Debt calculation. Pixabay Image.
This article presents the debt and liquidity of Nio Inc. (NYSE:NIO).
Apart from the debt figures, we also look at Nio’s total cash which primarily consists of cash & cash equivalents, and short-term investments.
Nio’s net debt, calculated as total debt less total cash, is another measure that we will find out.
The debt-to-equity and debt-to-asset ratios which measure the company’s debt leverages will also be explored.
Nio’s credit score or credit ratings will be determined by its ability to repay and service its debt.
Therefore, we will check on the company’s total liquidity to find out whether the company is capable of repaying as well as servicing its debt.
In this aspect, the interest coverage ratio, calculated as operating income (a GAAP measure) divided by interest expense net of interest income, is another metric that will be investigated.
Finally, we will look into Nio’s debt maturities and the amount of debt due that needs to be repaid in the next several years.
Nio’s total liquidity may consist of its own cash and pre-approved bank facilities.
From the total liquidity, we can find out if the company has sufficient cash to cover the necessary debt payments when they are due.
That said, let’s start with the following topics!
Table Of Contents
Debt And Cash
A1. Total Debt
A2. Total Cash
Net Debt
A3. Total Debt Less Total Cash
Leverage Ratios
B1. Debt To Equity Ratio
B2. Debt To Asset Ratio
B3. Debt To Sales Ratio (Debt Margin)
Interest Coverage Ratio
C1. Operating Income Vs Interest Expense
Debt Schedules, Liquidity And Credit Rating
D1. Debt Payment Due
D2. Sources Of Liquidity
D3. Credit Rating
Summary And Reference
S1. Conclusion
S2. References and Credits
S3. Disclosure
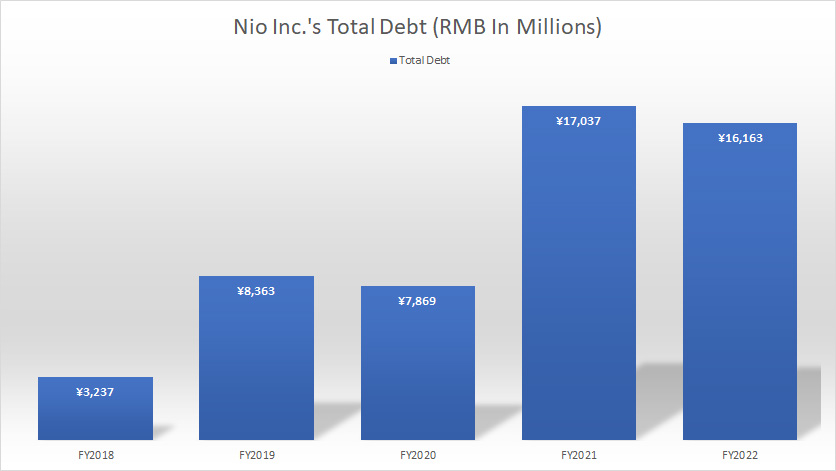
Nio Inc Total Debt
Nio Inc total debt
(click image to enlarge)
As of 31 Dec 2022, Nio Inc’s total debt outstanding was RMB16.2 billion (US2.3 billion), down slightly from a year ago but was up considerably over the past 5 years.
Of this amount, about RMB5.2 billion is classified as current liabilities which means that this total amount is due within a year from 31 Dec 2022.
Nio’s market capitalization was roughly US23 billion as of the date this article was published.
Therefore, the company’s total debt is considered minimal as it represents only about 10% of the firm’s market cap.
