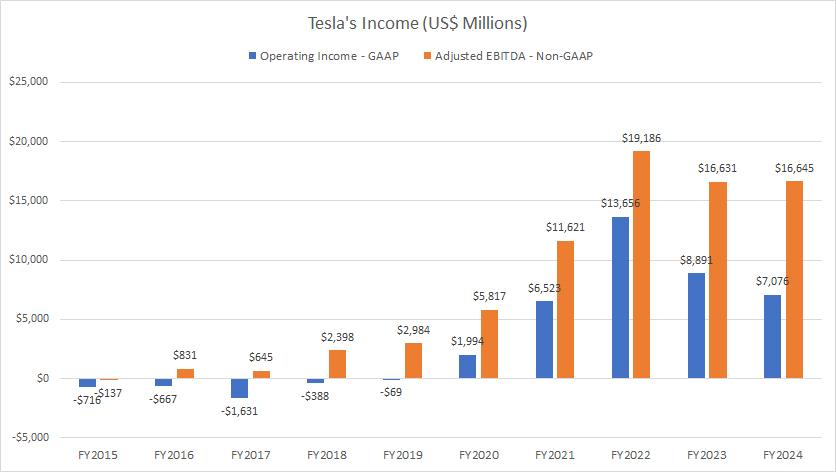
Tesla income
The operating income reflects Tesla’s profit before interest expense and taxes, while the EBITDA represents cash earnings.
Tesla’s operating income has experienced significant growth over the past several years, highlighting the company’s strong ability to generate profits.
Fiscal year 2020 marked a pivotal moment for Tesla, as it transitioned from an operating loss to achieving an operating profit. Since then, the company’s operating income has multiplied several times, reaching an impressive $7.1 billion in fiscal year 2024 — one of the highest figures recorded in the past three years.
Tesla’s EBITDA performance has been even more robust. In fiscal year 2024, the company achieved an EBITDA of $16.6 billion, another record-breaking milestone.
While Tesla has faced a decline in profitability over the last three years, the company has maintained its substantial profit levels. With an operating income exceeding $7 billion and EBITDA surpassing $16 billion, Tesla continues to demonstrate its resilience and profitability.
Interest Coverage With Respect To Operating Income & EBITDA
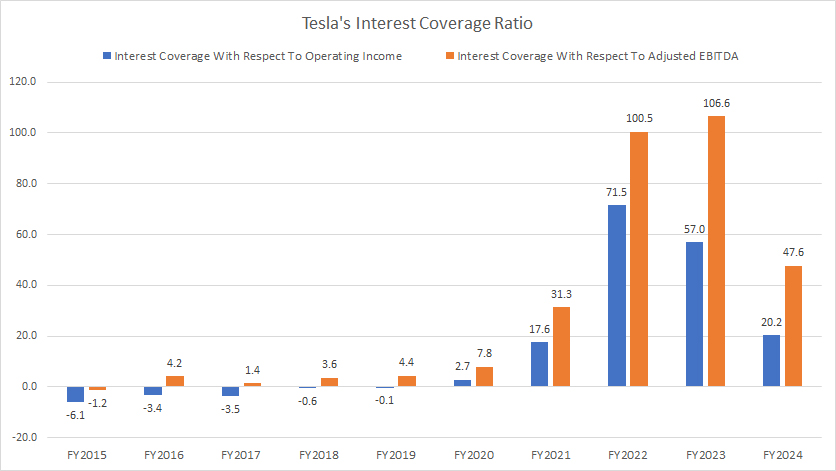
Tesla interest coverage ratio
The definition of interest coverage ratio is available here: Interest Coverage Ratio.
Tesla remains massively profitable with an operating income exceeding $7 billion and an EBITDA of over $16 billion.
As a result, its interest coverage ratio amounted to 20.0X based on the oeprating income and 47.6X calculated using EBITDA, demonstrating that Tesla has no problem covering its interest expenses with the massive profitability.
Insight
Tesla’s interest expense has seen a notable decline in recent quarters, largely attributed to a reduction in debt levels.
Despite these changes, Tesla continues to maintain substantial profitability, reporting an operating income exceeding $7 billion and an EBITDA surpassing $16 billion.
This strong financial performance allows Tesla to easily cover its interest expenses multiple times over, reflecting the company’s impressive ability to manage both its debt obligations and profitability effectively.
As a result, Tesla should have no problems servicing its debt.
References and Credits
1. All financial figures presented were obtained and referenced from Tesla’s quarterly and annual statements published on the company’s investor relations page: Tesla Investor Overview.
2. Flickr Images.
Disclosure
We may use artificial intelligence (AI) tools to assist us in writing some of the text in this article. However, the data is directly obtained from original sources and meticulously cross-checked by our editors multiple times to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media. Additionally, providing a link back to this article from any website can help us create more content like this in the future.
Thank you for your support and engagement! Your involvement helps us continue to provide high-quality, reliable content.