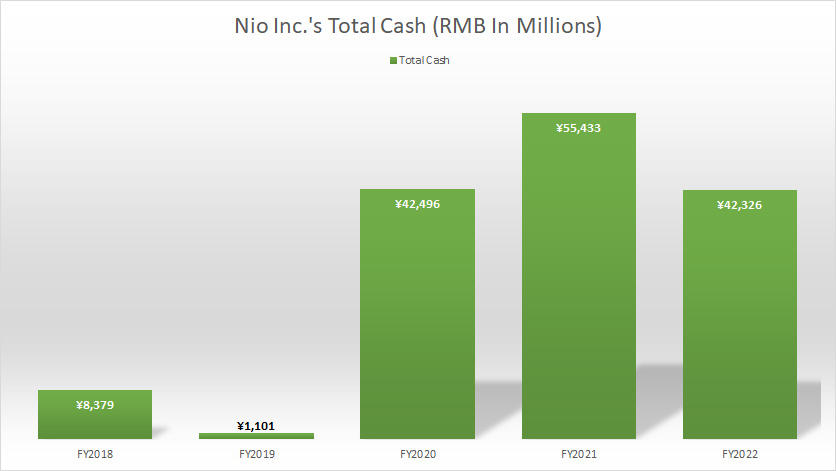
Nio Inc Total Cash
Nio Inc total cash
(click image to enlarge)
In terms of cash, Nio Inc had quite an amount of cash, totaling RMB42.3 billion (US6 billion) as of the end of fiscal 2022.
Of this amount, about RMB23.2 billion was cash & cash equivalents while the rest was made up of short-term investments.
Nio’s cash had increased considerably over the past 5 years and was more than sufficient to repay the company’s entire debt if it wanted to.
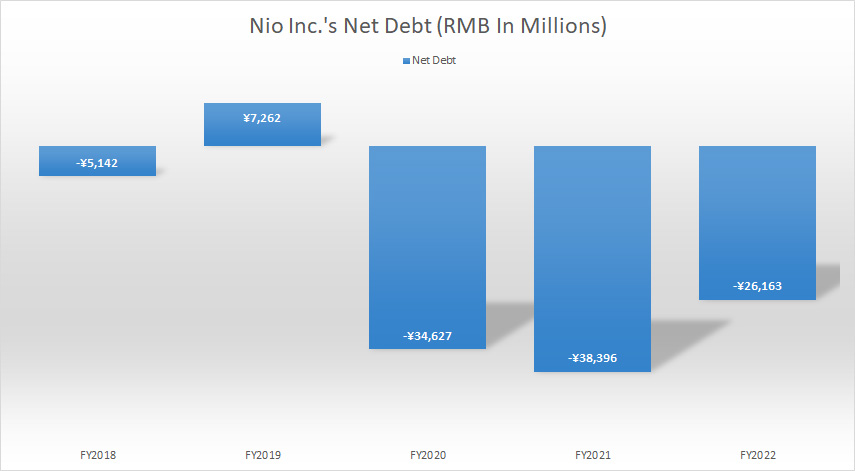
Nio Inc Total Debt Less Total Cash
Nio Inc net debt
(click image to enlarge)
Nio Inc owes nothing as of the end of fiscal 2022 after taking into account the cash assets of the company.
Therefore, Nio’s net debt amounted to -RMB26.2 billion as of fiscal 2022 as the company’s cash was much higher than the indebtedness.
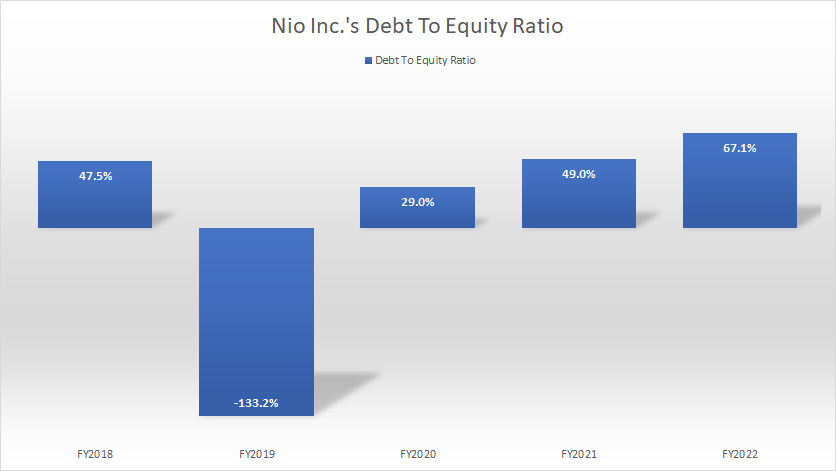
Nio Inc Debt To Equity Ratio
Nio Inc debt to equity ratio
(click image to enlarge)
Nio’s debt-to-equity ratio has risen considerably since fiscal 2018 and totaled 67% or 0.67X as of the end of fiscal 2022.
Despite the significant growth of the ratio over the years, Nio’s debt leverage with respect to total equity was still moderately low as the company had only RMB0.67 of debt for every RMB1 of equity.
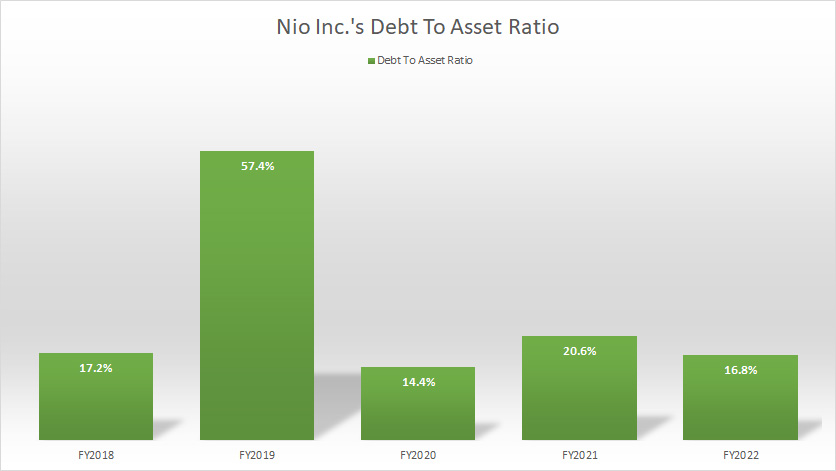
Nio Inc Debt To Asset Ratio
Nio Inc debt to asset ratio
(click image to enlarge)
The debt-to-asset ratio reflects Nio’s capital structure, also known as the debt structure.
As of fiscal 2022, Nio’s total debt accounted for only 17% of the company’s total assets, suggesting that debt made up only a small portion of the company’s capital structure.
This ratio has remained roughly the same over the past 5 years, due probably to the consistent policy of the management when it comes to debt.
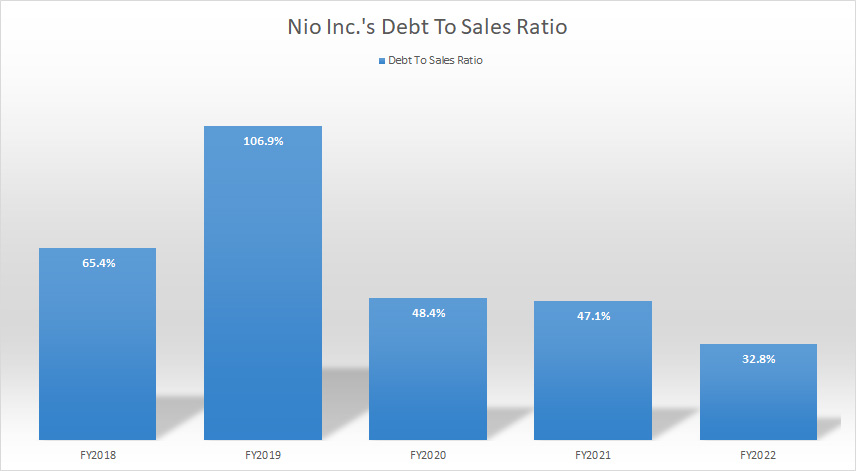
Nio Inc Debt To Sales Ratio (Debt Margin)
Nio Inc debt to sales ratio
(click image to enlarge)
Although Nio’s debt levels have been on the rise, it is decreasing with respect to sales revenue.
As seen in the chart above, Nio’s debt-to-sales ratio or debt margin has been on the decrease since fiscal 2018 and reached only 33% or 0.33X as of fiscal 2022, a record low in the past 5 years.
The decreasing ratio illustrates the company’s record growth of revenue over the years.
Therefore, it is a good indication that the ratio is decreasing.
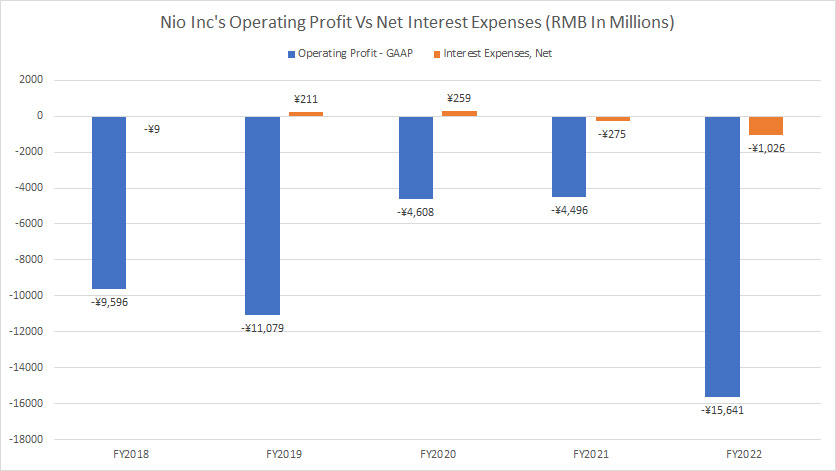
Nio Inc Operating Profit Vs Interest Expense
Nio Inc operating income vs interest expense
(click image to enlarge)
For your information, Nio Inc has never been profitable as seen in this article – Nio Profitability.
Therefore, Nio’s operating profit, a GAAP measure, has been negative as seen in the chart above.
While the company is not making any profit, its interest expense also comes in negative in most fiscal years.
The reason is that Nio also derives interest income from its short and long-term investments.
In most fiscal years, Nio’s interest income was much higher than interest expense, resulting in the negative interest expense as shown in the chart above.
While Nio may not be able to cover its interest expense with its operating profit, it can do so with its interest income.
As seen in the chart above, in fiscal 2022, Nio’s interest income was much higher than the respective interest expense.
In this case, Nio’s interest coverage ratio was not applicable.
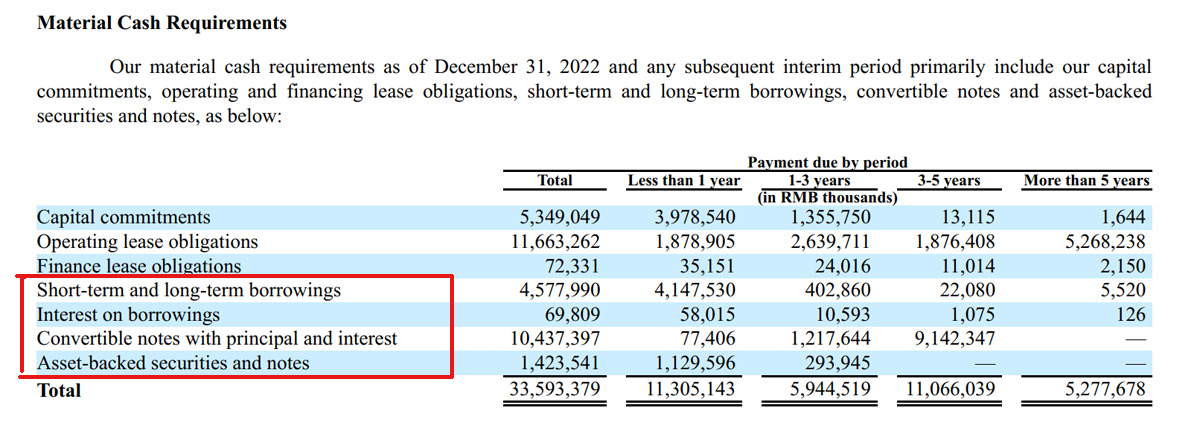
Nio Inc Debt Payment Due
Nio Inc debt payment due
(click image to enlarge)
An analysis of Nio’s debt and liquidity will not be conclusive without a mention of the corresponding debt maturity date.
As shown in the snapshot above, Nio’s total payment due in less than 1 year from 31 Dec 2022 was RMB11.3 billion (US1.6 billion).
Of this amount, debt payment alone represents RMB5.5 billion or about half of the total payment due.
For 1 to 3 years (from fiscal 2024 to 2026), Nio’s total payment due amounts to RMB5.9 billion.
Therefore, in the next 4 years (from fiscal 2023 to 2026), Nio’s total payment due is RMB17.2 billion (US2.5 billion).
Does Nio have enough liquidity to meet the respective debt payment in 2023 and the years after?
We will find out in the next section.
Nio Inc Sources Of Liquidity
Nio Inc’s total liquidity as of 31 Dec 2022.
| Sources Of Liquidity | RMB In Billions | |
|---|---|---|
| Committed Capacity | Available Capacity For FY2023 | |
| Cash & Cash Equivalents | – | ¥23.2 |
| Short-Term Investments | – | ¥19.2 |
| Non-Collateral-Based Bank Facilities | ¥28.4 | ¥22.0 |
| Collateral-Based Bank Facilities | ¥27.7 | ¥18.9 |
| Operating Cash Flow | – | ¥0.0 (estimated) |
| Total | – | ¥83.3 |
Nio Inc’s sources of liquidity include cash and cash equivalents, short-term investments and credit facilities from banks.
Nio’s cash from operating activities had been unstable in the past 3 years and averaged 0.
Even without operating cash flow, Nio’s cash and cash equivalents alone are able to pay off the entire debt payment due in 2023 which totals RMB11.3 billion.
Not only that, Nio’s cash and cash equivalents alone are also able to cover the entire debt payment due between 2023 and 2026 which totals RMB17.2 billion.
The following quote shows what Nio said about its liquidity in the 2022 annual report:
- “We believe that our current cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments balance as of December 31, 2022 is sufficient to fund our operating activities, capital expenditures and other obligations for at least the next twelve months.”
In short, Nio Inc has enough liquidity to meet its payment obligations all the way to fiscal 2026 and possibly beyond.
Nio Inc Credit Rating
Nio Inc’s credit ratings as of 31 Dec 2022.
| Rating Institutions | Types Of Indebtedness | Outlook | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Long-Term Debt | Short-Term Debt | ||
| Standard & Poor’s | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. |
| Moody’s | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. |
| Fitch | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. |
As of 31 Dec 2022, Nio Inc has not published any credit rating regarding its debt obligation in its 2022 annual reports.
Conclusion
In summary, Nio Inc had RMB16.2 billion of debt as of the end of fiscal 2022.
Despite the seemingly high indebtedness, Nio’s leverages were moderate and had somewhat declined.
Moreover, the company had investment income which had been able to cover its interest expenses.
Also, Nio had sufficient liquidity to meet all debt obligations until 2026 and possibly beyond.
References and Credits
1. All financial figures presented in this article were obtained and referenced from Nio Inc.’s SEC filings, earnings reports, financial statements, news releases, etc, which are available in Nio’s Financial Results.
2. Featured images presented in this article are used under creative commons licenses and sourced from Pixabay.
Disclosure
References and examples such as tables, charts, and diagrams are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant the full correctness of all content.
The content in this article is for informational purposes only and is neither a recommendation nor a piece of financial advice to purchase a stock.
If you find the information in this article helpful, please consider sharing it on social media and also provide a link back to this article from any website so that more articles like this one can be created in the future.
Thank you!